The fight between Apple and the FBI has led to a heightened focus on the importance of encryption. Regardless of the fact that everyone can have their own opinion on this case, there is no need to explain the importance of protecting their personal data, and it all starts from the smartphone.
These devices store personal photos, private messages, emails, and sometimes even sensitive health information. Leaving this data in the wrong hands can be devastating. Using an alphanumeric password is a step in the right direction, but you should also consider encrypting your device.
IPhones, iPads and most Android devices can be encrypted. Here's what you need to know.
iOS.
Apple introduced device encryption starting with iOS 8 in 2014. Turning on an encrypted device requires entering a password or fingerprints. While a basic four-digit PIN is fine here too, for better protection I recommend using a longer numeric passcode or alphanumeric password.- Enter "Settings".
- Select "Touch ID and Password" (or "Password" for older devices without a fingerprint sensor).
- Click on the "Enable Password" option.
- Enter complex password or a security code (Be sure to write it down somewhere, do not rely on your memory. If you forget the password, you will not be able to enter the phone, you will have to reset it factory condition with the loss of all data.)
Android.
In Android, this process is a little more complicated. Nexus phones and tablets come with encryption enabled by default. Most of the newer devices that ship with Android 6.0, such as the Galaxy S7 and Galaxy S7 Edge, also come with active encryption capabilities. Similar to the iPhone, all you have to do is add a password or fingerprints to enable encryption itself.- Enter "Settings".
- Go to the Security page.
- Select "Screen Lock".
- Create a password.
For older devices, however, such as the Moto X Pure and Galaxy S6, you will need to manually encrypt it. Before starting, make sure your phone is plugged in as the process can take up to an hour depending on the amount of data on your device. Next, create a password using the steps above and follow these steps:
- Open "Settings".
- Select "Security".
- Click on "Encrypt Phone".

You can also encrypt your SD card to keep your data safe and prevent the card from being read by another device (unless you erase it first). Go to "Settings", select "Security", then on "Encryption external card SD "and click the Enable button. Unlike device encryption (which requires you to completely wipe your phone to disable this encryption), SD card encryption can be easily reversed in the Settings menu.
Reasons for not encrypting your Android device.
There are several reasons why you might want to postpone encryption. The encryption method is different for each device. Motorola, for example, allows the PIN and security pattern to continue after the phone has been encrypted, but Samsung only allows the password or fingerprints to be used.Samsung also requires you to enter a password after every reboot. While this makes it less likely for an attacker to gain access to your data, it can be too inconvenient for you.
The device will also show a slight drop in performance when encrypting it. This fall is barely noticeable on latest phones high-end, however older models and weak devices may suffer. I recommend using encryption only on the latest high-end devices like Galaxy S6, LG G4, Htc one M10, and their newer models (Galaxy S7, LG G5, etc ...).
In short: If you use a pattern to access the phone, then 99% of this is enough for no one without your knowledge to be able to access the information on the phone. If the data on the phone is very sensitive, then the built-in full encryption of the phone should be used.
Today, almost all smartphones have become carriers of important personal or corporate data. Also, through the owner's phone, you can easily access his accounts, such as Gmail, DropBox, FaceBook and even corporate services. Therefore, to one degree or another, it is worth worrying about the confidentiality of this data and use special means to protect your phone from unauthorized access if it is stolen or lost.
- Who should protect your phone data from.
- Built-in data protection in Android.
- Full Phone Memory Encryption
- Outcomes
What information is stored on the phone and why should it be protected?
A smartphone or tablet often acts as a mobile secretary, freeing the wearer's head from storage a large number important information... The phone book contains the numbers of friends, employees, family members. V notebook often write credit card numbers, access codes to them, passwords to social networks, e-mail and payment systems.
The list of recent calls is also very important.
Losing your phone can be a real disaster. Sometimes they are stolen on purpose to infiltrate personal life or share the profit with the owner.
Sometimes they are not stolen at all, and they are used for a short time, unnoticed, but a few minutes is quite enough for an experienced attacker user to find out all the details.
Loss of confidential information can turn into financial ruin, personal ruin, family breakdown.
I wish I didn't have it! - the former owner will say. - How good that you had it! - the attacker will say.
And so you need to protect on your phone:
- Accounts. This includes, for example, access to your mail mailbox gmail... If you have set up sync with facebook, dropbox, twitter. Logins and passwords for these systems are stored in open form in the phone profile folder /data/system/accounts.db.
- History of SMS-correspondence and phone book also contain confidential information.
- Web browser program. The entire browser profile must be protected. It is known that Web Browser(built-in or third-party) remembers all passwords and logins for you. All this is stored in open form in the program profile folder in the phone memory. Moreover, usually the sites themselves (using cookies) remember you and leave access to the account open, even if you did not specify to remember the password.
If you are using sync mobile browser(Chrome, FireFox, Maxthon, etc.) with a desktop version of the browser for transferring bookmarks and passwords between devices, then you can assume that you can access all passwords from other sites from your phone. - Memory card. If you store confidential files on the memory card or download documents from the Internet. Typically, the memory card stores photos and videos.
- Photo album.
Who should protect phone data from:
- From a random person who finds your lost phonel because from “accidental” phone theft.
It is unlikely that the data in the phone will be of value to the new owner in this case. Therefore, even simple protection with a graphic key will ensure the safety of data. Most likely, the phone will simply be reformatted for reuse. - From prying eyes(co-workers / children / wives), who can access the phone without your knowledge, taking advantage of your absence. Simple protection will ensure the safety of data.
- Granting access under duress
It happens that you are voluntarily forced to provide a phone and open access to the system (information). For example, when your wife, a government official, or an employee of the service center asks you to look at your phone number, where did you take the phone for repair. In this case, any protection is useless. Although there is a possibility using additional programs, hide the fact that some information is available: hide part of SMS correspondence, part of contacts, some files. - From targeted theft of your phone.
For example, someone really wanted to know what was on your phone and made an effort to get it.
In this case, only full encryption phone and SD card.
Built-in data protections on Android devices .
1. Lock screen with Pattern.
This method is very effective in the first and second cases (protection against accidental loss of the phone and protection from prying eyes). If you accidentally lose your phone or forget it at work, then no one can use it. But if you deliberately fell into the wrong hands for your phone, then it is unlikely to save. Hacking can even happen at the hardware level.
The screen can be locked with a password, PIN and Pattern. You can choose a blocking method by running the settings and selecting the Security -> Screen lock section.
Graphic Key(Pattern) - c the most comfortable and at the same time reliable way protect your phone.

None- lack of protection,
Slide- to unlock, you need to slide your finger across the screen in a certain direction.
Pattern- this is the Graphic Key, it looks something like this:
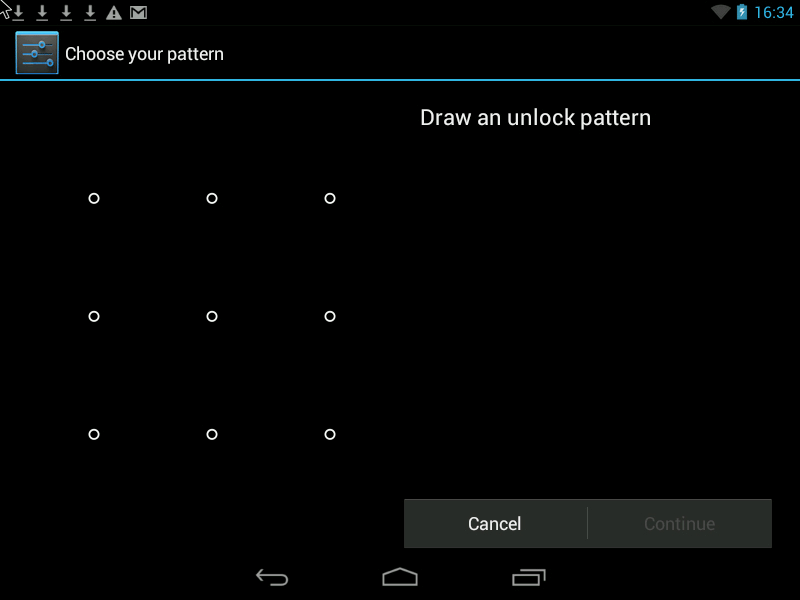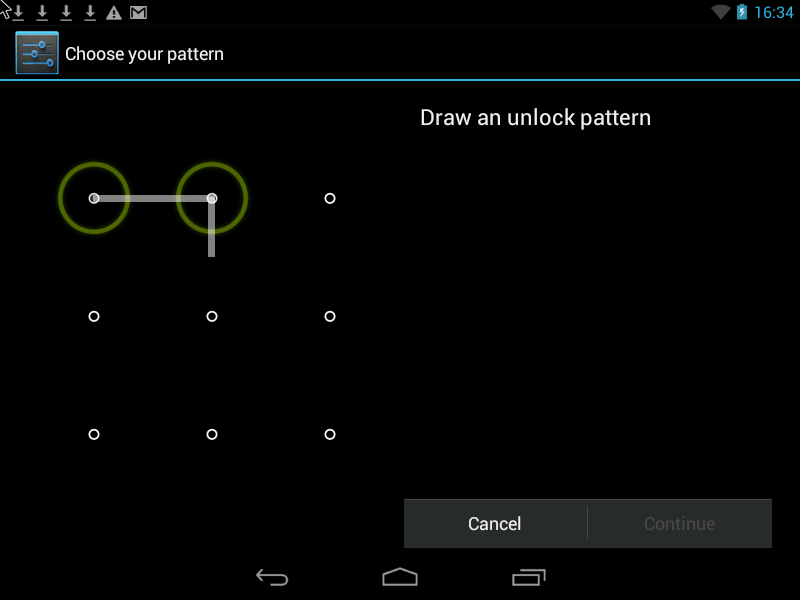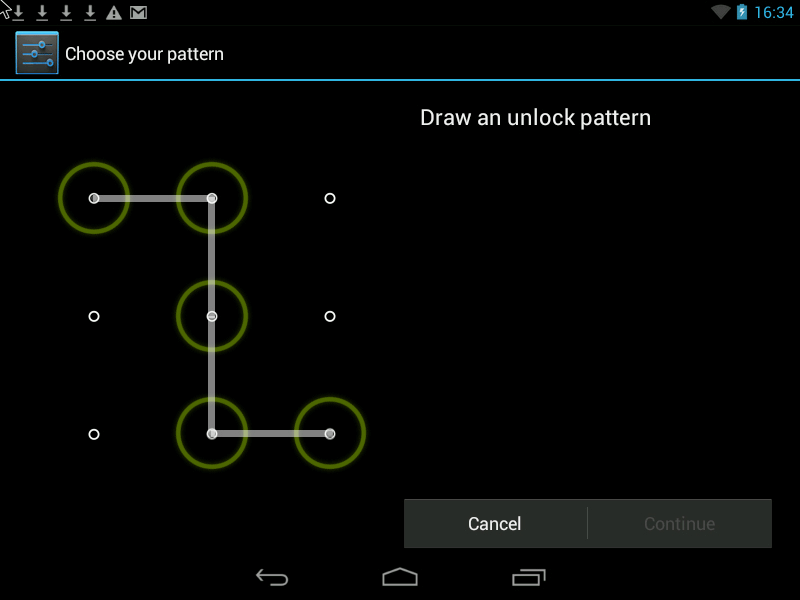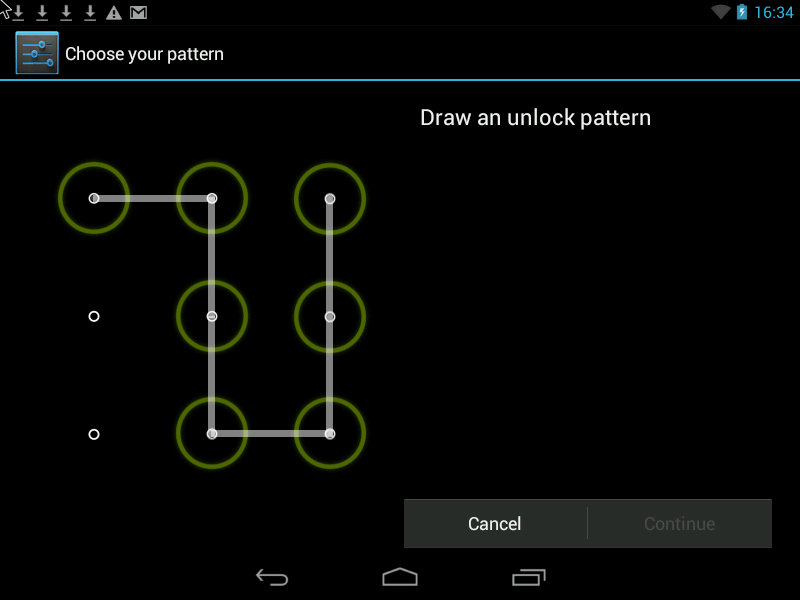
There are two ways to improve security.
1. Increase the input field of the Pattern key. It can vary from 3x3 dots on the screen to 6x6 (Android 4.2 is found in some models, depends on Android version and phone model).
2. Hide the display of points and the "path" of the pattern on the smartphone screen so that it is impossible to peep the key.
3. Set automatic screen lock after 1 minute of inactivity of the phone.
Attention!!! What happens if you forget your pattern:
- The number of incorrect attempts to draw the Pattern Key is limited to 5 times (in different models phone, the number of attempts can be up to 10 times).
- After you have tried all your attempts, but still have not drawn the Pattern Key correctly, the phone is locked for 30 seconds. After that, you will most likely have a couple of tries again depending on your phone model and Android version.
- Next, the phone asks for the login and password of your Gmail account, which is registered in the phone's Accounts settings.
This method will only work if your phone or tablet is connected to the Internet. Otherwise deadlock or reboot to manufacturer settings.
It so happens that the phone falls into the hands of a child - he starts playing, draws the key many times and this leads to the key being blocked.
PIN Is a password consisting of several numbers.
Finally, Password- the most reliable protection, with the ability to use letters and numbers. If you decide to use a password, then you can enable the Phone encryption option.
Phone memory encryption.
The function is included in android package version 4.0 * and higher. for tablets. But this feature may not be available on many budget phones.
It allows you to encrypt the internal memory of the phone so that it can be accessed only by a password or PIN-code. Encryption helps protect information on your phone in the event c
targeted theft. Attackers will not be able to gain access to your data from the phone in any way.
A prerequisite for using encryption is to set up a screen lock with a password.
This method is used to save user data located in the phone memory, for example phone book, browser settings, passwords used on the Internet, photos and videos that the user received with the camera and did not transfer to the SD card.



- SD card encryption is enabled as a separate option.
- Encrypting memory may take up to an hour depending on the amount of memory on your device. The phone cannot be used during encryption.
What if you forgot your password?
Password recovery in this case is not provided. Can be done by phone or tablet full RESET, i.e. reinstall Android, but the user data from the phone or tablet memory will be erased. Thus, if an attacker does not know the password to unlock the phone, he will not be able to use it. It will also be impossible to see data from the phone memory using other programs by connecting the phone to a computer, because all internal memory is encrypted. The only way to get the phone working again is to reformat it.
Attention, the full encryption function is present only starting from Android OS 4.0 - 4.1 and may simply be absent on some phone models. Most often found in phones from Samsung, HTC, LG, Sony. Some Chinese models also have encryption function. On some phones, this function is located in the "Memory" section.
Flaws:
- You will have to constantly enter a rather complex password (6-10 characters), even if you just want to call. Although it is possible to set large interval time (30 minutes) during which the password will not be requested when the phone screen is turned on. On some phone models, the minimum password length can be 3 characters or more.
- On some phone models, it is not possible to turn off encryption if you want to opt out of entering your password permanently. Encryption is disabled only by restoring the phone to factory settings and deleting all data.
External SD card encryption
The function is included in standard package Android 4.1.1 for tablets. Absent in many budget builds.
The function provides reliable protection data on external SD card... Personal photos can be stored here, text files with information of a commercial and personal nature.
Allows you to encrypt files on the SD card without changing their names, file structure, preserving preview graphic files (icons). The function requires a lock password to be set on a display with a length of at least 6 characters.




It is possible to cancel encryption. When the password is changed, it is automatically re-encrypted.
If the user has lost the memory card, the encrypted files cannot be read through the card reader. If you put it on another tablet with a different password, then the encrypted data also cannot be read.
Other Encryption Properties:
- Transparent encryption. If the card is inserted into the tablet and the user has unlocked the screen with a password, any application sees the files in decrypted form.
- If you connect the tablet to a computer via a USB cable, the encrypted files can also be read on the computer by first unlocking the card from the screen of the mobile device.
- If you write any other unencrypted files to the card through the card-reader, they will also be encrypted after the card is inserted into the tablet.
- If you have an encrypted card, you cannot cancel the lock password.
- The data is encrypted at the file level (the names of the files are visible, but the contents of the file are encrypted).
Disadvantage of the program:O Absence in most Android assemblies.
It should be emphasized that the best data safety is a complete copy of it on your Computer in Smartphone is fragile enough small size, which means there is always a possibility of its breakdown or loss.
Improving the usability of a secure smartphone
Fully encrypting your phone provides the strongest level of protection, but constantly entering a 6-digit password makes it difficult to use. But there is a solution.
V Android system from version 4.2 * it is possible to bring some applications \ widgets to the lock screen, and thus you can perform simple actions without permanently unlocking the phone (without entering a 6-digit password).
Outcomes:
- Built-in and free features to protect your phone are very reliable. They are able to protect against prying eyes user's contacts, his correspondence and calls, accounts in various programs and networks, as well as files and folders located both in the phone memory and on the removable SD card.
- Before buying a phone, you should make sure how the required protection works in this particular phone model: the requirement to use a too complex PIN-code or password on the lock screen (the Pattern Key is not suitable), the irreversibility of encryption internal memory phone, i.e. the only way refuse encryption is full reset phone settings.
- Important! Make sure that in case you forgot your password or Pattern, you can restore access to the phone or you can easily restore the phone settings and information in case you have to do a hard reset (reset the phone to factory settings with the loss of all data).
- Keep backup confidential data is only needed on your Computer, on DVD disc or in the cloud.
Data encryption in Android OS is closely related to two problems: control of access to memory cards and the transfer of applications to them. Many programs contain activation data, billing information, and confidential information. Its protection requires management of access rights, which are not supported by typical cards. file system FAT32. Therefore, in each version Android approaches to encryption have changed dramatically - from complete absence cryptographic protection removable media before their deep integration into a single section with encryption on the fly.
WARNING
Each gadget with Android OS has its own significant differences - both in the firmware and at the hardware level. Even different versions of the same model can be very different. Memory cards also have their own characteristics. So detailed guides using encryption on one device often doesn't work without modification on another. Generic Methods doesn't exist here. There is only general approaches, which are described in this article.
The special role of the memory card
Initially android developers assumed the use of the memory card only as a separate storage for user files. It was just a multimedia warehouse with no security or reliability requirements. MicroSD (HC) cards with FAT32 coped with the role of the simplest storage, freeing the internal memory from photos, videos and music.
The ability to transfer to a memory card not only multimedia files but the app first appeared in Android 2.2 Froyo. It was implemented using the concept of encrypted containers for each application, but it only protected it from falling into the wrong hands of a card - but not a smartphone.
In addition, it was a half measure: many programs were partially transferred, leaving part of the data in the internal memory, and some (for example, system or containing widgets) were not transferred to the card at all. The very possibility of transferring applications depended on their type (pre-installed or third-party) and internal structure... For some, the directory with user data was immediately located separately, while for others - in a subdirectory of the program itself.

If applications heavily used read / write operations, then the reliability and speed of the cards could no longer satisfy the developers. They deliberately did so that the porting of programs regular means became impossible. Due to such a trick, their creation was guaranteed to receive registration in the internal memory with a large rewriting resource and high performance.
With the fourth version, Android has the ability to choose where to place the application. It was possible to designate a memory card as a drive for installing programs by default, but not all firmwares correctly supported this function. How does she work in specific device- I could only find out empirically.
Fifth Android Google again decided to return the original concept and did everything to make it as difficult as possible to transfer applications to a memory card. Major manufacturers caught the signal and added their own monitoring functions to the firmware, which determine the user's attempts to forcefully move applications to the card using the root. More or less only the option with creating tough or symbolic links. In this case, the application was identified by the standard address in the built-in memory, but in fact was located on the card. However, the confusion was caused by file managers, many of which were handling links incorrectly. They showed the wrong volume free space, because it was believed that the application allegedly takes up space both in the built-in memory and on the card at the same time.
Adapt it!
V Android Marshmallow there was a compromise called "Adaptable storage" - Adoptable Storage... This is Google's effort to keep the sheep safe and the soldiers happy.
The Adoptable Storage function allows you to combine a user partition in the on-board memory with a partition on a card into one logical volume. In fact, it creates an ext4 or F2FS partition on the card and adds it to the user's internal storage partition. It's clean logical operation unification, vaguely reminiscent of the creation compound volume from multiple physical disks in Windows.

In the process of combining with the internal memory, the card is reformatted. By default, the entire volume will be used in the consolidated volume. In this case, the files on the card can no longer be read on another device - they will be encrypted with a unique device key, which is stored inside the trusted runtime environment.
Alternatively, you can reserve space on the card for a second FAT32 partition. Files stored on it will be visible on all devices as before.
The way to divide the card is set either through the Adoptable Storage menu, or through debug bridge for Android (Android Debug Bridge - ADB). The last option used in cases where the manufacturer has hidden Adoptable Storage from the menu, but has not removed this function from the firmware. For example, it is hidden in Samsung Galaxy S7 and top smartphones LG. V Lately in general, there is a tendency to remove Adoptable Storage from flagship devices... She is considered a crutch for budget smartphones and tablets that do not have enough built-in Flash memory.
However, it is not marketers who decide how we use our devices. Via ADB on a computer with Windows function Adoptable Storage is included as follows.
- We make a backup of all data on the card - it will be reformatted.
- Java SE Development kit from Oracle website.
- Install latest version Android SDK Manager.
- Turn on USB debugging on your smartphone.
- Launch SDK Manager and in command line write: $ adb shell $ sm list-disks
- We write down the disk number under which the memory card is determined (usually it looks like 179: 160, 179: 32 or similar).
- If you want to add the entire volume of the card to the internal memory, then write in the command line: $ sm partition disk: x: y private
where x: y is the number of the memory card.
- If you want to leave a part for a FAT32 volume, then change the command from p. 7 to this: $ sm partition disk: x: y mixed nn
where nn is the percentage of the remaining volume for a FAT32 volume.
For example, the command sm partition disk: 179: 32 mixed 20 will add 80% of the card's capacity to the built-in memory and leave a FAT32 volume on it in 1/5 of its capacity.
On some smartphones, this method “as is” no longer works and requires additional tweaks. Manufacturers are doing everything to artificially divide their products into market niches. Top models are produced with different amounts of built-in memory, and there are fewer and fewer people willing to overpay for it.
Some smartphones do not have a slot for a memory card (for example, the Nexus series), but support the connection of USB-Flash media in OTG mode... In this case, the flash drive can also be used to expand the amount of built-in memory. This is done by the following command:
$ adb shell sm set-force-adoptable true
By default, the ability to use USB-OTG to create customized storage is disabled because unexpectedly ejecting it may result in data loss. Probability sudden shutdown the memory card is much lower due to its physical placement inside the device.
If adding volume removable media If you have problems with partitioning it, first remove all information about the previous logical markup from it. This can be done reliably using the gparted Linux utility, which on a Windows computer runs with boot disk or in a virtual machine.
According to the official Google policy, applications can be immediately installed in the adaptable repository or transferred to it if the developer has specified this in the android: installLocation attribute. The irony is that not all own applications Google still allows you to do this. There are no practical limits for the "adapted storage" in Android. Theoretical limit for Adoptable Storage is nine zettabytes. There are not so many even in data centers, and even more memory cards of larger capacity will not appear in the coming years.
The encryption procedure itself when creating an adapted storage is performed using dm-crypt - the same module Linux kernels, which performs full-disk encryption of the built-in memory of the smartphone (see the previous article ""). The AES algorithm is used in ciphertext block concatenation (CBC) mode. A separate salted initialization vector (ESSIV) is generated for each sector. The length of the SHA hash convolution is 256 bits, and the key itself is 128 bits.
Such an implementation, although inferior in reliability to AES-XTS-256, is much faster and is considered reliable enough for user devices... A curious neighbor is unlikely to open an encrypted adapted storage in a reasonable time, but intelligence agencies have long learned to exploit the shortcomings of the CBC scheme. Besides, in reality, not all 128 bits of the key turn out to be completely random. Unintentional or intentional weakening of the built-in generator pseudo-random numbers is the most common cryptography problem. It affects not so much Android gadgets as all consumer devices in general. Therefore, the safest way to ensure privacy is not to store confidential data on your smartphone at all.
INFO
If you reset to factory settings after combining memory using Adoptable Storage, the data on the card will also be lost. Therefore, you should first make a backup of them, or better, immediately assign cloud sync.
Alternative encryption of data on the memory card
Now that we have figured out the features of storing files on a memory card in different versions Android, let's go directly to their encryption. If you have a device with the sixth Android and newer, then with a high probability it is possible to activate the Adoptable Storage function in one way or another. Then all data on the card will be encrypted, as in the built-in memory. Only the files on the additional FAT32 partition will remain open, if you wanted to create one when reformatting the card.
Continuation is available only to subscribers
Option 1. Subscribe to "Hacker" to read all materials on the site
Subscription will allow you to read ALL paid materials on the site within the specified period. We accept payment bank cards, electronic money and transfers from the accounts of mobile operators.
One of the innovations in the fifth version of Android is the ability to fully encrypt the contents of the device's memory. In theory, it completely excludes unauthorized access to files on a lost or stolen smartphone or tablet if logging into the operating system password protected... In addition, encryption prevents data theft viral applications and Trojans. Even if an attacker steals some information, he will not be able to read it, since the encryption key is generated every time the device is turned on.
Google originally required manufacturers to enable full encryption on all Lollipop devices, but in early March made changes to the Android Compatibility program. Now it states that manufacturers recommended enable full encryption, but this is not required. It is known that on Google nexus 6 and Nexus 9 have this protection installed, and on Motorola moto E and Samsung Galaxy S6, it is disabled by default.
Full encryption helps keep your personal data safe from outsiders, but can negatively impact device performance. For example, Galaxy S6 and Galaxy S6 Edge with encryption enabled show only 48 thousand points in AnTuTu, and without it about 70 thousand.

Benchmark readings are one thing, but how fast the device works in real life, completely different. Some people can get used to small freezes, while others cannot, so enabling or not enabling full encryption is a personal matter for each user. If data privacy is more important to you, it is better to enable it. And if you do not store anything on your smartphone or tablet that could embarrass you, you can leave it turned off (or turn it off) - in this case, you may notice an increase in device performance.
You can check if you have encryption enabled in system settings... If you decide to encrypt data, find the appropriate item in the settings and specify a password that will subsequently be used to cancel encryption. The device will restart, start encryption, and turn on after a few minutes. How long it takes depends on the amount of data being processed. The contents of a memory card can also be encrypted, but after that it will no longer be read by other devices.

You can cancel encryption in the same menu item. You will need to enter the password that you specified earlier, after which the device will reboot, remove the encryption and turn on again. Please be aware that all personal data and installed applications at the same time they will be erased.
It is not recommended to disable encryption on Nexus 6 and Nexus 9, as this process triggers bootloader unlocking, which in rare cases causes device breakdown.



