The hard disk of a computer is a device that, perhaps, fails more often than other parts of computer technology. This is often due to the fact that the computer's hard disk is very sensitive to mechanical and electrical influences, such as vibration and shock, as well as to voltage surges and insufficient supply current.
Signs of a hard drive malfunction may include: slow loading of the computer's operating system; errors in copying, moving, reading files; BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) - the so-called blue screen of death, a critical error during computer operation. Often, the operating system may not load at all or the load does not reach the end; in the Windows system it hangs at the Microsoft logo. On some models of computers and laptops, when the computer is turned on, the corresponding error may be displayed - SMART HDD BAD, HDD ERROR, etc.
In especially severe cases, the HDD may not be detected by the computer (you cannot see it in the BIOS), when you turn on the computer, it immediately turns off, extraneous sounds like clicks, friction sounds, squeak.
It is not difficult to diagnose a malfunction of a computer's HDD, especially since today there are many different programs. Of course, if there is a lot of noise from the HDD during its operation or attempts to turn it on, etc. signs, then there is no need to guess about the reasons for the failure of the computer - we change the hard drive. But more often than not, you will have to use a useful program to troubleshoot a problem.
So, what do you need to know about a hard drive to determine how efficient it is?
Basically, it is enough to pay attention to 2 points:
1. S.M.A.R.T hard drive.
S.M.A.R.T. (from English self-monitoring, analysis and reporting technology - technology of self-monitoring, analysis and reporting) - a technology for assessing the state of a hard disk with built-in self-diagnostic equipment, as well as a mechanism for predicting the time of its failure. In fact, it is an HDD recorder, which records all its parameters during the life of the HDD, according to these parameters, one can conclude about the "health" of the hard disk.
2. The state of the surface (sectors) of the hard disk.
Information on a hard disk is stored in sectors (sector capacity can be 512 bytes or 4096 bytes), respectively, one file can be located in hundreds of such sectors. Information is also read from them, and the more this speed corresponds to the technical characteristics of the HDD, the more it speaks about its performance. Read delays indicate a problem with the HDD.
To check these parameters of the hard drive, we will focus on the Victoria 4.46b program.
The program does not require installation, just download and run the "vcr446f" application file.
When the program starts, the "Standart" tab window appears:
On the right side of the interface (2) of the program, you need to indicate the hard disk under test, while on the left (1) information about the hard disk will be displayed - serial number, model, memory size, etc.

And we press the "Get SMART" button, the status is written to the right of the button, in this case "GOOD", this means that the program automatically determines our disk to be good based on the SMART indicators, otherwise there will be a red inscription "BAD". However, do not rely on this inscription, as it often happens that one of the SMART indicators is in a critical state, while the program displays "GOOD".
SMART Attributes (click)
01 Raw Read Error Rate
The frequency of errors when reading data from a disk, the origin of which is caused by the disk's hardware. For all Seagate, Samsung (F1 and newer) and Fujitsu 2.5 ″ drives, this is the number of internal data corrections made before being issued to the interface, so you can react calmly to frighteningly large numbers.
02 Throughput Performance
Overall disk performance. If the value of the attribute decreases, then there is a high probability that there is a problem with the disk.
03 Spin-Up Time
Time to spin up a disk pack from rest to operating speed. It grows with wear of the mechanics (increased friction in the bearing, etc.), it can also indicate poor-quality power supply (for example, a voltage drop at the start of the disk).
04 Start / Stop Count
Total number of spindle start-stop cycles. Some manufacturers' drives (for example, Seagate) have a power saving mode counter. The raw value field stores the total number of starts / stops of the disk.
05 Reallocated Sectors Count
The number of sector remapping operations. When the disk detects a read / write error, it marks the sector "reassigned" and transfers the data to a dedicated spare area. This is why bad blocks cannot be seen on modern hard drives - they are all hidden in remapped sectors. This process is called remapping, and the remapped sector is called remap. The higher the value, the worse the surface condition of the discs. The raw value contains the total number of remapped sectors. An increase in the value of this attribute may indicate a deterioration in the condition of the surface of the disk pancakes.
06 Read Channel Margin
Reading channel margin. The purpose of this attribute is not documented. Not used in modern drives.
07 Seek Error Rate
The frequency of errors in the positioning of the magnetic head unit. The more of them, the worse the condition of the mechanics and / or the surface of the hard drive. Also, the parameter value can be affected by overheating and external vibrations (for example, from neighboring disks in the cage).
08 Seek Time Performance
Average productivity of the positioning operation with the magnetic heads. If the attribute value decreases (positioning deceleration), then there is a high probability of problems with the mechanical part of the actuator.
09 Power-On Hours (POH)
The number of hours (minutes, seconds - depending on the manufacturer) spent in the switched on state. The passport mean time between failure (MTBF) is chosen as a threshold value for it.
10 Spin-Up Retry Count
The number of retries to spin up disks up to operating speed if the first attempt was unsuccessful. If the value of the attribute increases, then there is a high probability of problems with the mechanical part.
11 Recalibration Retries
The number of retries of recalibration requests in case the first attempt was unsuccessful. If the value of the attribute increases, then there is a high probability of problems with the mechanical part.
12 Device Power Cycle Count
The number of complete on-off cycles of the disk.
13 Soft Read Error Rate
The number of reading errors due to the fault of the software that could not be corrected. All errors are not mechanical in nature and only indicate incorrect layout / interaction with the program disk or the operating system.
184 End-to-End error
This attribute is part of HP SMART IV technology, which means that after the data buffer is transferred through the data buffer cache, the data parity between the host and the hard disk does not match.
187 Reported UNC Errors
Errors that could not be recovered using hardware error recovery techniques.
188 Command Timeout
The number of aborted operations due to HDD timeout. Usually this attribute value should be zero, and if the value is much higher than zero, then most likely there will be some serious power problem or oxidized data cable.
190 Airflow Temperature (WDC)
Air temperature inside the hard drive enclosure. For Seagate drives, it is calculated using the formula (100 - HDA temperature). For Western Digital drives - (125-HDA).
191 G-sense error rate
The number of errors resulting from shock loading. The attribute stores the readings of the built-in accelerometer, which records all shocks, bumps, falls, and even inaccurate installation of the disk into the computer case.
192 Power-off retract count
The number of shutdown cycles or emergency failures (power on / off of the drive).
193 Load / Unload Cycle
The number of cycles of movement of the block of magnetic heads in the parking zone / in the working position.
194 HDA temperature
The readings of the built-in thermal sensor for the mechanical part of the disk - cans (HDA - Hard Disk Assembly) are stored here. Information is taken from the built-in thermal sensor, which is one of the magnetic heads, usually the bottom one in the bank. The bit fields of the attribute record the current, minimum and maximum temperatures. Not all programs that work with SMART parse these fields correctly, so their readings should be taken critically.
195 Hardware ECC Recovered
The number of error correction by the hardware of the disk (reading, positioning, transferring to the external interface). On disks with a SATA interface, the value often deteriorates with an increase in the system bus frequency - SATA is very sensitive to overclocking.
196 Reallocation Event Count
The number of remapping operations. The "raw value" field of the attribute stores the total number of attempts to transfer information from the reassigned sectors to the spare area. Both successful and unsuccessful attempts are counted.
197 Current Pending Sector Count
The number of sectors that are candidates for replacement. They have not yet been identified as bad, but reading from them is different from reading the stable sector, these are the so-called suspicious or unstable sectors. In the event of a successful subsequent reading of the sector, it is excluded from the list of candidates. In case of repeated erroneous reads, the drive tries to restore it and performs a remaping operation. An increase in the value of this attribute may indicate physical degradation of the hard disk.
198 Uncorrectable Sector Count
The number of unrecoverable errors when accessing the sector. (Probably, it meant "the number of uncorrected (by means of the disk) sectors", but not the number of errors themselves В случае увеличения числа ошибок велика вероятность критических дефектов поверхности и/или механики накопителя.
!}
199 UltraDMA CRC Error Count
The number of errors that occur when transferring data via an external interface in UltraDMA mode (packet integrity violations, etc.). A rise in this attribute indicates a bad (wrinkled, kinked) cable and poor connections. Also, such errors appear when overclocking the PCI bus, power failures, strong electromagnetic interference, and sometimes due to the fault of the driver. Perhaps the reason is a poor-quality train. To fix it, try using a SATA cable without latches and tightly connected to the pins of the drive.
200 Write Error Rate /
Multi-Zone Error Rate
Shows the total number of errors that occur while writing a sector. Shows the total number of disk write errors. Can serve as an indicator of the surface quality and mechanics of the drive.
201 Soft read error rate
The frequency of "software" errors when reading data from a disk. This parameter shows the frequency of errors during read operations from the disk surface due to the fault of the software, not the hardware of the drive.
202 Data Address Mark errors
Number of Data Address Mark (DAM) errors (or) vendor-specific.
203 Run out cancel
The number of ECC errors.
204 Soft ECC correction
The number of ECC errors programmatically corrected.
206 Flying height
Height between the head and the surface of the disc.
207 Spin high current
The magnitude of the current when spinning the disk.
209 Offline seek performance
Drive's seek performance during offline operations.
220 Disk Shift
Distance of displacement of the block of discs relative to the spindle. It is mainly caused by being hit or dropped. The unit is unknown. As the attribute increases, the disk quickly becomes unusable.
221 G-Sense Error Rate
The number of errors due to external stress and shock. The attribute stores the readings of the built-in shock sensor.
222 Loaded Hours
The time spent by the head unit between unloading from the parking area to the working area of the disk and loading the unit back into the parking area.
223 Load / Unload Retry Count
The number of new attempts to unload / download the magnetic head unit to / from the parking area after an unsuccessful attempt.
224 Load Friction
The magnitude of the frictional force of the magnetic head unit when it is unloaded from the parking area.
225 Load Cycle Count
The number of times the head unit has been moved to the parking area.
226 Load "In" -time
The time it takes for the drive to unload the magnetic heads from the parking area onto the working surface of the disc.
227 Torque Amplification Count
The number of attempts to compensate for torque.
228 Power-Off Retract Cycle
The number of times to automatically park the head assembly as a result of a power off.
230 GMR Head Amplitude
Amplitude of "jitter" (distance of repeated movement of the magnetic head unit).
231 Temperature
Hard disk temperature.
240 Head flying hours
Head positioning time.
250 Read error retry rate
The number of errors while reading the hard disk.
As you can see from the SMART indicators, you can learn a lot about the state of the HDD. Not necessarily all attributes will be shown on a specific drive. Pay particular attention to indicators
187 Reported UNC Errors
196 Reallocation Event Count
200 Write Error Rate
If the readings are greater than 0, then there is a reason to think about replacing the HDD.
191 G-sense error rate is an indicator of mechanical impact, if it is significant (more than 100), then you should also think about replacing it.
Figure 2 shows the case when the program says "GOOD", but the HDD has problems and it is better to change it, the operating system hangs on this disk, the programs run slowly.
Let's move on to testing the surface of the hard drive. To do this, select the "Test" tab and click "Start". The graphical form shows the results of testing the HDD sectors. The color of the sectors from green to red indicates read delays. If the sector is marked with a yellow X on a blue background, then such a sector is not readable at all, the disk must be replaced.

Thus, with the help of one program, you can diagnose the HDD and make a timely replacement and make a backup copy of the data, if the disk is even less efficient.
Regardless of your operating system (Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8), go to Computer (My Computer, This Computer) click on the drive you want to check with the right mouse button, select " Properties".
In the properties window, go to the " Service"and press the button" Check".

We put both checkboxes
Automatically fix system errors.
Check and repair system sectors.
and press " Running".

If you are checking the system volume (the drive on which the operating system is installed, usually drive C) you will see the message " Windows cannot check the hard drive that is currently in use", click" Disk check schedule".

Then restart your computer / laptop, during boot, the process of checking and fixing errors on the disk will start. It will last from a few minutes to an hour (depending on the size of the partition and the physical characteristics of the hard disk). When finished, the operating system will boot.

Checking the hard disk using the chkdsk utility.
CHKDSK (short for check disk) is a standard application in DOS and Microsoft Windows operating systems that checks a hard disk or floppy disk for file system errors (for example, the same sector is marked as belonging to two different files). CHKDSK can also fix found file system errors. (from Wikipedia)
In order to run the chkdsk utility, you must run the command line with administrator rights, for this:
V Windows XP click - "Command line"
V Windows 7 click "Start" - "All Programs" - "Accessories" "Command line" and select "Run as administrator".
V Windows 8.1 right click on "Start" - "Command line (administrator)".
This will open the command line console.
First of all, we will find out the syntax of the chkdsk utility:
CHKDSK [volume [[path] filename]]]
Volume Specifies the mount point, volume name, or letter of the scanned drive followed by a colon.
File name Files scanned for fragmentation (FAT / FAT32 only).
/ F Correction of errors on the disk.
/ V For FAT / FAT32: displays the full path and name of each file on the disk. For NTFS: Display cleanup messages (if any).
/ R Find bad sectors and restore surviving content (requires / F).
/ L: size NTFS only: Sets the size of the log file (in KB). If no size is specified, the current value of the size is displayed.
/ X Pre-dismount the volume (if necessary). Any open descriptors for this volume will be invalid (requires / F).
/ I NTFS only: Less stringent check of index entries.
/ C NTFS only: Skip checking loops inside the folder structure.
/ B NTFS only: Re-evaluate bad clusters on disk (requires / R)
The / I or / C options shorten the execution time of Chkdsk by skipping some of the volume checks.
Of all the command attributes, the two most commonly used to check the disk for errors are / f and / r. The final command looks like this:
chkdsk C: / F / R
With this command we will check section C, fix errors on the disk and recover information from bad sectors (if any).
After entering this command, you will be prompted to check the volume at the next system reboot, click Y and the key Enter.

Now you need to reboot the system, at boot you will see a window offering verification, do not click anything, just wait 10 seconds.

Checking for hard disk errors with Victoria.
Victoria program is designed to check for errors hard drives with IDE and Serial ATA interfaces. The program is a completely ready-made solution for a comprehensive, deep, and at the same time the fastest possible assessment of the real technical condition of the HDD.
First of all, download the ISO image of the program from official site ... Unzip the downloaded archive and burn it to a CD / DVD disc, how to do this is described in the article How to burn to CD / DVD ... After that, boot from the burned disc, how to do it step by step is described in the article How to boot from CD / DVD disc or USB stick .
After booting from the disk within 10 seconds, select the program for your device (Victoria will load for the computer by default).

The program interface will start. Press the F2 key, in order for the program to find the disk itself, if this does not happen, you need to do it manually. To do this, press the "P" key. You will have to do the same if there are several hard drives in the system and you need to select one of them. If you have hard drives with SATA interface, then in the appeared menu Select HDD port select - " Ext. PCI ATA / SATA". Moving is carried out with the cursor keys" up "," down ", and the selection - with the" Enter "key.


Next, to check the surface of the disk, press the F4 key. In the HDD scan menu: select the required scan parameters. By default, it is suggested to scan the entire disk from the beginning of "Start LBA: 0" to the end of "End LBA: 20971520". I recommend leaving these default values. The next menu item - I recommend leaving the "Linear reading" as it is intended for the fastest and most accurate diagnostics of the surface condition. In the fourth paragraph, I recommend choosing the mode BB = Advanced REMAP, since this mode checks the disk with the best quality and fixes errors on it without deleting the information.

After that, a check for hard disk errors will start, correcting bad areas. This procedure can take from several tens of minutes to several hours. Depends on the volume and speed of the spindle.

When finished, remove the disc from the drive and restart your computer.
Video of checking the hard drive using the Victoria utility. Error elimination - Missing DRSC + DRDY or the screw does not remove BUSY
The work of any computer is based on the collection and processing of information. All your files are saved on your hard drive (or hard drive). It is worth knowing that this memory device is used to store information with available or random access to files, and the principle of operation of the "hard drive" is a magnetic recording of information.
Where did the name "hard drive" actually come from? In this device, all recording is made on glass or aluminum plates, which are covered with a layer of ferromagnet (in most cases, this is chromium dioxide). There can be one or several plates, if there are several, then they are independent of each other, but are attached on one axis.
The main characteristics of hard drives are
- Data transfer speed (this parameter in modern drives ranges from 25 to 62 MB per second).
- Rotational speed of the plates. Its essence: the faster the platters rotate, the more efficient the hard disk is.
- Disk space (this parameter is always the first of interest to users).
With a lot of information, the hard drive may not cope with its duties. And before you check your hard drive, remember that some applications or programs may not work after checking it.
Checking the hard drive
To check the hard drive for errors without using special programs, you will need:
- Click "Start", in it select the "Computer" tab.
- On the shortcut of the hard drive, right-click and select "Properties".
- On the "Service" tab, find "Disk check" and click the "Run check" button (if the hard drive is password-protected, then enter it in the field that the system will display in the request form).
- By checking the box "Automatically fix system errors", the system will do everything automatically. If this option is not enabled, notifications will be sent, but no corrections will be made.
- For a more thorough disk check, click the button next to the "Check and repair bad sectors" option. In this case, the system will correct physical errors on the hard disk, if, of course, such errors are identified. This operation takes longer than the previous one.
- Checking the hard disk will be much more optimal if you use the items "Automatically fix system errors" and "Check and repair bad sectors" together.
Checking the health of the hard drive
A hard drive is one of the most vulnerable places in a computer, because when this device fails, the files that were once stored on it cannot be returned. And therefore, in order to know how to check the health of a hard drive, you first need to assess the state of the "hard drive". And besides, you do not need to immediately run to service centers, or moreover, buy a new hard drive.
Hard disk check programs
At the moment there are many software with a free license for them to check the hard drive. The Victoria program, which is considered primarily a utility, works with disk drives starting at the lowest tier. That is, this software not only tests the equipment, but also carries out minimal repairs to the broken sectors of the "hard drive". Also using this program you can:
- Enable SMART - hard disk tests.
- Control the noise level of your equipment.
- Changing the rotational speed of the plates and the reading head.
The HD Tune program, in comparison with "Victoria", has less potential and is easier to use. With it, you can monitor the performance of your hard drive, look for errors, safely erase data from the drive, and other functions. This software is very fast, for example, an 80 GB hard drive is checked in about half a minute.
A better known program for testing hard drives is HDDScan, it is designed to search for information about downed hardware blocks, view SMART, power management and much more.
Checking laptop hard drive
As for the question of how to check a laptop hard drive, it is worth noting that there are some peculiarities here. Laptop Winchester is smaller and is more likely to be affected by temperature. Therefore, the way out of this situation is to install slow hard drives. This, on the other hand, will reduce the power consumption of the laptop and extend the life of the device.
Checking a hard drive on a laptop is no different from checking on a computer. The main thing is to arm yourself with patience and a set of useful programs.
Good day!
How many things could be corrected if we knew in advance what awaits us ...
And if in life it is almost impossible to predict some events, then in the case of a hard disk - some of the problems, nevertheless, can be predicted and foreseen!
To do this, there are special utilities that can find out and analyze the SMART * readings of the disk (show them to you, if necessary), and on the basis of this data assess the health of your disk, along the way calculating how many years it will still be able to serve.
The information is extremely useful, in addition, such utilities can monitor your disk online, and as soon as the first signs of unstable work appear, notify you right there. Accordingly, you will have time to make a backup in time and take action (although a backup should always be done, even when everything is fine ☺).
And so, I will consider in the article several methods (and several utilities) for analyzing the state of the HDD and SSD.
* Note:
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) is a special technology for assessing the state of a hard disk by an integrated hardware self-diagnosis / self-monitoring system. The main task is to determine the likelihood of a device failure, preventing data loss.
Perhaps this is one of the most popular questions asked by all users who first encounter problems with a hard drive (or are thinking about the safety of storing their data). Everyone is interested in the time that the disk will work until it completely "stops". Let's try to predict ...
Therefore, in the first part of the article, I decided to show a couple of utilities that can get all the readings from the disk and analyze them independently, and give you only the finished result (in the second part of the article, I will give utilities for viewing SMART readings for independent analysis).
Method number 1 - using Hard Disk Sentinel
One of the best utilities for monitoring the status of computer disks (both hard drives (HDD) and "newfangled" SSDs). What impresses the most about the program is that it will independently analyze all the data received about the state of the disk and show you a ready-made result (very convenient for novice users).
In order not to be unfounded, I will immediately show the main window of the program, which appears after the first launch (the analysis of the disk will be done immediately automatically). The health and performance of the disk is estimated as 100% (ideally, it should be so), the time that the disk will still work in normal mode is estimated by the program at about 1000 days (~ 3 years).

What's with the disk according to Hard Disk Sentinel
In addition, the program allows you to monitor the temperature: both current and average and maximum during the day, week, month. If the temperature goes beyond the "normality" - the program will warn you about this (which is also very convenient).
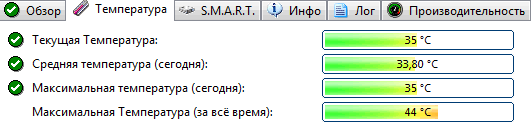
Also, Hard Disk Sentinel allows you to view SMART readings (however, to evaluate them, you need to understand the disks well), get complete information about the hard disk (model, serial number, manufacturer, etc.), see what the hard disk is loaded with (i.e. . get performance information).
In general, in my humble opinion, Hard Disk Sentinel is one of the best utilities for monitoring the status of disks in the system. It should be added that there are several versions of the programs: professional and standard (for the professional version with extended functionality, there is a portable version of the program that does not need to be installed (for example, you can even run it from a USB flash drive)).
Hard Disk Sentinel works in all popular Windows (7, 8, 10 - 32 | 64 bits), supports the Russian language in full.
Method # 2 - using HDDlife
This program is similar to the first, it also clearly shows the current state of the disk: its health and performance (in percentage terms), its temperature, the amount of time worked (in months). In the upper part of the window, based on all this data, HDDlife shows the final summary for your disk, for example, in my case "ALL RIGHT" (which means that everything is in order with the disk).
By the way, the program can work online, monitoring the state of your disk, and in case something goes wrong (at the first signs of problems) - immediately notify you about it.

As an example, the screenshot below shows an SSD drive received a warning: its health is still within acceptable limits, but reliability and performance are below average. In this case, you should not trust the disk with any important data, and, if possible, you need to prepare for its replacement.

By the way, in the main window of the program, next to the amount of disk time worked, there is a link "Disk tincture" (allows you to change some of the parameters you want). By opening it, you can control the balance between noise / performance), very useful with disks that make a lot of noise), and adjust the power consumption settings (useful for laptops that run out of battery quickly).

Add-on: HDDlife works on both PCs and laptops. Supports HDD and SSD drives. There are portable versions of the program that do not need installation. It can be configured so that the program runs along with your Windows. HDDlife works in Windows: XP, 7, 8, 10 (32 | 64 bits).
How to view your SMART reading
If the previous utilities independently assessed the state of the disk based on SMART data, then the utilities below will give you more freedom and data for self-analysis. In the reports it will be possible to find a fairly large set of parameters, on the basis of which it will be possible to roughly assess the state of the disk and make a forecast for its further work.
Method number 1 - using СrystalDiskInfo
СrystalDiskInfo
An excellent free utility for viewing the status and SMART readings of a hard drive (SSD drives are also supported). What the utility wins over - it provides you with complete information about the temperature, technical condition of the disk, its characteristics, etc. that "and for beginners who need a hint).
For example, if something is wrong with the temperature, then you will see a red indicator on it, i.e. СrystalDiskInfo will inform you about it.

The main window of the program can be conditionally divided into 4 zones (see the screenshot above):
- "1" - all your physical disks installed in the computer (laptop) are listed here. Next to each is shown its temperature, technical condition, and the number of sections on it (for example, "C: D: E: F:");
- "2" - the current temperature of the disk and its technical condition are shown here (the program makes an analysis based on all the data received from the disk);
- "3" - disk data: serial number, manufacturer, interface, rotation speed, etc .;
- "4" - readings SMART. By the way, what the program bribes with - you don't need to know what this or that parameter means - if something is wrong with any item, the program will mark it yellow or red and notify you about it.
As an example to the above, I will give a screenshot showing two disks: on the left - with which everything is fine, on the right - which has problems with reassigned sectors (technical condition - anxiety!).

As a reference (about reassigned sectors):
when the hard drive detects, for example, a write error, it transfers data to a specially designated spare area (and this sector will be considered "reassigned"). Therefore, bad blocks cannot be seen on modern hard drives - they are hidden in reassigned sectors. This process is called remapping and the reassigned sector is remap.
The higher the value of the remapped sectors, the worse the surface condition of the disks. Field "raw value" contains the total number of reassigned sectors.
By the way, for many disk manufacturers, even one reassigned sector is already a warranty case!
To the utility CrystalDiskInfo monitored online the status of your hard disk - in the "Service" menu, put two checkmarks: "Agent start" and "Autostart"(see screenshot below).

Then you will see the program icon with temperature next to the clock in the tray. In general, you can now be more calm about the state of the disk ☺ ...

Method number 2 - with the help of Victoria
Victoria- one of the most famous programs for working with hard drives. The main purpose of the program is to assess the technical condition of the drive, and to replace the damaged sectors with backup workers.
The utility is free and allows you to work from both Windows and DOS (which in many cases shows much more accurate data about the state of the disk).
Of the minuses: working with Victoria is quite difficult, at least I highly do not recommend pressing buttons in it at random (you can easily destroy all the data on the disk). I have one fairly large article on my blog, where it is analyzed in detail how to check the disk using Victoria (including finding out the SMART readings - an example in the screenshot below (in which Victoria pointed out a possible temperature problem)).
Instructions for working with Victoria:

SMART tab || utility Victoria
On this I will round off, good luck to everyone!
Additions on the topic are welcome ☺
Hard drives are the most unreliable component of a modern computer. As a rule, modern hard drives last up to 3 years, after which they have to be replaced. The worst thing about this situation is that it is very difficult to predict exactly when a hard drive will break. Because of this, inexperienced users often lose important data. In this article, we will talk about how to check a hard drive for serviceability and correctly assess its condition. Step # 1. Checking the health of the hard drive using CrystalDiskInfo If you want to test the hard drive for serviceability, the first thing to do is to install the CrystalDiskInfo program. This free program collects all available information about the hard drive and, based on it, gives an assessment of its technical condition. If the hard disk is fully functional, then the technical condition of the hard disk will be indicated as "Good". If there is a problem with the hard disk, then you will receive a rating of "Anxiety". Well, in those cases when the hard drive is on the verge of death, the program gives the rating "Bad".
Also in the CrystalDiskInfo program you can view the original data of S.M.A.R.T. (their program uses them to assess those conditions), the temperature of the hard disk, the number of times the hard disk is turned on, as well as the number of hours worked. Step # 2. Check the hard drive for errors using HD Tune. It is also very important to check the hard drive for errors. The easiest way to do this is to use the free HD Tune program (or its paid version HD Tune Pro). So, in order to check the hard drive for errors, run the HD Tune program, go to the tab and click on the "Start" button.
Then HD Tune will start checking the hard disk for good condition. During the check, you will be able to observe this process. Normal areas of the hard drive will be marked in green, and damaged areas in red.
There should be no damaged (red) blocks on a fully functional hard disk. Step number 2. We check the hard disk for serviceability manually. In addition to testing with programs, the hard drive can be manually checked for serviceability. To do this, just try to write a large number of small files (a couple of megabytes in size) to disk. For example, you might try to copy a large folder of photos to disk.
If the test with writing files went well, then try testing how the disk works when reading data. To do this, try copying data from the test disk. Conclusions A fully functional hard drive should pass all three tests described above without any problems. CrystalDiskInfo should be Good, HD Tune should be error-free, and manual write / read testing should be fine. If everything is exactly like this, then most likely your hard drive is in order and will work for a long time. But, naturally, there are no guarantees here and cannot be. Therefore, the only way to reliably protect your data is to back up. The most important data (personal photos, videos, documents) must be stored on multiple hard drives.



