The HDD Scan program is designed to check hard drives under Windows 2000 and Windows XP. In this article I will consider HDD Scan v2.6 - the latest released version at the time of writing this review. (By the time this article was published, version 2.7 was already available.)
The main features of the program:
- Viewing S.M.A.R.T. Information
- Checking the disk surface in three modes: Verify, Read, Erase.
- Control of the noise characteristics of the hard drive.
- Starting and stopping the spindle motor.
HDD Scan does not require installation and takes about 350 Kb on disk.
This program is absolutely free. You can download it from the HDDGURU.COM website.
The program interface is made entirely in English. However, the program is very easy to use even for novice users.
Rice. 1. HDDScan interface.
Choosing a hard drive
From the drop-down menu under Source Disk, you can select the hard drive with which the program will work. Below is the basic information about the selected hard drive: model ( Model), firmware version ( Firmware), serial number ( Serial) and the number of available physical sectors ( LBA).
View S.M.A.R.T.
To view S.M.A.R.T. parameters. you must press the button S.M.A.R.T. located in the upper part of the program window. 
Rice. 2. View S.M.A.R.T. parameters.
Description of table columns:
- Attribute- attribute number.
- Description- the name of the attribute.
- Value- the value of the attribute. It can range from 1 to 255 (the higher the number, the better).
- Worst- the lowest value of the attribute ever.
- RAW- the value of the attribute in hexadecimal notation (except for Temperature, the value of which the program indicates in degrees Celsius).
- Threshold- the threshold value of the attribute. Used to compare with the value of the parameter (Value).
The indicator color means the state of the attribute:
- Green - attribute is normal.
- Yellow - deviation of the attribute from the norm.
- Red - a strong deviation of the attribute from the norm.
In this case, the obtained information is automatically saved to the SMART.txt file located in the directory with the program.
Checking the disc surface
Surface check options are found under Process.
- Start LBA and End LBA- the sector from which the check begins and the sector where the check stops. If you want to check the entire disk, you do not need to change this parameter.
- Command- selection of the type of check ( Verify- verification, Read- full reading of sectors, Erase- writing to all sectors of zeros). Selecting the Erase parameter will result in a complete loss of all data on the disk!
- Start and Stop- starting and stopping the test.
- Block size- the number of sectors in one block. The default is 256 sectors (not recommended to change).
During the disk check, the elapsed time (Process time), the current sector (Current LBA) and the read speed (Kbytes / s) are indicated. 
Rice. 3. The result of checking the surface of the disc.
In the tab Map the disk map is located. On the left there is a pointer, in which the colors of the rectangles on the map are indicated, depending on the access time. Blue rectangle ( Bads) shows bad blocks (bad sectors). To the right of the colored rectangles is the number of sectors with this access time found during disk check. 
Rice. 4. Text report of surface inspection.
In the tab Report the text report of the check is located. It contains information about sectors with an access time of more than 50 ms (green, orange and red rectangles), as well as bad blocks. 
Rice. 5. Graph of reading speed.
In the tab Graph is a graph of the speed of reading the disk. The X-axis is the sector numbers, the Y-axis is the reading speed.
Noise management
In the tab IDE Features, in the upper left section, you can change the noise level emitted by the hard drive. This can be done only if such a possibility is allowed by the manufacturer (a green indicator and the inscription Enabled to the left of it). It should be noted that reducing the noise entails a decrease in the speed of the hard drive. 
Rice. 6. Control of the noise characteristics of the hard drive and the start / stop of the spindle motor.
Starting and stopping the spindle motor
In the tab IDE Features, In chapter Spindle Start / Stop you can start and stop the spindle motor of the hard drive. It is not recommended to stop the spindle motor on the system disk.
This article reviewed the main features of the HDD Scan program. This program has some other features, but they are not so important and are practically not used.
HDD Scan is a convenient and functional program in its class.
Is one of the most unreliable computer components. With active use, modern hard drives live on average 3 years. Therefore, in order not to lose your data, it is very important to regularly check the status of the drive (and do not forget to make backups). In this article, we will look at several ways to test a hard drive for health.
Checking the status of the hard disk using S.M.A.R.T.
If you want to check the hard disk for operability, then you should start with the data from the "S.M.A.R.T." system, which can be viewed in the CrystalDiskInfo program. This program is completely free and you can.
CrystalDiskInfo program receives hard disk data from "S.M.A.R.T." and gives an assessment of its technical condition. If the hard drive is in good condition, you will see the rating “ Good condition e ". If there are any problems with the device, then you will receive the rating “ Anxiety ". Well, in case of serious problems, you will receive an assessment of the technical condition "Bad".
If you wish, you can independently analyze the information from the "S.M.A.R.T." To do this, examine the list of options at the bottom of the CrystalDiskInfo window. As a cheat sheet on the parameters "S.M.A.R.T." can be used .
Checking the health of the hard drive under load
If "S.M.A.R.T." does not show any problems, then the hard drive needs to be checked under load. To do this, just try to copy a large number of small files (2-5 megabytes each) to it. For example, you might try to write a large folder of photos to your hard drive. If it is defective, then the following symptoms should appear when copying files:
- A sharp decrease in copying speed;
- Jumping copying speed;
- Freezing of the copying process;
- Freezing of the computer or Windows Explorer;
- Unpleasant sounds (crackling, grinding, squeaking);
- Disconnecting the drive;
If such a manual check did not reveal any obvious problems, then you can resort to more serious methods of testing the drive.
Checking your hard drive with HD Tune
The next option is to check the health of the disk using HD Tune. This program is free and you can. Just don't confuse it with the paid HD Tune Pro, which is linked on the same page.
Launch HD Tune on your computer and go to the “Error Scan” tab. On this tab, you need to start the scan using the "Start" button and wait for it to finish.

If a large number of errors were found during the scan, then this means that your hard drive is in poor condition. Perhaps it will soon fail.
Checking the hard disk in Victoria 3.5
For the most accurate check, you need to use the program, you can download it as an iso-file, for example, (here version 3.5, it is optimal for checking the HDD outside the operating system). The resulting iso-file must be written to a CD (or USB flash drive) and booted from it to the computer. After booting from the CD, you will need to select one of the options for launching the Victoria program. If you have a desktop PC, then choose "Victoria for Desktop", "Victoria for Notebook" is suitable for a laptop, the rest of the items run DOS and the Volkov Commander program.

Press the F4 key to start scanning the entire surface of the HDD. As a result, a menu will open in which you need to select "Ignore Bad Blocks" and "Linear reading"... Please note that you do not need to use the options "Write (erase)", "Write from file", as well as "BB = Erase 256 sect", as they erase information from the drive.

In order for the scanning to begin, you need to press the F4 key again. After that, you need to wait until the program finishes checking the hard disk. At the end of testing, if the HDD has no problems, then you will see the following result.

If the drive has some problem areas, orange and red spots will appear in the scan window. The more such stains, the worse the drive's condition. If the number of red spots is especially large, then, most likely, the hard disk is inoperative and it is already time to throw it away. Detailed information about the problems will be displayed in the "Defects" block on the right side of the window.
Checking the hard disk in the Victoria 4.46 program (under Windows)
Also, the hard drive can be checked for operability using the Victoria 4.46 program from the Windows operating system. In this case, you do not need to write iso images and do not need to boot from them. Everything is done right in the Windows environment.
You can download the Victoria 4.46 program for Windows, for example,. The downloaded archive will need to be unpacked into any folder and run the vcr446f.exe program. After starting, the main window of the Victoria program will appear, which looks something like the screenshot below.
First, let's look at the "Standart" tab. Here, on the right side of the window, all the drives that Victoria was able to determine are indicated, information about the currently selected drive is indicated at the top left (if necessary, you can choose another), and below is a record of all actions, errors and other information.

To test the hard drive, go to the "Tests" tab. Here you first need to press the "Passp" button (this will allow you to get information about the selected drive), after that you need to start the test using the "Start" button.


During the scan, the program will detect bad and problem sectors, the number of which can be seen in the column on the right, as well as at the bottom of the screen.
As you know, all computer data is stored on a small, but often very capacious storage device - a hard disk, or hard drive, HDD (Hard Disk Drive). So, like any device, a hard drive gradually wears out, which affects its performance and performance. You can notice this: if your PC (laptop, netbook) is a "seasoned" comrade who has been working for more than a year, it may start to freeze, "think" for a long time when accessing certain folders, etc. These are sure signs of the appearance of "bad" sectors on the hard disk. In this case, he simply needs your help in the form of checking and, if possible, correcting errors in his work. This can be done in several ways, I'll tell you about everything in order. If you decide to figure out how to check your hard drive for errors, then my recommendation is to read this article to the end, and only then start following the steps described in this article.
In order to competently maintain your hard drive and extend its life for many years, you need to understand some of the basics of the drive's functioning. Therefore, first I will try to tell you in the simplest possible way what happens inside the hard drive, and because of what it loses its "former grip" over time, and after that I will mention which programs will help you in maintaining and fixing the hard drive. If you do not have a desire to delve into the problem literally from the inside, and just plan to go over the instructions like "click here - click here" - move to the second part of the article with a description of methods and programs for checking the hard drive. The first section of the material will be devoted to theory, and I will try to make it as interesting and understandable as possible. Go!
How a hard drive works and formatting
A hard drive is a device made up of multiple glass / aluminum plates coated with a ferromagnet. Above the surface of each plate (disk), at a distance of about ten nm, there are magnetic heads that read and write information to the disk.
In the production of hard disks, the final stage is the application of tracks, sectors and marks on the magnetic surface of the disk. This process is called low-level formatting. Thus, service information is applied to the disk. In simple terms, the "magnetization" of the service information is higher than that with which we will subsequently fill the disk. That is why user data and files can be written and erased many times, but service information cannot.
IMPORTANT: if you have read / heard somewhere that low-level formatting will help fix hard disk errors, and you can do it using any program, remember: this operation is performed once and only at the factory using expensive equipment. It's impossible to do low-level formatting with software at home! Of course, you can format it, but this will not be the formatting that we would like.
Sometimes I resort to this formatting (there are special utilities), but this procedure I do to format the disk when other programs refuse to do it. Ask why is this happening? Because some programs, if they cannot format the disk, write a message, for example, "Formatting the hard disk could not be completed", and if you use special programs that format several times in the same area, sometimes this option works - when the disk cannot be easily formatted.
The hard drive is equipped with a kind of operating system (not Windows, which we all know and use). With the help of labels and OS commands applied to the disk, the drive "understands" exactly where the magnetic head needs to be delivered at the current time for reading / writing. The table of tracks, sectors and labels, as well as the OS of the disk - Firmware, firmware - is stored in a special section, closed from the BIOS and our usual operating systems, zone. Therefore, if you suddenly wonder whether you need to update the firmware of your hard drive, know: you don’t need to do this. After all, a hard drive is not an IPhone, and it does not need updates for a modern hard drive to work properly.
Bad HDD sectors - physical, logical, software
We are getting closer and closer to the problem - the loss of performance by the hard drive.
So, the disks are divided into tracks and the tracks are divided into sectors. By the way, the minimum size of a hard disk sector available to the user is 512 bytes. What happens if a sector suddenly becomes unusable? The hard drive controller gives the command to make several more read attempts (at this moment, on the other side of the monitor, we can notice how the PC slightly "dulls"), and if the operation was unsuccessful, then the system marks the sector as faulty (bad, bad block ), and the information that should have been written to this sector is written to another working sector in the backup partition. At the same time, information is entered into the table of labels that this sector is now considered inoperative. The process of redirecting from bad sectors to spare sectors is called "remapping", or "remap" in slang.
Note: Imagine: the magnetic head cannot always continuously move along the tracks sector by sector - because of the broken sectors, it has to jump to the backup track and back every now and then. For this reason, by the way, you can hear extraneous sounds, crackling from the HDD. Naturally, the more bad sectors on the disk, the slower the hard drive works.
Bad sectors are of several types:
- Physical bad block... Such sectors arise as a result of physical, mechanical damage to the hard disk - shattering of a ferromagnet, cracks, chips. It is logical to assume that their occurrence is due to a physical effect - vibration, shock or high temperature (overheating), dust penetrating into the disk. The physical bad sector cannot be fixed by any software; the only solution is to enter it into the defects table and assign it a “deputy” on the backup track. Therefore, do not knock on your laptop and also be attentive to the computer system unit, which is usually placed under the table.
- Logical bad block... They are the result of a violation of the logic of the hard disk and are divided into two categories: recoverable and unrecoverable.
- Incorrigible logical bad block. In this case, the service information is violated - the sector label, address, etc., which can sometimes be corrected, but available only to narrow specialists in the presence of expensive equipment.
- Correctable logical bad block. Together with the information, an additional parameter is written into the sector - a checksum, or Error Correction Code (ECC), which allows information to be restored even in the event of a failure. It so happens that you turn off the computer (for example, from the outlet while the system was still working), the information was written to the hard disk, but the checksum was not entered into the table. It is in this case that the programs for HDD recovery come to the rescue, which, "without asking" the sector, forcibly write zeros in them, and, accordingly, new checksums. After that, the sector returns to work, and the disk is formatted without any problems using standard Windows tools. If you do not format it, the hard disk will repeatedly access the disk and your computer or laptop will freeze due to an incorrect checksum.
- Software bad block... The name itself tells us that such blocks arise in the course of the program's operation, which means that with the help of any program such badges can be fixed. This includes incorrectly marked sectors and other "small things" that can be corrected by regular formatting.
IMPORTANT: I'm sure you all know this perfectly well, but just in case I'll say it: formatting will destroy all your data on the disk. Therefore, before formatting the disk, make sure that all the necessary information from it has been copied to another medium. Otherwise, you will simply lose it.
Standard Windows utilities for checking hard drives
With the theory sorted out, let's move on to practice. There are several applications for dealing with "problem" hard drives that have proven to be powerful and reliable tools. All in order.
By tradition, I will say a few words about standard Windows tools. The functionality, of course, leaves much to be desired, but it will do for the prevention of disk errors. To check the disk by means of the OS, open "Explorer", right-click on any of the disks and select the "Properties" line from the menu.
In the window that opens, go to the "Service" tab and see that we have few options - you can check for file system errors or run defragmentation. We will not dwell on the check (we press the button and check), but I will say a few words about defragmentation. As the name implies, this process is the reverse of the process of disk fragmentation as a result of remap (this was discussed in the theoretical part of the article above). In simpler terms, defragmentation is the ordering of the disk table and spare sectors for faster access to the latter and faster response of the hard drive as a whole. It is recommended to run disk defragmentation occasionally. However, remember: any operation to check or repair a hard drive is a lengthy process, so take some time.
Conclusion: you need to check the disk for errors in the file system and you can also defragment the disk.
Another way to check the disk using standard tools is through the command line. Launch it - press "Win" + "R" on the keyboard, then enter "cmd" and click "OK". Next, we write the command "chkdsk C: / f / r", where "C:" is the letter of the drive to be checked, "/ F" and "/ R" are parameters indicating that it is necessary to automatically correct errors, as well as check bad sectors and try restore information.
Attention! If you fail to use this command, namely, you will not have enough privileges to use this command, then below I will tell you what to do in this situation.
Note: the method that I described above does not save much when it does, so I highly recommend the chkdsk utility, which saved me more than once.

You should also take into account that if your physical disk is divided into logical drives, for example, C, D, etc., then you need to check all your logical drives.
If the disk you are checking is in use at the moment, the system will prompt you to schedule a disk check at the next reboot of the PC, you need to press the Y key: “Y” - “Yes” (“Yes”), and “N” - “No” (“No” ). Then you must reboot your device.
If the disk is free, then a check will be carried out, the results of which the program will display on the screen. Perhaps the program will ask you to unmount the volume (local disk), in this case, just press the "Y" key on the keyboard. Below I showed an example of this message:

If you run the command "chkdsk /?", The program will display a complete list of parameters that can be used with this utility, but in most cases the method described above is sufficient for diagnostics.
If the utility writes that you do not have privileges to execute the command, then you need to run it as administrator. This is easy to do. For users who have Windows 8 or 10 installed, press the "Win" + "X" keys, a menu will open where you need to select "Command prompt (administrator)". After that, you can safely enter the command you need. If Windows 7 or XP is installed on your computer, then you need to find "cmd" or "command line" through the search, right-click on it and select run as administrator.

By the way, you can return to the results of the disk check later, even after closing the command line and restarting the PC. For this:
- Press "Win" + "R", write "eventvwr.msc" in the line, press "OK".
- In the "Event Viewer" window, open the "Windows Logs", right-click on the "Application" item and select "Find ..." in the menu that appears.
- Enter "chkdsk" into the search bar and find the corresponding entry in the log.

Well, we figured out the standard verification tools, now let's go through the software from third-party manufacturers.
If Windows does not boot, then connect the tested hard drive to another computer. Thus, you will boot from another hard drive, and you will check your own (which may have errors).
Checking a Disk Using Seagate SeaTools
This program, as the name implies, was released by the manufacturer of the HDD of the same name - Seagate, but this does not prevent it from being "omnivorous" and working with any disks. You can download it from the official website, the software is free:. At the time of this writing, you need to click on the SeaTools Diagnostic Software for Windows link on the left. After downloading and installing the program, you need to launch it.
Next, select the disk that you are trying to restore to normal operation (by checking the box on the left) and click "Basic Tests". Here you can select options for working with your hard drive. In the picture below, I have shown what verification capabilities this utility has. You can use all the options that this program offers. You can click on the picture below to see the program interface:
Like any self-respecting utility, there is a boot disk image (Seagate for DOS) here, starting from which will allow you to use the check functions before loading the OS. For example, when the system does not boot. It is advisable to check the hard drive in this particular mode. Because this way you will have no problem checking.
In addition, the program has a "Help" section, which is completely in Russian.
Checking Western Digital drives
The next utility is more focused and is designed to work exclusively with Western Digital HDDs. Her name is Western Digital Data Lifeguard Diagnostic. To download the program, go to the manufacturer's website http://support.wdc.com/downloads.aspx?lang=ru, find the program in the list and download it. Next, start the program, right-click on the desired drive and select "Run Diagnostics".
Traditionally, there is a version of the bootable iso-image and the capabilities are similar to the previous software, the interface is elementary.
Disk analysis with HDDScan
I will mention one more worthy representatives of the "army" of fighters with hard disk errors. It is worth noting here the test function in the linear recording mode - "Test" - "Erase". When the program starts, sector by sector, it forcibly writes data, thereby returning most of the bad sectors to work (this was also mentioned above). By the way, if it is possible to disconnect the hard drive from your PC and connect it to another one with HDDScan installed on board, then use this check option. This will maximize your verification efficiency. You can download the program on the website. After downloading, you need to unpack the archive, go to the unpacked folder and run the file "HDDScan.exe".
To run the test, on the left, select your hard drive, then click on the picture with the hard drive and select "Surface Tests".
In the window that opens, leave everything by default - "Read" and click "Add Test". So, we started scanning, now we can click on the entry "RD-Read" by double-clicking the left mouse to open a window where there will be detailed information about working with the hard disk.
If you have a lot of latency - from 20ms and above, it means that your disk is already very bad and you have to think about where to copy all the important data that is on the hiring. In the future, you need to replace the bad hard drive with a new one. It is advisable to use the program on another computer so that no processes interfere with checking your disk.
Recovering a hard drive in Victoria
So we got to, perhaps, the most popular tool for "revitalizing" magnetic storage devices. This program is sometimes very problematic to download from the official site and therefore I will give you a link to another site where you can download this program http://www.softportal.com/software-3824-victoria.html. I always try to give links only to official sites, but sometimes developer sites do not open for some reason and therefore I had to provide a link to a third-party resource. This site is popular and therefore you don't have to worry about viruses.
After downloading the archive, unpack it and run the program as administrator. Be sure to take this step!

At the beginning of work, select the "Standard" tab, and in the window on the right, select the desired disk, and then click on the "Passport" button. In the logs window below, you will see how your HDD was identified. If an entry appears in the log, it means that the program was able to read information from this hard disk.
If this did not happen and you saw “Get S.M.A.R.T. command ... Error reading S.M.A.R.T! " - the HDD controller is probably not operating in the mode we need. To change it, you will have to enter the BIOS and go through the following path: "Config" - "Serial ATA (SATA)" - "SATA Controller Mode Option" - change from "AHCI" to "Compatibility" (IDE). Save changes in BIOS and continue working with the program.
Note: do not forget to return everything to its place after finishing work with Victoria.
So we got to the disk test: go to the "Test" tab, click "Start".
As the check progresses, the cells in the left window will be filled with multi-colored rectangles. It is in our interest that they are all gray - this is the color of the healthy sector. But the blue and red ones are an indication of the bad sectors of the disk. If after the check there are especially many blue cells, then you need to start the check again, having enabled the "Remap" option (located on the bottom right) before that. As a result of such a check, the program will try to isolate the broken blocks (I also talked about this in theory), hiding them. It is also worth noting that orange and green rectangles mean that there are sectors on your disk with very high latencies. If they are present, then this is also very bad.
IMPORTANT: if the disk check results are disappointing, I recommend copying the information to a backup disk, or be ready to replace it. Once the disk has started to "lose" sectors, then, most likely, this process will continue. How long the disc will last you is impossible to predict. If this hard disk does not contain the necessary files, and you only use it for surfing the Internet, then of course you do not need to buy a new storage medium. If the next time you have problems with this hard drive, it means that it is already unstable, and you will need to buy a hard drive.
I have tried to describe theory and practice as simply as possible. Of course, it will be difficult for an ordinary user to study the material in 5 minutes, and therefore devote enough time to your disk to resolve the issue with its unstable operation.
In this article, I gave an example of the utilities used by computer wizards, and if you use other programs, then there is nothing to worry about. After all, the most important thing in your case is the result. Namely, to understand what to do with your media - to restore or it's time to buy a new hard drive.
I hope you found this article helpful. Good luck in checking and only high-quality hard drives!
Video to help you work with Victoria:
HDDScan
The program is designed to check hard drives and SSDs for bad sectors, view S.M.A.R.T. attributes, changing special settings, such as: power management, start / stop of the spindle, adjusting the acoustic mode, etc. The storage device temperature value can be displayed in the taskbar.
Capabilities and requirements
Supported drive types:- HDD with ATA / SATA interface.
- SCSI HDD.
- HDD with USB interface (see Appendix A).
- HDD with FireWire or IEEE 1394 interface (see Appendix A).
- RAID arrays with ATA / SATA / SCSI interface (tests only).
- Flash drives with USB interface (tests only).
- SSD with ATA / SATA interface.
- Linear verification test.
- Test in linear reading mode.
- Linear recording test.
- Butterfly Reading Test (Artificial Random Reading Test)
- Reading and Analyzing S.M.A.R.T. parameters from disks with ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire interface.
- Reading and analyzing log tables from SCSI disks.
- Launching S.M.A.R.T. tests on ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives.
- Temperature monitor on ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI drives.
- Read and analyze identification information from ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI drives.
- Changing AAM, APM, PM parameters on ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives.
- View information about defects on a SCSI drive.
- Spindle start / stop on ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI drives.
- Saving reports in MHT format.
- Printing reports.
- Support for "skins".
- Command line support.
- Support for SSD drives.
- Operating System: Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 (NEW).
- The program should not be run from a read-only drive.
User interface
The main view of the program at startup
Rice. 1 Main view of the program
Main window controls:
- Select Drive is a drop-down list that contains all supported drives in the system. The drive model and serial number are displayed. There is an icon next to it that determines the type of the drive.
- S.M.A.R.T. button - allows you to get a report on the state of the drive, based on the attributes of S.M.A.R.T.
- TESTS button - shows a pop-up menu with a choice of read and write tests (see Fig. 2).
- TOOLS Button - Displays a pop-up menu for selecting available controls and functions on the drive (see Figure 3).
- More button - Shows a drop-down menu with program controls.
When you press the TESTS button, a pop-up menu offers you one of the tests. If you select any test, the test dialog box will open (see Fig. 4).
Rice. 2 Test menu

When you press the TOOLS button, a pop-up menu will prompt you to choose one of the following options:
Rice. 3 Function menu

- DRIVE ID - generates an identification information report.
- FEATURES - opens a window of additional program features.
- S.M.A.R.T. TEST - opens the S.M.A.R.T. window. tests: Short, Extended, Conveyance.
- TEMP MON - Starts the temperature monitoring task.
- COMMAND - opens a command line build window.
Test Dialog Box
Rice. 4 Test Dialog Box

Control elements:
- The FIRST SECTOR field is the starting logical sector number for testing.
- The SIZE field is the number of logical sector numbers to be tested.
- BLOCK SIZE field - block size in sectors for testing.
- Previous button - returns to the main program window.
- Next button - adds a test to the task queue.
- Only one surface test can be run at a time. This is due to the fact that the author of the program has not yet managed to obtain stable high-quality results when running 2 or more tests simultaneously (on different drives).
- The Verify test may have a block size limit of 256, 16384, or 65536 sectors. This is due to the peculiarities of Windows.
- The Verify test may not work properly on USB / Flash drives.
- When testing in the Verify mode, the drive reads the data block into the internal buffer and checks their integrity; no data is transferred through the interface. The program measures the readiness time of the drive after performing this operation after each block and displays the results. Blocks are tested sequentially - from minimum to maximum.
- When testing in the Read mode, the drive reads data into the internal buffer, after which the data is transmitted via the interface and stored in the temporary buffer of the program. The program measures the total readiness time of the drive and data transfer after each block and displays the results. Blocks are tested sequentially - from minimum to maximum.
- When testing in Erase mode, the program prepares a data block filled with a special pattern with a sector number and transfers the data to the drive, the drive writes the received block ( information in the block is irretrievably lost!). The program measures the total time of transmission and writing of a block and readiness of the drive after each block and displays the results. Blocks are tested sequentially - from minimum to maximum.
- Testing in Butterfly Read mode is similar to testing in Read mode. The difference lies in the order in which the blocks are tested. Blocks are processed in pairs. The first block in the first pair will be Block 0. The second block in the first pair will be Block N, where N is the last block of the given section. The next pair will be Block 1, Block N-1, etc. Testing ends in the middle of the specified area. This test measures reading and positioning times.
Task management window
Rice. 5 Task manager

This window contains the task queue. This includes all tests that the program runs, as well as the temperature monitor. The manager allows you to remove tests from the queue. Some tasks can be paused or stopped.
Double-clicking on an entry in the queue brings up a window with information about the current task.
Test information window
The window contains information about the test, allows you to pause or stop the test, and also generates a report.
Graph Tab:
Contains information about the dependence of the testing speed on the block number, which is presented in the form of a graph.
Rice. 6 Graph Tab

Map Tab:
Contains information about the dependence of the testing time on the block number, which is presented in the form of a map.
Rice. 7 Map Tab

You can select “Block Processing Time” in milliseconds. Each block tested that took longer than the "Block Processing Time" will be logged in the "Report" tab.
Report tab:
Contains information about the test and all blocks, the test time of which is longer than the "Block Processing Time".
Rice. 8 Report Tab
Identification information
The report contains information about the main physical and logical parameters of the drive.
The report can be printed and saved to an MHT file.
Rice. 9 Sample Identity Window

S.M.A.R.T. report
The report contains information about the performance and "health" of the drive in the form of attributes. If, according to the program, the attribute is normal, then next to it is a green icon. Attributes that should be paid attention to are indicated in yellow, as a rule, they indicate some kind of malfunction of the drive. Attributes that are outside the normal range are shown in red.
Reports can be printed or saved to an MHT file.
Rice. 10 Sample S.M.A.R.T. report

Temperature monitor
Allows you to evaluate the temperature of the drive. Information is displayed in the taskbar, as well as in a special window for information about the test. Rice. 11 contains readings for two drives.
Rice. 11 Temperature monitor in taskbar

For ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives, the information window contains 2 values. The second value is displayed in the taskbar.
The first value is taken from the Airflow Temperature attribute, the second value is taken from the HDA Temperature attribute.
Rice. 12 Temperature monitor for ATA / SATA disk

For SCSI drives, the information window contains 2 values. The second value is displayed in the taskbar.
The first value contains the maximum allowable temperature for the drive, the second shows the current temperature.
Rice. 13 Temperature monitor for SCSI disk

S.M.A.R.T. tests
The program allows you to run three types of S.M.A.R.T. tests:
- Short test - usually lasts 1-2 minutes. Checks the main nodes of the drive, and also scans a small area of the drive surface and sectors in the Pending-List (sectors that may contain read errors). This test is recommended for quick assessment of the drive's health.
- Extended test - usually lasts from 0.5 to 60 hours. Checks the main components of the drive, and also scans the entire surface of the drive.
- Conveyance test - usually lasts a few minutes. Checks the nodes and logs of the drive that may indicate improper storage or shipping of the drive.
A SMART test can be selected from the SMART Tests dialog box accessed by pressing the SMART TESTS button.
Rice. 14 SMART Tests Dialog Box

Once selected, the test will be added to the Tasks queue. S.M.A.R.T.information window test can display the progress and completion status of the task.
Rice. 15 S.M.A.R.T.information window test

Additional features
For ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives, the program allows you to change some parameters.
- AAM - this function controls drive noise. Enabling this function allows you to reduce drive noise due to smoother head positioning. At the same time, the drive loses a little in performance during random access.
- APM - the function allows you to save power to the drive by temporarily reducing the rotation speed (or complete stop) of the drive spindle during idle time.
- PM - the function allows you to set the spindle stop timer for a specific time. When this time is reached, the spindle will be stopped, provided that the drive is in idle mode. Any program accessing the drive forces the spindle to unwind and resets the timer to zero.
- The program also allows you to stop or start the drive spindle forcibly. Any program accessing the drive will force the spindle to unwind.
Rice. 16 Information window of additional features of ATA / SATA drive

For SCSI drives, the program allows viewing defect lists and starting / stopping the spindle.
Rice. 17 Information window of additional features of SCSI drive

Using the command line
The program can build a command line to control some drive parameters and save this line to a .bat or .cmd file. When such a file is launched, the program is called in the background, changes the drive parameters in accordance with the specified ones, and closes automatically.
Rice. 18 Command line build window

Appendix A: USB / FireWire Drives
If the drive is supported by the program, then tests are available for it, S.M.A.R.T. functions and additional features.
If the drive is not supported by the program, then only tests are available for it.
USB / FireWire drives supported by the program:
| Storage device | Controller IC |
| StarTeck IDECase35U2 | Cypress CY7C68001 |
| WD Passpopt | Unknown |
| Iomega PB-10391 | Unknown |
| Seagate ST9000U2 (PN: 9W3638-556) | Cypress CY7C68300B |
| Seagate External Drive (PN: 9W286D) | Cypress CY7C68300B |
| Seagate FreeAgentPro | Oxford |
| CASE SWEXX ST010 | Cypress AT2LP RC7 |
| Vantec CB-ISATAU2 (adapter) | JMicron JM20337 |
| Beyond Micro Mobile Disk 3.5 "120GB | Prolific PL3507 (USB only) |
| Maxtor Personal Storage 3100 | Prolific PL2507 |
| In-System ISD300A | |
| SunPlus SPIF215A | |
| Toshiba USB Mini Hard Drive | Unknown |
| USB Teac HD-15 PUK-B-S | Unknown |
| Transcend StoreJet 35 Ultra (TS1TSJ35U-EU) | Unknown |
| AGEStar FUBCP | JMicron JM20337 |
| USB Teac HD-15 PUK-B-S | Unknown |
| Prolific 2571 | |
| All Drives That Support SAT Protocol | Majority of Modern USB controllers |
USB / FireWire drives that the program may support:
| Storage device | Controller IC |
| AGEStar IUB3A | Cypress |
| AGEStar ICB3RA | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB3A4 | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB5A | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB5P | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB5S | Cypress |
| AGEStar NUB3AR | Cypress |
| AGEStar IBP2A2 | Cypress |
| AGEStar SCB3AH | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar SCB3AHR | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar CCB3A | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar CCB3AT | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar IUB2A3 | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar SCBP | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar FUBCP | JMicron JM2033x |
| Noontec SU25 | Prolific PL2507 |
| Transcend TS80GHDC2 | Prolific PL2507 |
| Transcend TS40GHDC2 | Prolific PL2507 |
| I-O Data HDP-U series | Unknown |
| I-O Data HDC-U series | Unknown |
| Enermax Vanguard EB206U-B | Unknown |
| Thermaltake Max4 A2295 | Unknown |
| Spire GigaPod SP222 | Unknown |
| Cooler Master - RX-3SB | Unknown |
| MegaDrive200 | Unknown |
| RaidSonic Icy Box IB-250U | Unknown |
| Logitech USB | Unknown |
USB / FireWire drives not supported by the program:
| Storage device | Controller IC |
| Matrix | Genesis Logic GL811E |
| Pine | Genesis Logic GL811E |
| Iomega LDHD250-U | Cypress CY7C68300A |
| Iomega DHD160-U | Prolific PL-2507 (modified firmware) |
| Iomega | |
| Maxtor Personal Storage 3200 | Prolific PL-3507 (modified firmware) |
| Maxtor One-Touch | Cypress CY7C68013 |
| Seagate External Drive (PN-9W2063) | Cypress CY7C68013 |
| Seagate Pocket HDD | Unknown |
| SympleTech SympleDrive 9000-40479-002 | CY7C68300A |
| Myson Century CS8818 | |
| Myson Century CS8813 |
Appendix B: SSD Drives
Support for a particular drive largely depends on the controller installed on it.
SSD drives supported by the program:
| Storage device | Controller IC |
| OCZ Vertex, Vertex Turbo, Agility, Solid 2 | Indilinx IDX110M00 |
| Super Talent STT_FTM28GX25H | Indilinx IDX110M00 |
| Corsair extreme series | Indilinx IDX110M00 |
| Kingston SSDNow M-Series | Intel PC29AS21AA0 G1 |
| Intel X25-M G2 | Intel PC29AS21BA0 G2 |
| OCZ Throttle | JMicron JMF601 |
| Corsair performance series | Samsung S3C29RBB01 |
| Samsung SSDs | Samsung Controllers |
| Crucial and Micron SSDs | Some marvell controllers |
SSD drives that the program may support:
Additional Information
HDDScan 3.3 can be downloaded from 2.8
| Support: |
Good hour everyone!
I think that many users have encountered suspicious work of the hard disk: long copying / reading of files, brakes, loading up to 100%, clicking, inability to read any files, etc.
This behavior of the disk may indicate a serious problem with it. In order to determine what is wrong with it, you have to resort to specialized service utilities.
In this article, I want to highlight some of the best utilities that can view S.M.A.R.T. (special technology of hard disk self-monitoring,), check the disk surface for the presence of bad blocks and try to restore its operability (that is, try to reassign the bad sectors to the spare, for more details on this, see the link below).
What is a bad block, how to check the disk with the Victoria utility (in detail for beginners, with examples and screenshots), see this article -
6 best utilities to check disk for bad blocks
Victoria / Victoria
Developer site: http://hdd-911.com/

One of the best utilities for checking and treating bad blocks on your hard drive. The program conducts testing, diagnostics, and treatment of the disc at a low level. Besides HDD, Victoria supports other types of media: FDD, CD / DVD, USB / Flash / SCSI, she also "sees" drives under Windows through APIs and ports.
Note: I described how to work with Victoria in one of my previous articles, the link to it is presented just above.

Key features:
- support for IDE / SATA controllers;
- the ability to view S.M.A.R.T. disk;
- the ability to control acoustic noise;
- tests to check the mechanics and surface of the disc;
- getting full tech. disk information;
- the ability to work from under Windows and DOS;
- work on laptops is supported;
- support for low-level HDD formatting;
- Benchmark functions.
HDDScan
One of the best programs for checking hard drives from under Windows. Allows you to quickly assess the state of the hard drive, check the drive for bad sectors, view S.M.A.R.T. attributes.
In addition, the program allows you to control the power supply, adjust the acoustic mode, control the temperature of the drive (the data can be displayed on the taskbar).

Key features:
- Support for SSD drives;
- HDD support with interfaces: ATA / SATA, SCSI, USB, FireWire or IEEE 1394;
- Drive test in linear verification mode, linear reading and linear writing;
- Reading and analyzing identification information from hard drives with ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI interface;
- Changing the AAM, APM, PM parameters on disks with ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire interface (useful for those who have a lot of hard disk noise during operation);
- Works in all popular Windows OS: XP, 7, 8, 10.

HDTA2
![]()
HDAT2 is a system utility needed to diagnose and "cure" hard drives. One of the main differences between this utility and Victoria (presented above) is support for a much larger type of disks (note: supported interfaces: ATA / ATAPI / SATA, SSD, SCSI and USB).
HDAT2 can operate in 2 modes:
- disk level: diagnostics and "treatment" of bad sectors on certain drives. By the way, in addition to diagnostics, you can get any information about the disk (which can only be obtained programmatically);
- file level: searching, reading and checking records in FAT 12, 16, 32 file systems. Ability to check, delete and restore records of bad sectors, flags in the FAT table.

Important!
I recommend using HDAT2 from a bootable disk or USB stick. The program will most likely not work correctly under Windows. On the developer site, use the version "CD / DVD Boot ISO image"- it must be correctly written to a USB flash drive / disk, like any bootable media. You can read about this in one of my articles:.
MHDD
Developer site: http://mhddsoftware.com/
MHDD is a service utility for accurate diagnostics and repair of drives (HDD). The utility allows you to work with disks at a low level, through the ports of the IDE controller. The program has a fairly high speed of scanning and "cleaning" the disk from "soft" -bad sectors.
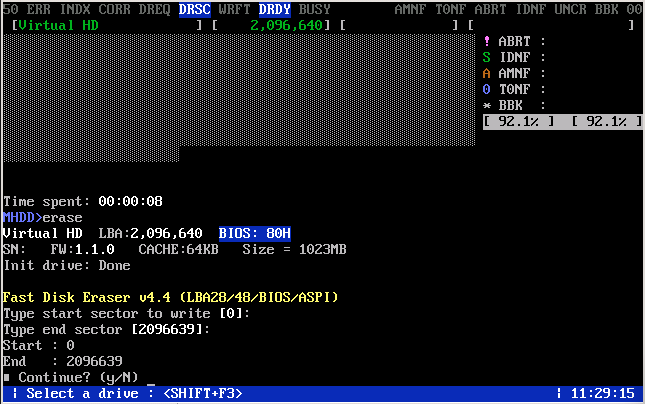
Main functions:
- accurate and very fast diagnostics of the state of the hard disk, the optimal algorithm for correcting bad sectors;
- the ability to adjust the noise from the drive (AAM);
- viewing S.M.A.R.T. readings;
- error logs;
- the ability to delete all information on the disk without the possibility of its recovery;
- an attempt to warm up the drive and test it in extreme conditions;
- the ability to test several hard drives at once.
Macrorit Disk Scanner
![]()
Macrorit Disk Scanner is a good and working tool to check your hard drive for bad sectors. By the way, I want to especially note that the utility scans the disk very quickly- 1.5-2 times faster than, say, the famous Victoria! True, it will not help "cure" the disk - there is simply no functionality that Victoria has.
You can scan the entire disk or a specific range of sectors (useful on large disks, when scanning can take too much time).
The utility allows you to work with all popular types of drives: IDE, HDD, SSD, SCSI, FireWire, RAID, SD cards, etc.

Macrorit Disk Scanner main window
In general, it is a good alternative to previous programs, especially when you need to simply and quickly find out the state of the disk.
Ashampoo HDD Control
Developer site: https://www.ashampoo.com/ru/rub/pin/0365/system-software/hdd-control-3

Multifunctional program for monitoring the status of all your drives in the system. Thanks to the minute-to-minute control over the status of your disks, the program will prevent the loss of information, warning you in time about all problems.
By the way, those who have used Ashampoo products know that their programs are designed so that any novice user can simply and easily work with the program. HDD Control is no exception to this rule, anyone who wants it will deal with it ...

Main functions:
- monitoring the status of drives online;
- the ability to test the disk (there are several tests available to get a "complete picture" of the state of the drive);
- notification about the dangerous state of the disk, leading to a failure or possible loss of information;
- the ability to defragment the disk;
- support for drives with the interface: IDE, ATA, hard drives connected via USB and Firewire;
- supports drives connected via RAID controllers;
- viewing information about the disk: registration number, cache size, number of partitions, etc .;
- it is possible to quickly clean the disk from junk files;
- the ability to export data about the state of the disk and the tests performed.
PS
No matter how good the readings are after testing and diagnosing the disk, do not forget to backup important documents and files. As they say, once a year a stick shoots ...
Better to spend 5 extra minutes on backups than days and weeks of wasted work.



