As practice shows, such a parameter as the range of a wifi router plays an important role when choosing a router. After all, the further operation of your wireless network will depend on this.
Imagine it is not very pleasant if the WiFi signal does not reach some point of your home, or the signal is there, but the speed indicators will be weak. Therefore, let's look at what the maximum range of a WiFi network can be, and how it can be increased.
Why increase the range of a wifi router
Usually, for an ordinary city apartment, the most ordinary router is enough, its signal spreads to all corners of the home. But if you want to make a single network with a neighbor, this is where problems may arise.
It so happens that a person lives in a private house and wants the Internet to be present in the garage and summer kitchen. This is where you have to think about how far your router will "penetrate" and how this distance can be increased.
What can be the range
If we draw an analogy, then the operation of a wireless router can be compared with the operation of a mobile operator's tower, with the only difference that the router has a much smaller coverage area, and it communicates via WiFi. The range of a standard router is approximately 100-200 meters, and then this is if there are no obstacles, and if there are reinforced concrete walls or metal structures in its path, then the coverage area can drop to 50 meters.
Factors affecting the range of the network:
- 802.11 protocol type
- Antenna gain
- Transmitter power
- Signal obstacles and interferences
- Length and attenuation in cables for connecting antennas
Radius dependence on 802.11 protocol
There are several ways to extend the range of your wireless network. This parameter is influenced by both the location of the router itself and its settings. Let's figure out what you can do to increase the coverage of your network.
Correct router configuration
Your wireless network's coverage area can be significantly reduced due to interference from nearby WiFi devices, a microwave oven, or even a regular baby monitor.
To avoid this, you should pay attention to which channel your router is operating on. If the channels coincide with a nearby router, then there may be network problems and a significant decrease in the range. So go to your router's settings and see which channel it works on.

Configuring the router's channel
The most ideal option would be if you set the channel selection in automatic mode. Then the router will independently analyze the channel load and choose the optimal one for better network performance.
It will be nice if your router and its receivers can operate at 5 GHz, then you can switch to this frequency range. The reception range will decrease slightly, but there will be less interference and the network will work more stable and faster.
Correct router installation
The router should be placed in the center of the building in an elevated position. In this case, you should take into account where your receiving devices will be located and the number of obstacles to them. After all, if in some distant room there is a laptop with a weak receiver, and there are several reinforced concrete walls and a closet to the router, then the signal may not reach it. Then you can move the router a little closer to this room, the main thing is not to overdo it and not to remove it far from other devices.
It also happens that, as a router, do not move, but the signal does not reach some point, then you can use a wireless repeater (repeater). Place this device so that it can confidently receive the signal from your router. There is one drawback here - if the router operates in repeater mode, then its bandwidth is halved.

Correct repeater location
Using an optional antenna
The stores sell special antennas that can increase the range of the network. They also have one advantage, with the help of a cable, they can be placed higher than the router itself, thereby increasing the coverage area.

Microwave cable for connecting antennas
For owners of country houses, you can use a directional parabolic antenna. Everything is simple here - you install the antenna outside the building, connect it to the router, and direct it to the side where the receiving device will be located. Several such antennas can be installed.

Parabolic antenna
Firmware upgrade
It also happens that the router has outdated firmware. Typically, a firmware update will result in a stronger signal and faster data transfer rates. To download the firmware, visit the manufacturer's official website. It is usually written on a sticker located on the back of the router.
How to strengthen the signal of a Wi-Fi router
I had an old netbook that was almost ten years old. And for the entire time of its operation, I experienced a little discomfort, since it was very poor at catching Wi-Fi. I did not give special attention to this fact until I got my hands on a laptop, the short one had just excellent reception of even a weak signal.

The same router was caught on different machines in different ways: on my PC there was one division, and on the other laptop there was a full reception level. And then I thought.
Redesigning the built-in antenna
After reading the forums, I learned that the Wi-Fi receiving antennas are located near the display. The first thing I did was to take a look at them.He pulled out the plugs with a clerical knife.

Unscrewed the screws and removed the front panel.

There were two antennas, which were located on the sides of the camera. They were made on a printed circuit board according to the dipole principle.

A long wire went to them, which went around the perimeter of the display.

Further, it turned out that the built-in antenna was partially hidden under the aluminum foil that shielded the screen.

As a result:
- A long cable gave significant attenuation.
- The native antenna had a terribly poor sensitivity.
- Plus, all over it was partially covered by the screen, which simply ruined it.
You will need:
- Round thin metal tube 25 mm long.

Cut off the built-in modules to the root. We put on the pipe. We place the future whip antenna approximately in the middle.

Next, we clean the braid-screen of the wire to the tube and fluff the tip.

The tube is compatible with the end of the braid.

We solder it carefully without melting the central insulation of the middle conductor.

Now we cut off the center wire at a distance of 25 mm from the beginning of the tube.

Our new antenna is ready. We do the same for the other side of the display.

And lo and behold! The sensitivity has increased and is no worse than the other laptop.

Now the old built-in antennas can be thrown away and enjoy normal computer operation.

This is a fairly simple method with which you can modify any laptop and increase it sensitively, since native antennas may not always work well.
The most important thing is to strictly observe the distance when making a whip homemade antenna. For any deviation, even by a millimeter, can significantly impair its reception characteristics.
The range of a wifi router depends on the type of router or access point used. The factors that determine the range of the router (access point) are:
- total transmitter power;
- the type of 802.11 protocol used;
- length and attenuation of cables connected to the antenna;
- obstacles and interference in the signal path in this room;
- antenna gain of the router.
The range of an 802.11g wifi router with a standard antenna (gain of about 2dBi) is approximately 150 m in open areas and indoors - 50 m.But brick walls and metal structures can reduce this range by 25% or more. The 802.11a standard uses frequencies higher than the 802.11b / g standards, so it is more susceptible to various obstacles. In addition, the range of 802.11b or 802.11g Wi-Fi networks is strongly affected by interference from microwave ovens. Tree foliage is also a strong obstacle, as it contains water, which absorbs microwave radiation in the used range. For example, heavy rain attenuates the signal in the 2.4GHz range to 0.05 dB / km, thick fog - 0.02 dB / km, and forest (dense foliage, branches) - up to 0.5 dB / meter.
Having chosen a Wi-Fi router, the range can be approximately calculated using a special calculator, which is located just below, it is intended for D-Link equipment, but the formulas and methods used there are suitable for any other.
If you create a radio bridge between two networks, then it must be borne in mind that the space around a straight line drawn from the receiver to the transmitter must be free of
absorbing and reflecting obstacles in a radius equal to 0.6 of the radius of the first Fresnel zone. The size of this zone can be calculated using the following formula:

In real conditions, the signal level at different distances from the transmitting device can be measured with a special device (Wi-Fi detector).
If you need to increase the range, the Wi-Fi router can be combined into a chain of several routers or wireless access points, or you can replace the standard antennas with more powerful ones.
Powerful Wi-Fi router
If you choose a powerful router, its range and reception quality should satisfy your requirements.
Power is largely determined by the power of the signal amplifiers in it.
A powerful router based on the Realtek 8187L chipset is distinguished not only by a high power of 1 watt, but also by large-scale support. The drivers for this chipset are supported by all operating systems. If you use an external additional antenna, the distance can be up to 5 km.

Distributed brands Alfa, NEtsys, Senao EnGenius EUB Ext High-Power, Wifly city 8G, 20G, AIRLIVE, G-Sky GS-27USB-50, KASENS.
Amped Wireless has released the most powerful R20000G High Power Wireless-N router, featuring 600mW of 2.4GHz amplifiers.

The R20000G is capable of operating in two networks: 5000 MHz and 2400 MHz. The router provides indoor coverage up to 930 sq. m. Two powerful antennas with a gain of 5 dB / inch are connected to the router, but they can be replaced with more powerful ones.
How to increase the range of a router
There are many solutions to the question of how to increase the range of the router.
If the router does not provide the required coverage area, then to increase the range, you can install a WiFi repeater that will act as an amplifier for the router. The repeater receives the signal and transmits it further. The repeater must be installed in the middle, between your computer and the router (access point).

A less costly method is to replace the standard antenna of the router with an antenna with a high gain or a directional one.
When installing a wi-fi network in a room, you need to place the router at approximately the same distance from all rooms so that the signal strength is approximately the same throughout the room.
There should be as few brick walls and iron structures as possible between the router and the computer, which can greatly weaken the signal. You should also consider possible interference from microwave ovens. To increase the range of the router, you can use a special signal amplifier by connecting it instead of the antenna.
How to increase the power of the router

To increase the signal strength of the router, you can use the signal reflection method. Reflective tape can be used. As a reflective film, ordinary foil is suitable, from which a screen is made, which prevents the signal from spreading in an unnecessary direction.
Help in setting up the router
First, you need to check the hardware version of the router by looking at the sticker on the bottom of the router.
By marking the router on the Internet, you can download a new version of the firmware (firmware) for the router. The new version of the firmware significantly improves the performance of the device.

To configure, you need to configure the computer, set the protocol and the type of connection to the provider.
In the Windows XP operating system, you need to select: "Start" → "Control Panel" → "Network Connections".

In the operating system Windows Vista / Windows 7
you need to choose:
"Start" → "Control Panel" → "Network and Sharing Center" → "Manage network connections".

If the connection protocol is DHCP or Static IP, then opening the Network Connections folder you will see the following:

To clarify the protocol, right-click the Local Area Connection shortcut and select Properties from the menu. In the window that appears, select the TCP / IP v4 protocol and click the "Properties" button. A new window will open.

If in the window that opens, the dots are opposite the inscription "Obtain an IP-address automatically", then the connection protocol is DHCP.

If the dots mark "Use the following IP address", and in the windows next to the inscriptions "Subnet mask", "IP address" and "Default gateway" there are numerical values, then the connection type is Static IP.
These numbers need to be written down, and having marked "Obtain an IP-address automatically" click the "OK" button.

After clarifying the protocol and the type of connection to the provider, you need to correctly connect the router.

After that, you need to determine the factory IP address of the router. You can find it out from the instructions for the device. This IP address is entered into the address bar of the Internet browser and the "Enter" key is pressed.

After authorization, you can start configuring the router. In the opened web interface, go to the "Main" section, select the "WAN" subsection and then select "DHCP Client or Fixed IP" in the "Connection Type" menu. Click the "Clone MAC Address" button and then the "Apply" button.

For the DHCP protocol, the steps taken are enough to configure access to the Internet.
For the Static IP protocol (when the provider has assigned a static IP address for the computer's network card), in the "Main" section, select the "WAN" subsection, and in the "Connection Type" menu, select "DHCP Client or Fixed IP" and click the "Clone MAC Address ". Then put a full stop next to “Specify IP” and enter in the three fields “Subnet mask”, “IP address” and “Default gateway address” that you wrote down earlier.

When the "Applly" button is pressed, the computer for which the configuration was performed will have access to the Internet.
A weak WiFi signal is an urgent problem for residents of apartments, country houses and office workers. Dead zones in the WiFi network are characteristic of both large rooms and small-sized apartments, the area of which is theoretically capable of covering even a budget access point.
The range of a WiFi router is a characteristic that manufacturers cannot clearly indicate on the box: the WiFi range is affected by many factors that depend not only on the technical specifications of the device.
This material presents 10 practical tips to help eliminate the physical causes of poor coverage and optimize the range of a WiFi router, it's easy to do it yourself.
The radiation of the access point in space is not a sphere, but a donut-shaped toroidal field. For WiFi coverage within one floor to be optimal, radio waves must propagate horizontally - parallel to the floor. For this, there is the possibility of tilting the antennas.

The antenna is the "donut" axis. The angle of propagation of the signal depends on its slope.

When the antenna is tilted relative to the horizon, part of the radiation is directed outside the room: dead zones are formed under the plane of the "donut".

A vertically installed antenna radiates horizontally: indoors, maximum coverage is achieved.
On practice: Placing the antenna vertically is the easiest way to optimize your indoor WiFi coverage.
Place the router closer to the center of the room
Another reason for the occurrence of dead zones is the poor location of the access point. The antenna emits radio waves in all directions. In this case, the radiation intensity is maximum near the router and decreases as it approaches the edge of the coverage area. If you install the access point in the center of the house, then the signal is distributed among the rooms more efficiently.
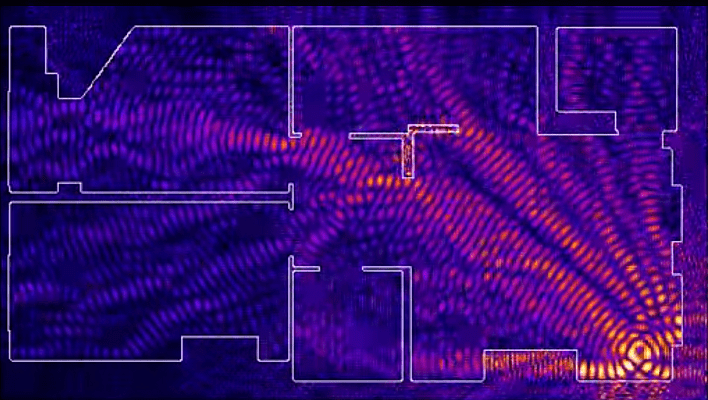
A router installed in a corner gives off some of the power outside the house, and distant rooms are at the edge of the coverage area.

Mounting in the center of the house allows for an even distribution of signal in all rooms and minimizes dead zones.
In practice: Installing an access point in the “center” of the house is far from always feasible due to complex layouts, lack of sockets in the right place, or the need to lay a cable.
Provide line of sight between the router and clients
WiFi signal frequency is 2.4 GHz. These are decimeter radio waves that poorly bend around obstacles and have low penetrating power. Therefore, the range and stability of the signal directly depend on the number and structure of obstacles between the access point and clients.
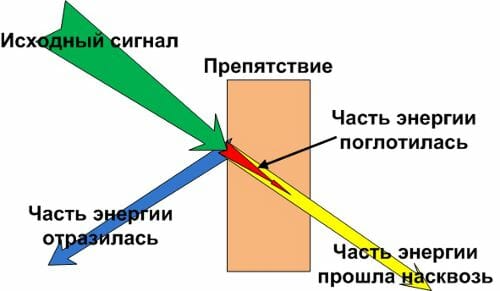
Passing through a wall or ceiling, an electromagnetic wave loses some of its energy.
The amount of signal attenuation depends on the material that the radio waves travel through.
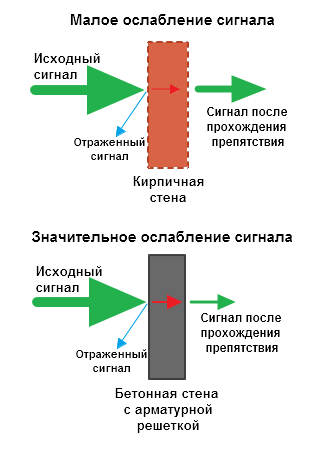

* Effective distance is a value that determines how the radius of a wireless network changes compared to an open area when a wave passes an obstacle.
Calculation example: A WiFi 802.11n signal propagates in line-of-sight conditions over 400 meters. After overcoming the non-capital wall between the rooms, the signal strength decreases to 400 m * 15% = 60 m.The second wall of the same kind will make the signal even weaker: 60 m * 15% = 9 m.The third wall makes signal reception almost impossible: 9 m * 15 % = 1.35 m.
Such calculations will help to calculate the dead zones that arise from the absorption of radio waves by walls.
The next problem in the path of radio waves: mirrors and metal structures. Unlike walls, they do not attenuate, but reflect the signal, scattering it in arbitrary directions.
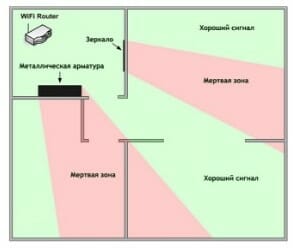
Mirrors and metal structures reflect and scatter the signal, creating dead zones behind them.

If you move the elements of the interior that reflect the signal, it will be possible to eliminate the dead zones.
In practice: It is extremely rare to achieve ideal conditions when all gadgets are in direct line of sight with a router. Therefore, in a real home, you will have to work separately to eliminate each dead zone:
- find out what interferes with the signal (absorption or reflection);
- think over where to move the router (or piece of furniture).
Place the router away from sources of interference
The 2.4 GHz band does not require licensing and therefore is used for the operation of consumer radio standards: WiFi and Bluetooth. Despite its low bandwidth, Bluetooth can still interfere with the router.

Green areas - stream from WiFi router. Red dots are Bluetooth data. The proximity of two radio standards in the same range causes interference, which reduces the range of the wireless network.
The magnetron of the microwave oven emits in the same frequency range. The radiation intensity of this device is so great that even through the protective screen of the oven, the radiation of the magnetron is able to “light up” the radio beam of the WiFi router.
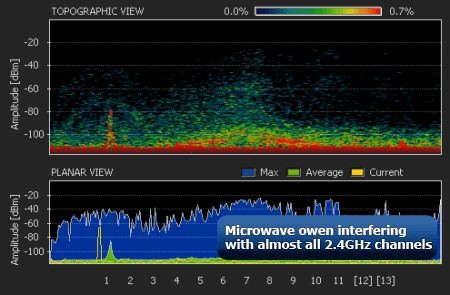
Microwave oven magnetron radiation causes interference on almost all WiFi channels.
On practice :
- When using Bluetooth accessories near the router, turn on the AFH parameter in the settings of the latter.
- The microwave is a powerful source of interference, but it is not used as often. Therefore, if it is not possible to move the router, then it will simply not be possible to make a Skype call while preparing breakfast.
Disable support for 802.11 b / g modes
WiFi devices of three specifications work in the 2.4 GHz band: 802.11 b / g / n. N is the latest standard and offers greater speed and range than B and G.

The 802.11n (2.4 GHz) specification provides longer range than the legacy B and G standards.
802.11n routers support previous WiFi standards, but the mechanics of backward compatibility are such that when a B / G device, such as an old phone or a neighbor's router, appears in the N router's area, the entire network is switched to B / G mode. Physically, the modulation algorithm changes, which leads to a drop in the speed and range of the router.
In practice: Putting the router in “pure 802.11n” mode will definitely have a positive effect on the quality of the coverage and throughput of the wireless network.
However, B / G devices will not be able to connect via WiFi. If it's a laptop or TV, they can be easily connected to the router via Ethernet.
Choose the optimal WiFi channel in the settings
Almost every apartment today has a WiFi router, so the density of networks in the city is very high. Signals from neighboring access points overlap each other, draining energy from the radio path and greatly reducing its efficiency.

Neighboring networks operating at the same frequency create mutual interference interference, like circles on water.
Wireless networks operate within range on different channels. There are 13 such channels (in Russia) and the router switches between them automatically.
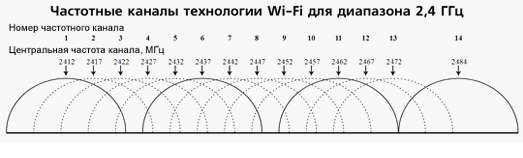
To minimize interference, you need to understand which channels the neighboring networks operate on and switch to a less loaded one.
Detailed instructions for setting up a channel are presented.

In practice: Selecting the least congested channel is an effective way to expand the coverage area, which is relevant for residents of an apartment building.
But in some cases, there are so many networks on the air that not a single channel gives a tangible increase in the speed and range of WiFi. Then it makes sense to turn to method number 2 and place the router away from the walls bordering neighboring apartments. If this does not work, then you should think about switching to the 5 GHz range (method no. 10).
Adjust the transmitter power of the router
The transmitter power determines the energy of the radio path and directly affects the range of the access point: the more powerful the beam, the further it hits. But this principle is useless in the case of omnidirectional antennas of household routers: in wireless transmission, two-way data exchange occurs and not only clients must “hear” the router, but vice versa.
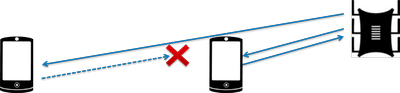
Asymmetry: the router “reaches out” to a mobile device in the back room, but does not receive a response from it due to the low power of the smartphone's WiFi module. The connection is not established.
In practice: The recommended value for the transmitter power is 75%. It should be increased only in extreme cases: the power turned 100% not only does not improve the signal quality in distant rooms, but even worsens the stability of reception near the router, since its powerful radio stream “clogs” the weak response signal from the smartphone.
Replace the original antenna with a more powerful one
Most routers are equipped with standard antennas with a gain of 2 - 3 dBi. The antenna is a passive element of the radio system and is not able to increase the flow power. However, increasing the gain allows the radio signal to be refocused by changing the directional pattern.
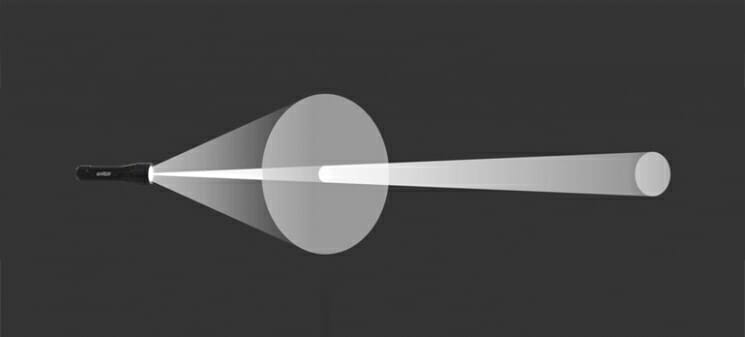
The higher the antenna gain, the further the radio signal propagates. In this case, the narrower stream becomes similar not to a “donut”, but to a flat disc.

There is a large selection of antennas for routers with a universal SMA connector on the market.



In practice: Using an antenna with a high gain is an effective way to expand the coverage area, because simultaneously with the signal amplification, the antenna sensitivity increases, which means the router begins to “hear” remote devices. But due to the narrowing of the radio beam from the antenna, dead zones arise near the floor and ceiling.
Use signal repeaters
In rooms with complex layouts and multi-storey buildings, it is effective to use repeaters - devices that repeat the signal of the main router.


The simplest solution is to use an old router as a repeater. The disadvantage of this scheme is half the throughput of the child network, since along with the client data, the WDS access point aggregates the upstream from the upstream router.
Detailed instructions for configuring the WDS bridge are presented.

Specialized repeaters are free from the problem of bandwidth cuts and are equipped with additional functionality. For example, some models of Asus repeaters support the roaming function.

In practice: No matter how complicated the layout is, repeaters will help you deploy a WiFi network. But any repeater is a source of interference. With free air, repeaters do their job well, but with a high density of neighboring networks, the use of repeater equipment in the 2.4 GHz band is impractical.
Use 5 GHz band
Budget WiFi devices operate at 2.4GHz, so the 5GHz band is relatively free and has little interference.

5 GHz is a promising range. It works with gigabit streams and has an increased capacity compared to 2.4 GHz.
In practice: “Moving” to a new frequency is a radical option that requires the purchase of an expensive dual-band router and imposes restrictions on client devices: only the latest models of gadgets work in the 5 GHz band.
The problem with the quality of the WiFi signal is not always related to the actual range of the access point, and its solution in general terms boils down to two scenarios:
- In a country house, it is most often required, in free air conditions, to cover an area that exceeds the effective range of the router.
- For a city apartment, the range of a router is usually sufficient, and the main difficulty lies in eliminating dead zones and interference interference.
The methods presented in this material will help to identify the causes of poor reception and optimize the wireless network without resorting to replacing the router or the services of paid specialists.
Found a typo? Select the text and press Ctrl + Enter
Very often we have to increase the range of the robots of a Wi-Fi router in order to transfer data between several computers without any problems. There are many ways to address this issue. And which method to choose is up to you.
Some modern Wi-Fi transmitters can be connected to an external antenna through a special connector. To choose it correctly, you need to know the frequency ranges in which the device operates. You can buy the antenna in computer stores, or even make it yourself like "Cantenna". It, like a Wi-Fi router, should be placed higher and turned towards your computer. The PC should also be configured. If you work with a laptop or netbook, then it is worth purchasing an external receiving device instead of the monitor built into the cover. It should not be connected directly, but via a USB extension cable. With the help of such a cable, it will turn out to win an extra five meters.

And in conclusion, it should be said that it is illegal to increase the range of robots Wi-Fi devices with a power of more than 0.1 W (100 mW). It is also illegal to increase the range of the signal if you do not own the access point, even if they are free and publicly available.



