Free virtualization software VirtualBox is used to create virtual machines. Created in VirtualBox virtual machine, it will be possible to install a guest operating system that will run on the computer simultaneously with the main (host) operating system.
On the guest system, you can conduct experiments, test programs, learn how to work in a new OS (Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, etc.), run old applications that no longer work on your main operating system, etc. You can even completely "kill" Windows, or another system, your computer will not suffer from this, since the virtual machine works in isolation from the main system.
For creating virtual machine, where the operating system will be installed in the future, it will be necessary to install a program for virtualization on the computer. In this article, we will consider installing a free VirtualBox programs, which is fully translated into Russian.
From the manufacturer's website, it will be possible to download the VirtualBox program for a specific operating system... You will need to download the version of the program for the operating system that is in this moment installed on your computer.
download virtualbox
On the official VirtualBox website (site in English), select the VirtualBox for Windows program (in our case) for downloading, as well as VirtualBox Extension Pack(extension pack) that is suitable for all operating systems.
Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack will enhance the functionality of VirtualBox once it is installed on your computer.
First, you will need to install VirtualBox on your computer, and then the extension pack. Installation of the Virtual Box program is carried out in English.
Installing Oracle VM VirtualBox
In the first window of the Oracle VM VirtualBox installation wizard, click on the "Next" button.
In the next window for selecting components for installation, leave all the default settings in order to install the virtualization program VirtualBox on the computer in a complete set, with all modules. Click on the "Next" button in this window.

In the new window, click on the "Next" button.


In the next window, click on the "Install" button to install the VirtualBox program on your computer.

During the installation process, windows may open in which you will need to agree to the installation of the software by clicking on the "Install" button.

After the installation process is completed, the final window of the installation wizard will open, in which you will need to click on the "Finish" button. Before that, it will be possible to uncheck the box in order not to start the program, since immediately after that, it will be necessary to install the Extension Pack.

Installing the VirtualBox Extension Pack
Run installing VirtualBox VM Extension Pack. Immediately after that, the main window of the VirtualBox program will open, in which you will see open window with a question. Click on the "Install" button to install extensions (plugins) that increase the functionality of VirtualBox.

In the VirtualBox License window, you will need to scroll down the scroll bar in order to become active button"I agree".

After the installation of the VirtualBox Extension Pack is complete, a window will open with information about it.

Next, you can run the VirtualBox program on your computer. After opening the main window of Virtual Box, you will see that the application is already working in Russian. The VirtualBox software has been installed on your computer in a complete set.

Now you can create and configure a virtual machine for the subsequent installation of the operating system. You will learn more about this from the following articles on my site (you will find links under this article).
Conclusions of the article
You can install the free VirtualBox program on your computer in order to create a virtual machine on which you can install a guest operating system. After that, you can simultaneously use several operating systems on your computer: main and guest.
If you want to install one or more operating systems on your computer, and completely different ones, it would be very wrong to try to install these operating systems on hard disk partitions. We come across such an error quite often. This approach bodes well for boot problems and wasting hard drive space. How to get out of the situation? There is a great solution - a virtual machine! How to install and configure a virtual machine using Oracle VM VirtualBox as an example? Read in this article ...
One of the reasons why we need this was named and sounded like the need to get anonymous access to the Internet. What else could motivate you to create a VirlualBox virtual machine? For example, you have never seen the Linux operating system in operation, but there is a desire to try, but you do not want to "demolish" a working Windows at all. Or you need to try a new one software package, v stable work which you are not sure or doubt that you even need it. All this can be done without harm to the main operating system using a virtual machine.
A few terms for correct understanding themes. The operating system (OS) on which the virtual machine (VM) is launched is called the host operating system or simply the Host. The operating system we run is called the guest operating system. The Guest OS can be of the same type as the Host. For example, we can run Windows 7 on top of Windows 7, this is the easiest option for virtualization systems. It is much more interesting to experiment with different types OS, for example, run Linux on top of Windows, which we will do today as an example.
First, we need a VM distribution, or in common people setup file... Finding it is as easy as shelling pears, but in order not to overwhelm you with unnecessary workouts, I'll just give a link to the download page:
You just need to select the link corresponding to your OS, for the Windows case, at the time of this writing, it looks like this: VirtualBox 4.1.18 for Windows hosts x86 / amd64. This means that the same distribution will be used for both 64-bit and 32-bit OS. Download the file from the link corresponding to your OS and start the installation. V Windows case 7 you will be asked to confirm the launch and allow making changes.

After starting the installation, click Next, which in Russian means "next", do not change the set of components offered by the installer.

For a successful installation, we need about 140 MB free space on the system disk... Yes, and to install the Guest OS, we still need from 5 to 25 GB free space on any section hard disk for placement virtual disk Guest OS.
We receive a warning about a possible short-term loss of the network connection. This is due to the installation of additional network drivers VM.

Click Yes and wait a few minutes for the installation to complete.


Hooray! The first stage is almost over. It remains to click Finish, leave the launch mark after installation highlighted, which after the installation is complete should lead to the launch of the VirtualBox VM.
If during the installation phase there were no failures, this window will open as a result. Only one button in the form of a blue sun with a signature will be active in it - Create. To create a VM and further install the guest OS, we need it.

Now let's move on to creating a VM. Click Create, enter the name of our future system(it can be, in principle, arbitrary), select Linux as the OS type, and leave Ubuntu as the version.

After clicking Next, you will be prompted to install the required amount of memory available to the Guest OS. Make sure that the slider does not go beyond the green zone, but it is sufficient. If your computer has 1GB random access memory, no more than 512MB will be available for the Guest OS. In general, no more than half of the amount of memory installed in your computer can be allocated for the Guest OS.

Now it's time to allocate space for the Guest OS virtual disk. The proposed 8GB of space should be enough for the installation of the system, if you do not plan to save all your data on the VM disk in the future.

We leave the disk type VDI - this is the native format for VirtualBox. Once again Next, now we see a choice between dynamic and fixed disk types. Each type has its advantages, the dynamic will take up less space and grow as it fills, and the fixed will immediately take up the full volume allocated to it, but will work faster. I personally prefer dynamic.

By default, the VM disk will be located in the c: \ Users \ Username \ VirtualBox VM \ folder, where “Username” is the name of your account in Windows 7. In other operating systems, everything will be slightly different. We leave the proposed volume of the VM disk unchanged or change it in case it is necessary to shrink or allocate additional space. Pressing Next again.

We read what happened in the end, if everything is as you planned - we confirm by clicking the Create button.
The machine is already ready, to start the VM it remains to connect the image boot disk to the VM drive or indicate that we will use a physical optical drive if you already have the installation disc on a separate optical media... To do this, click the Properties button that has become available, select the Media section on the left. In the Form Media there is IDE controller to which it is attached virtual drive, it is now empty. On the right under the Attributes label, you must either select the Live CD / DVD item, if the optical disc is inserted into your CD / DVD drive, or by clicking the disk icon on the right, select the location of the Guest OS installation image.

After selection, everything should look like this:

Now about where to get the image. It is available via a link from this page: http://xubuntu.org/getxubuntu/.
To download the image, we need a program that can download torrent links. This can be the Opera browser, which can do this, or, for example, utorrent for Windows. You can download it from here: http://www.utorrent.com/intl/ru/downloads/complete?os=win. One can argue for a long time about the dangers and benefits of downloading via torrent links, but in in this case it is the simplest, most reliable and quick way receive necessary image disk.
Now you can start launching the created VM, and in one step and see how one of the varieties of Linux OS looks like. In the future, it will still be possible to delve into the VM properties, change different parameters and see how this affects the work of the VM, but we will leave it all for independent work by the curious.
After starting the VM, you need to wait for the appearance graphic screen with the choice of the installation language, select Russian and click the button - "Install Xubuntu". The system will check the parameters of your VM, and if everything is in order, it will continue with the installation. You can also select the items Install updates and Install software third party developers, this will eliminate the need manual setting Flash and codecs for listening to MP3. The installer will then prompt you to erase the disk and install Xubuntu. We boldly agree, tk. nothing except virtual partition in the Guest OS is not available, and on a real OS nothing will be lost or erased. The installer will carry out the planning and formatting of the disk on its own, so we choose to continue. It remains to choose a time zone, for each it has its own, and where you are reading this article - I can not even guess. We select our location on the map with the mouse, and the system itself knows which belt there is. For my computer, the system returned the location of Zaporozhje. Next, select the keyboard layout, most likely it will be Russian, if you do not prefer something else. It remains to enter your name and come up with a password, the system will check if the password matches in the two input fields and evaluate its complexity. Choose a password that you are able to remember, but do not enter something like: 123, qwerty, password, test, user, god, etc. - such passwords are calculated in a couple of minutes by a hardworking "breaker". You shouldn't be too smart, a password like - G% 4v $$ q12 & hB will be recognized as reliable, but it will surely be lost both in your head and on a piece of paper.
Now the system will install the necessary packages and upon completion will ask you to reboot the VM. During installation, it is desirable that the computer is connected to the Internet, this will allow you to immediately install some system updates. During installation in the form slide show the user gets acquainted with the main applications and features of the interface, so do not be lazy, look and read everything that is there on the slides. In the future, this will save time and effort to complete practical tasks in system. After the reboot, the final touch remains, install the guest OS add-ons. To do this, from the VM menu, select the Devices section and in it the Install Guest OS Add-ons item. In the virtual drive of the guest OS, a disk with additional drivers for the guest OS. In our case, you will need to run an application named VBoxLinuxAdditions.run for execution, moreover, you need to do it with administrator rights. Push right button mouse on an empty space in the window with the contents of the virtual drive. Selecting an item context menu Open terminal. In the window that opens, type the command:
sudo ./VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
Press Enter, then you will need to enter the password that we entered at the beginning of the installation, I hope you have not forgotten it yet, press Enter again and wait for the installation to complete. When finished, reboot the guest OS system. In the right upper corner on the screen there is an inscription with the username, left-click on it and select the Restart item.
This is the result that should await us in the final, if everything went smoothly. If something went wrong - write, we'll try to figure it out.

Once you've installed a virtual machine and realized how easy it is, you probably want to try to install something yourself. All that is needed for this is ISO image installation disk and choose the right type of OS. First investigate those systems that are in the VirtualBox list, do not grab right behind Mac setup OS X 10.8 Lion. Over time, you will learn to do this too, but only when you understand in detail all the intricacies of the VM. In the meantime, you can experiment with your Xubuntu installation, which I think deserves your attention.
We have successfully taken one of the steps that brought us closer to anonymity on the Internet. To complete the path, we have yet to install a package that allows us to hide the real IP address of our computer - the Tor Project, but more on that next time. Good luck and thanks for reading our blog!
GD Star Rating
a WordPress rating system
VirtualBox - free program, which allows you to run an operating system inside another, through virtualization. For example, by installing this program on Windows 10, you can run other Windows versions, Linux, Android and others. It works like this:
The program reserves part of your PC's resources (processor, RAM, video memory, storage space for the OS) for the operating system.
Installing VirtualBox
First you need where you can find latest versions programs for different OS. I'll download the Windows version.
There are no difficulties in installation, everything is as in regular programs... It is not recommended to change the components to be installed.


If you wish, you can uncheck some of the checkboxes, but I recommend leaving the second and fourth ones. Next, you will receive a warning that the Internet connection will be interrupted to install the virtual driver, we agree. Click "Yes".

After we press "Install".

The installation process will go, where you will be prompted to install the driver, for all such suggestions click"Install".

This completes the installation of VirtualBox. Click "Finish".
Creating a virtual machine on VirtualBox
There shouldn't be any difficulties in creating a virtual machine. Run the program and press the "Create" button.

In the next window, you will need to specify the name and type of OS you will install.

Next, we determine the size of the RAM to be allocated to the virtual machine. For Windows XP, I will allocate 512MB of RAM. It all depends on the amount of memory you have installed. If there is enough, then much more can be allocated.

In the next window, you are asked to choose the location and size where the OS will be installed. Since this is the first time we are setting up a virtual machine, we need to select "Create new virtual hard disk". Click "Create".
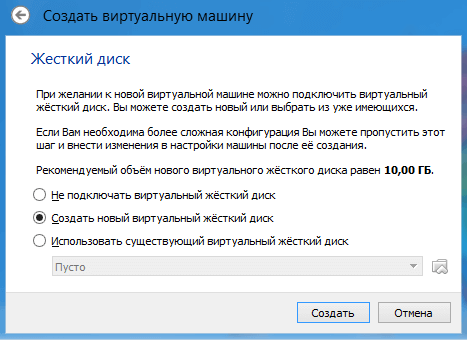

In the next window, you need to select the type of disk, fixed or dynamic. It depends on your preference, I will choose the fixed one.

Choose how many GB of memory you want to allocate for installing the OS and its programs. I will allocate 5GB. And also the place where the created disk will be stored, choose where it is free memory... Click "Create".

The process of creating a virtual disk will go.

This completes the creation, and you will see that you will have a virtual machine with the name you gave it earlier, I have it Windows XP.

Addition:
If you click on the "Configure" button, then you will see the sections in which you can customize the properties of the machine in more detail.

For example, how many cores you want to give and their load limit. And in the "Display" section, you can increase the amount of video memory for the video card.
Installing an operating system on VirtualBox
To start the installation, click on the green button (arrow) "Run". You will see a window asking you to select the path to the installation disk image.

We indicate the path to the previously downloaded OS image.
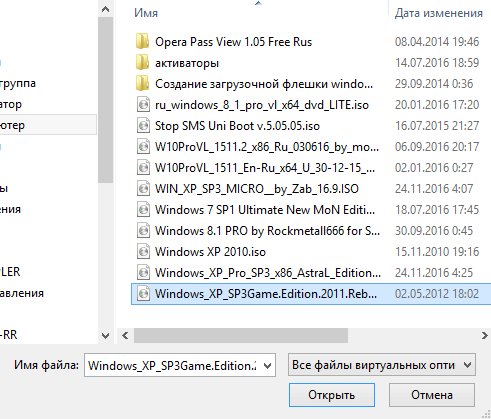
Click "Open". After that press "Continue". The usual for everyone will go normal installation OS. You will also need to create one or more local drives... When the installation is complete, you will need to remove installation image... To do this, click on the "Devices" tab,

select the sub-item “ Optical discs"And click" Remove disk from drive "there, and reboot the newly created OS. That's all for now, good luck.
Oracle VM VirtualBox is a kit application programs, system services and drivers that emulate new computer hardware in the operating system environment where VirtualBox is installed. On the virtual computer(virtual machine), you can install almost any operating system (guest OS) and use it in parallel with the main one. So, for example, on real computer with Windows, you can install a virtual machine (VM - Virtual Machine) with an operating system Linux family and use both OSes at the same time. In addition, you can configure the interaction between these systems on the local network, data exchange through removable media, shared folders and so on. Also, the current state of the virtual machine (and the state of the operating system installed on it) can be fixed, and, if necessary, at any time, you can perform a full rollback to this state. In other words, a virtual machine is very convenient tool for studying new operating systems, debugging software, conducting experiments without disrupting the operation of the main OS, researching viruses, diagnostic and recovery tools, and simply for the parallel operation of several operating systems on one computer.Installing Oracle VM Virtualbox
& nbsp & nbsp The current version of Oracle VM VirtualBox can be downloaded from the project download page, which contains links to download installation packages for Windows x86 / x64, Linux, Solaris and OS X.
Installation in Windows environment should be performed under account a user with administrator rights.
During the further installation of VirtualBox, a warning will be displayed:

This means that when installing the VirtualBox network drivers, the current network connections and a temporary disconnection from the network will occur. If, for example, in parallel with the plant, data is exchanged with network drive then it will fail. If the network is not working, then a short-term disconnection of the adapters will not have any consequences, and you need to allow the installation to continue by pressing the button Yes... Otherwise, you must first exit with network resources.
After the installation is complete, the main software module VirtualBox user - Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager (Oracle VM VirtualBox manager):
Installing Linux Ubuntu on Oracle VM VirtualBox
& nbsp & nbsp All actions to create virtual machines, change their settings, import and export configurations, etc. can be performed using the Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager (in Russian software - Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager) or using the utility command line VboxManage.exe... The latter has several great opportunities on setting up virtual machines, but more difficult to use.
Installing a guest OS on a virtual machine can be roughly divided into 2 stages:
Creation of the required virtual machine using VirtualBox;
The boot source (Linux distribution media) is determined by the settings of the virtual machine. It can be a real or virtual CD / DVD drive, floppy disk, HDD, boot disk image or local network. By default, the boot order is as follows - Floppy, CD-ROM, Hard Drive, Network. This order can be changed in the settings of the virtual machine.
When VirtualBox is launched for the first time, the main program window is displayed with a welcome screen and an activated button. Create to create a new VM:

When creating a new virtual machine, the following parameters are defined:
The name of the virtual machine. A directory with virtual machine files will be created in accordance with it. By default, this is a subdirectory in C: \ Documents and Settings \ Username \ VirtualBox VMs \ in Windows XP and C: \ Users \ User \ VirtualBox VMs \ for Windows 7 and older.
The type of operating system that will be installed on the virtual machine. In this case - Linux
OS version. In this case, Ubuntu.

Other parameters can be left by default, since they are already selected based on the hardware configuration of the real machine and in accordance with the type and version of the operating system installed on the virtual machine. If necessary, the parameters can be determined based on your own preferences, for example, to increase the amount of RAM allocated to the virtual machine.

Here is an example of allocating 1024 MB of RAM to a virtual machine, instead of the recommended 512 MB. When allocating memory, you need to take into account its real amount and the minimum requirements of the guest OS. If you have difficulty choosing of this paragraph- use the values recommended by the program. Inappropriate memory allocation between real and virtual machines can degrade the performance of both.
Virtual machine hard disk (virtual hard disk) is a special format file in file system Windows. A virtual disk can be created either dynamic or fixed. Dynamic disk is created not for the entire volume specified by the setting, but for its part, and increases as necessary during the operation of the virtual machine. For maximum performance of the guest operating system, it is better to choose a fixed virtual hard disk, and to save disk space- dynamic.

VirtualBox allows you to use several different data formats for virtual disks:

Most of the parameters defined during the creation of a new virtual machine can be changed at any time, if necessary.

For the created virtual machine, the button becomes active Tune, which allows you to change some of its settings, add or remove virtual devices, change their modes of operation, manage the distribution of resources of the real operating system. To get acquainted with the guest OS Ubuntu Linux is enough initial settings executed when creating the virtual machine. Therefore, you can immediately start starting the VM by pressing the button Run... After starting the VM, a usage message is displayed on the screen Auto-capture keyboard

This means that when the cursor is within the VM window, keyboard input will be performed for the virtual machine. By default, to switch keyboard input between real and virtual machine windows, use right Ctrl. Current state input is displayed in the status bar at the bottom of the virtual machine window.
Green color arrows in means that keyboard input will be performed for the virtual machine, gray - for the real one.
To install the operating system on a virtual machine, you will need to boot from the installation disk. In the VirtualBox environment, it is possible to download not only from standard devices(CD / DVD drive, flash drive, network ...) but also using a virtual drive created on the basis of the boot disk image. Usually Linux distributions are distributed as image files in the ISO-9660 format (files with the iso) and VirtualBox allows you to do without burning the image to a CD, and simply connect such a file directly to the virtual machine as a virtual drive with installed media based on the contents of the iso image. When you start the virtual machine for the first time, when there is no guest operating system installed yet, VirtualBox will prompt you to select a boot device

Instead of a physical drive, you can select an image file, for example ubuntu-13.04-desktop-i386.iso which will be connected as virtual device with Ubuntu 13.04 installation CD / DVD. By pressing the button Continue booting from the virtual drive and installing the guest operating system (Ubuntu)

The process of installing a guest OS is no different from installing on a real machine. You can select the language for the installed system (usually Russian), time zone, keyboard layout, etc. Most of the parameters can be left by default, including type of instalation

During installation, you need to set the computer name, user, password and login mode:

Further installation of Ubuntu is performed without any user intervention and ends with prompts to restart the computer. Compared to installing the system on a real computer equipment, installation in a virtual machine is expected to be slower. The degree of performance degradation mainly depends on the performance of the real computer hardware.
When booting a newly installed operating system for the first time, VirtualBox Manager will automatically unmount the virtual drive based on the disk image from distribution kit Ubuntu, loading will be done with virtual hard disk and upon completion, a login prompt will appear on the screen.
Changing Oracle VM VirtualBox Virtual Machine Settings
& nbsp & nbsp In some cases, such as when a virtual machine is included in a real local network as a peer with the ability external connection to his network services, you will need to change some of the default settings when the VM was created.
In the VirtualBox environment, it is possible to use 4 virtual network ethernet adapters configured in the properties window of the virtual machine on the tab Net

By pressing the button Additionally Expands the values of additional parameters of virtual network adapters that allow you to select the type of adapter that will be used by the virtual machine driver, promiscuous mode when the virtual adapter will accept all Ethernet frames regardless of the destination MAC address, the MAC address value that is assigned to the virtual network card.
For everybody network adapter you can specify in which of the following modes they will function (field Connection type):
Not connected- In this mode, VirtualBox informs the guest OS that the network adapter is present in the hardware configuration, but it is not connected - as if the Ethernet cable were not connected to the card.
NAT (Network Address Translation)- the main connection mode, set by default when creating a virtual machine. Allows the most simple implementation of network access using client software (mail, Web, Skype, etc.)
Network bridge- the mode of the bridge between the virtual and real network adapter, when data exchange between them is carried out directly without any change in the guest OS environment. This mode allows you to access the network services of the guest OS in the same way as for normal real hosts on the local network. Using this mode, you can easily simulate a local network from real and (or) virtual machines.
Internal network- used to create virtual network accessible from the virtual machine, but inaccessible from the real applications.
Virtual host adapter- is used to create a local network of virtual machines and a real machine where VirtualBox (host machines) operates. This mode does not use physical network adapter communication like loopback communication.
Universal driver(generic network interface) - allows you to enable a user-selectable driver in VirtualBox with additional extensions to combine virtual machines running on different hosts.
To connect a virtual machine to an existing local network with the ability to access its network services, use the mode Network bridge and configuring the virtual network adapter so that its IP address is in the range of addresses of the local network. For example, for the local network 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0, you need to assign the virtual adapter (manually or automatically via DHCP) a free address from the range 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.254.
The first step, in the settings of the newly created virtual machine, in the section Net VirtualBox manager for network adapter needs to be changed Connection type NAT on the Network bridge... Then, using the guest OS tools (in this case, Ubuntu tools), set the new IP-address value. This can be accomplished using System parameters - Net- Select a connection and click the button Parameters
 To change the IP address, you need to select the "Manual" mode
To change the IP address, you need to select the "Manual" mode
In the VirtualBox environment, just like on a real computer with an operating Linux system, you can use several virtual terminals, to switch between which use the keyboard shortcut CTRL - ALT + F1 ... F6(from the first terminal to the 6th). Thus, if necessary, you can simultaneously open several user sessions on different terminals and use them simultaneously. To switch to graphical shell used by CTRL-ALT + F7... On different distributions, the key combinations for switching may differ. When changing or viewing system parameters that require the execution of commands on behalf of root, you can, for example, use the first terminal, logged into the context of a superuser account. The second terminal (as well as the graphical one) can be used under the account regular user.
To switch to account context root you need to execute the command su on behalf of the superuser.
sudo su- go to the console with rights root
su allows you to run a command as another user. If username is not specified, then it is assumed root... Work under an account root not recommended as erroneous actions can cause serious damage or even system crash.
To view the current network settings the command is used ifconfig... When it is executed without parameters, the current settings for all network interfaces are displayed:
eth0 Link encap: Ethernet HWaddr A8: 00: 97: 6E: e9: 65
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp inet addr: 192.168.50.8 Bcast: 192.168.0.255 Mask: 255.255.255.0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp inet6 addr: fe80 :: a00: 27ff: fe6b: e965 / 64 Scope: Link
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU: 1500 Metric: 1
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp RX packets: 124 errors: 0 dropped: 0 overruns: 0 frame: 0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp TX packets: 166 errors: 0 dropped: 0 overruns: 0 carrier: 0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp collisions: 0 txqueuelen: 1000
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp RX bytes: 28340 (28.3 KB) TX bytes: 19383 (19.3 KB)
Lo & nbsp & nbsp Link encap: Loopback
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp inet addr: 127.0.0.1 Mask: 255.0.0.0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp inet6 addr: :: 1/128 Scope: Host
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU: 65536 Metric: 1
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp RX packets: 144 errors: 0 dropped: 0 overruns: 0 frame: 0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp TX packets: 144 errors: 0 dropped: 0 overruns: 0 carrier: 0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp collisions: 0 txqueuelen: 0
& nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp & nbsp RX bytes: 12445 (12.4 KB) TX bytes: 12445 (12.4 KB)
In this case, information about 2 network interfaces is displayed, eth0 and lo... First named eth0 is the interface of the local Ethernet networks and created on a network card with a MAC address A8: 00: 97: 6E: e9: 65 and IP address 192.168.50.8. Second - lo is a loopback interface with an IP address of 127.0.0.1, commonly used to emulate data transmission within a given system.
If desired, ready image VirtualBox virtual machine with OS installed Linux Ubuntu can be downloaded at. Usually, the bootable image of the virtual machine reflects its state at the time of completion. Ubuntu installations when using standard parameters. The username and password to login to the system are listed on the download page.
The Sourceforge project also maintains a download page for images of VirtualBox virtual machines with installed operating Android systems, FreeBSD, OpenSolaris, and dozens of Linux flavors.
For maximum flexibility, starting from VirtualBox versions 4.0, a mechanism for remote control of virtual machines is implemented through the additional interface VirtualBox Remote Desktop Extension (VRDE). Basic package VirtualBox only provides support this interface, and the support itself is implemented as an additional external module (plugin) VirtualBox extension package, which can be downloaded and installed as an addition to the basic package from the official website. Installation of this module performed by double clicking on the downloaded file with the extension vbox-extpack.
I started talking about what a virtual machine is and what it is for.
And now I will tell you about the program for working with virtual machines, how to install and configure it.
To work with virtual machines, there are many various programs, the most common: Oracle VirtualBox, VMWare Player, VirtualPC.
Each of the options has features, advantages and disadvantages, but VirtualBox absorbs all the advantages of the other options, is free and has very flexible configuration and support for many operating systems for virtualization. Of course, there are also disadvantages, but they will only be noticed by professionals who do this and use virtual machines for special needs, using different technologies.
And therefore, in the article I decided to show how to work with VirtualBox, and if someone becomes interested, then you can figure out other options without problems.
So, here we go ...
First of all, download the program Oracle VirtualBox... Go to the site: virtualbox
If you are using a Windows operating system, click on the "x86 / amd64" link opposite the "VirtualBox 4.3.12 for Windows hosts" line.
If the browser is configured so that a request is always issued before saving the file, then you will receive a window where you need to specify the location where the file will be downloaded. Select a convenient folder for downloading on your computer and click "Save":
If there is a setting in the browser that the files will be downloaded without a request to the specified folder, then such a window as above, accordingly, will not appear and the file will be downloaded to the folder specified in the settings.
The file size is about 100 Megabytes.
Run the downloaded file and the installation of the program will begin. In the first window, click "Next":
In the next window, you can disable some options and functions that you think will not be used in the program and this will reduce the size installed program... For all beginners and those who are not particularly computer savvy, I recommend leaving all options enabled and just clicking "Next":
Upon completion of the installation, they offer 3 options: bring the icon to start the program on the desktop; move the icon to the panel quick launch(for operating systems Windows Vista, 7, 8), associate the virtual machine files with the VirtualBox program. Turn the first 2 options on or off at your discretion, and I highly recommend enabling the last "Register file association":
Click "Yes" in the next window. Here we are warned that additional network connections for a virtual machine and the real connection may be broken. Nothing terrible will happen and you most likely will not even notice anything:
In the last window, before installing, click the "Install" button:
The installation process will begin and a window will appear near the end where you need to confirm the installation of the USB software (so that real USBs work in the Virtual Machine):
You just need to check the box "Always trust software Oracle Corporation"And click the" Install "button.
After installing the program, there will be a check mark in the window, which means that the program will start itself after clicking the Finish button. I recommend leaving this checkbox and clicking "Finish":
In any case, the program can be launched from the icon on the desktop or from the menu "Start"> "All Programs".
After installing and running the program, it will look like the image below:
Let's make some program settings right away. To do this, go to the "File"> "Settings" menu:
The first thing we will do is set a folder for storing virtual machine files. These will be complete systems and will take up enough space. For example, I use for my purposes a virtual machine with Windows XP, it is the fastest of the entire line of Windows. So I have all the updates installed in this virtual machine, Microsoft Office 2010, SafeSerf autosurfing software and 2 browsers ( Mozilla firefox and Google chrome) and the folder with the virtual machine already has a size of 8.74 GB. So, when choosing a folder for storing virtual machines, keep this in mind.
You can set the folder for storing virtual machines on the first General tab. There you need to open the list next to the "Folder for machines" and select "Other". Further indicate convenient folder for storing virtual machines. You can, of course, leave the default one, but it is best to store virtual machines on a disk that is not a system disk (the one on which Windows is installed) and on which there is a lot of free space, because the size of virtual machines can be 15 GB or more :
In the settings on the "Updates" tab, check that the "Check for updates" checkbox is ticked and I advise you to set the check period to "1 month" so that reminders do not come too often. It should also be noted "Stable release versions":
We finish with the settings, the rest does not require any changes for normal work... And if there is any need to change something, you can always refer to the settings.
Now our task is to install and run the virtual machine itself in VirtualBox. Let's get started.
Creating a new virtual hard disk for installing the operating system and configuring it.
Let's consider working with a virtual machine at Windows example XP. In most cases, I use this particular system as a virtual one, because it is the most productive in contrast to its successors (Windows Vista, 7, 8), and also requires the least resources and takes up the least space on the hard disk. I use Windows 7 as a virtual one only for special purposes, when I need to try something on it.
Of course, to install the system on a virtual machine, you will need the disk itself with the required operating system or an .ISO format image. You can find them on the Internet at free access on torrent trackers (for example http://pirat.ca/) and others, and it can also be found on simple sites / blogs.
So, we begin the process of preparing a virtual machine for work using the example of Windows XP:
We find a disk or image with the desired system.
Password for unpacking the archive: 123
Disable your antiviruses before unpacking, because most of them consider the file "help_3.4.exe", designed to activate the system, as a virus. It is not a virus, but the reaction of antiviruses is this because it is a hacking program, because it activates the system. Antiviruses are mistaken for all hacking programs as "dangerous".
To start the installation in VirtualBox select the menu "Machine"> "Create":
A window will appear in which you need to specify the name (in the "Name" field) of the virtual machine being created. Just indicate so that you yourself understand what kind of virtual machine it is (if there are several). In the "System Type" list, you can select the type of operating system to be installed, respectively. Since we are using Windows XP in the example, we leave everything at the default. In the "Version" list, select the required version. In our example, this will again be "Windows XP". Click "Next":
The next step is to select the amount of RAM that will be allocated for the virtual machine. For the simplest tasks and testing Windows XP, the recommended size (by default) is 192 MB. For newer systems, the recommended size will be different. But it is better not to set less than the recommended one, the virtual machine will slow down. If you plan to use a virtual machine to work in boxes and run many accounts at the same time, then you should allocate a lot of memory, and at least 2 GB. (2048 Mb.). But here it is worth starting from how much real RAM is installed in your computer. I recommend setting the amount of memory for running a virtual machine equal to half of the real one. For example, if you have 8192 MB of RAM (8 GB) on your computer, you can allocate 4096 MB (4 GB) for the virtual machine. You can do even more, but then already monitor the performance of the real operating system in which it is running. If it slows down, then reduce the amount of allocated memory. I will show you how to change the volume in the following steps.
So, you have selected the required amount of memory. Press the button "Next":
5. The next step is to select "Create a new virtual Hard disk". Pay attention to the recommended volume of hard disk for this system (later you will need to select). Click the "Create" button:
Now we will be asked to select the format of the virtual disk. This choice will depend on what other programs to create and run virtual machines you can use the created virtual HDD... The easiest way is to leave the default choice of "VDI" (VirlualBox disk format), since it is not worth using the created virtual machine with other programs. Click "Next":
7. At the next stage, you need to select the type of virtual disk to be created: physical or dynamic. I recommend choosing a dynamic one, because it is not uncommon for certain needs to have to expand its volume, and the physical does not allow this. So, select "Dynamic virtual hard disk" and click "Next":
8. Now you need to set the size of the virtual hard disk that will be used to run the virtual machine. How much you set, you will see this in the virtual machine. As you remember, the recommended volume for our system is 10 GB. When this window appears, this optimal volume will already be set here. If no programs and files that are particularly large in volume will be used in the system, then 10 GB is quite enough (I work with just such a volume). Calculate what you will use the system for, what volume of programs you will install on it, and roughly estimate how much volume it will take. Never choose less than 10 GB, it may simply not be enough for the system itself for updates and other things.
In the upper field, you can also specify the name of the created virtual disk. By default, it is the same as the name of the virtual machine and I recommend not changing anything. After selecting the volume of the disk, click the "Create" button:
After that, the virtual hard disk will be created, and the virtual machine as a whole, too, but without the operating system installed on it. You will be returned to the main VirtualBox window. Now let's go straight through the settings of the created virtual machine.
9. So, in the main window your created virtual machine will appear without a system yet. Select it with the mouse and click the "Settings" button and consider the main useful and desired settings:
In the first tab "General", and then on the right in the "Advanced" tab, there is a useful option "Remember changes during VM operation". If this option is enabled, then after each shutdown of the virtual machine, all changes on it will be saved. If you uncheck this box, then any changes made in the system will not be remembered. Those. you will turn on the virtual machine and each time you will see it in the same state as you started it the previous time. This allows you to 100% protect the system from viruses, and also just contain virtual system clean.
I recommend at the beginning to leave this checkbox in place (i.e. so that all changes are saved), do everything required settings systems, install and configure everything required programs in this system, and only then uncheck this box and not be afraid that your virtual machine will get clogged with something.
11. Switch to the tab "System"> " Motherboard". Here you can change the amount of RAM allocated for your virtual machine. If you remember, it was asked at the beginning of the process of creating a virtual machine. I had a set volume = 192 MB and in my example I will not change it.
Now let's switch to "Processor" in the same window. Set the "CPU Utilization Limit" to 90%. If you leave 100%, then the virtual machine will sometimes give an error at startup and will not start.
14. Now let's consider the last and very important function in the settings of the created virtual machine - "Shared folders".
While working with a virtual machine, you will probably need some files from real system... For example, in both systems, I use a file with data about accounts on buks and their wallets. It takes a very long time to open a file in a real system and rewrite logins and passwords manually into a virtual machine, if necessary, when entering a site, and the clipboard does not work. Those. you cannot just copy text from some file on a real system and paste it into a virtual system. For everything there is special function Shared folders. We need to add a folder from the real system we are working on and it will be available in our virtual machine.
So, in the settings of the virtual machine, open the "Shared folders" tab and then add new folder by clicking the button on the right (it is the only one available) with the image of a folder with a plus sign:
In the window that opens, in the "Path to folder" field, press the button of the drop-down list:
Now the window will display the folder we have selected and its name. Be sure to check the "Auto-connect" checkbox so that the folder is always immediately available when the virtual machine is booted. Check the "Read only" checkbox based on your own needs. If you check this box, then nothing can be written or copied from the virtual machine to the added shared folder.
I do not check this box so that you can copy any desired file from a virtual machine to a real system, or change something from a virtual machine to a real system file. After making the settings, click "OK":
Of course, you can add as many folders as you like to suit your needs and for your convenience. At this stage, the shared folders are configured on this, but in order for them to work later, it will be necessary already from installed system install the special "GuestEdition" add-on. It's quick and easy, and we'll come back to it after installing the virtual operating room. Windows systems XP.
On this, we examined the basic and necessary settings. Click "OK" in the main settings window:
Now the most important thing remains - to install the operating system on the created virtual hard disk. And that is all. Although installing an operating system is already quite separate question, but I'll still show this process using Windows XP as an example. Still, this is part of the topic at hand.



