Let's see what are the main differences between the processors of the world leaders - Intel and AMD.
We will also consider their positive and negative sides.
Major CPU manufacturers
Everyone is well aware that the market computer science there are two leading companies that are engaged in the development and production of the Central Processing Unit (central processing unit), or, more simply, processors.

These devices combine millions of transistors and other logic elements, and are electronic devices highest difficulty.
The whole world uses computers, the heart of which is an electronic chip either from Intel or AMD, so it's no secret that both these companies are constantly fighting for leadership in this area.
But let's leave these companies alone and move on to ordinary user, which faces a dilemma of choice - which is still preferable - Intel or AMD?
Say what you like, but there is no and cannot be an unequivocal answer to this question, since both manufacturers have a huge potential, and their CPUs are able to meet the current requirements.
When choosing a processor for your device, the user primarily focuses on its performance and cost - relying on these two criteria as the main ones.
The majority of users have long been divided into two opposing camps, becoming ardent supporters of Intel or AMD products.
Let's look at all the weak and strengths devices of these leading companies, so that when choosing a particular one, it should not be based on speculation, but on specific facts and characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of Intel processors

So, what are the advantages of Intel processors?
- First of all, this is a very high performance and speed in applications and games, which are most optimized for Intel processors.
- Under the control of these processors, the system works with maximum stability.
- It is worth noting that the memory of the second and third levels in the Intel CPU operates at higher speeds than in similar processors from AMD.
- Multithreading plays a big role in performance when working with optimized applications, which is implemented by Intel in CPUs such as Core i7.
Advantages and disadvantages of AMD processors

- The advantages of AMD processors are, first of all, their affordability in terms of cost, which is perfectly combined with performance.
- A huge plus is the multiplatform, which allows you to replace one processor model with another without the need to change the motherboard.
- That is, a processor designed for socket AM3 can be installed on socket AM2 + without any negative consequences.
- Not to mention multitasking, which many AMD processors are great at doing up to three applications at the same time.
- In addition, the FX series processors have pretty good overclocking potential, which is sometimes extremely necessary.
- The disadvantages of AMD CPUs include higher power consumption than those of Intel, as well as operation at lower speeds of second and third level cache memory.
- It should also be noted that most processors belonging to the FX line require additional cooling, which will have to be purchased separately.
- And another disadvantage is that fewer games and applications are adapted and written for the AMD processor than for Intel.
Actual connectors from Intel

Today, many leading manufacturers of central processing units are equipped with two current sockets. At by Intel they are as follows:
- LGA 2011v3 is a combined connector, which is focused on the operational assembly of a high-performance personal computer for both servers and the end user. The key feature of such a platform is the presence of a RAM controller that successfully operates in multi-channel mode. Thanks to this important feature- PCs with such processors are characterized by unprecedented performance. It must be said that an integrated subsystem is not used within such a platform. Unleashing the potential of such chips is possible only with the help of discrete graphics. For this, only the best video cards should be used;
- Thanks to the LGA, you can easily organize not only a high-performance computing system, but also a budget PC. For example, a socket LGA 1151 great for creating a computer station of an average price policy, at the same time it will have a powerful built-in graphics core Intel series Graphics and support DDR4 memory.
Current AMD Connectors
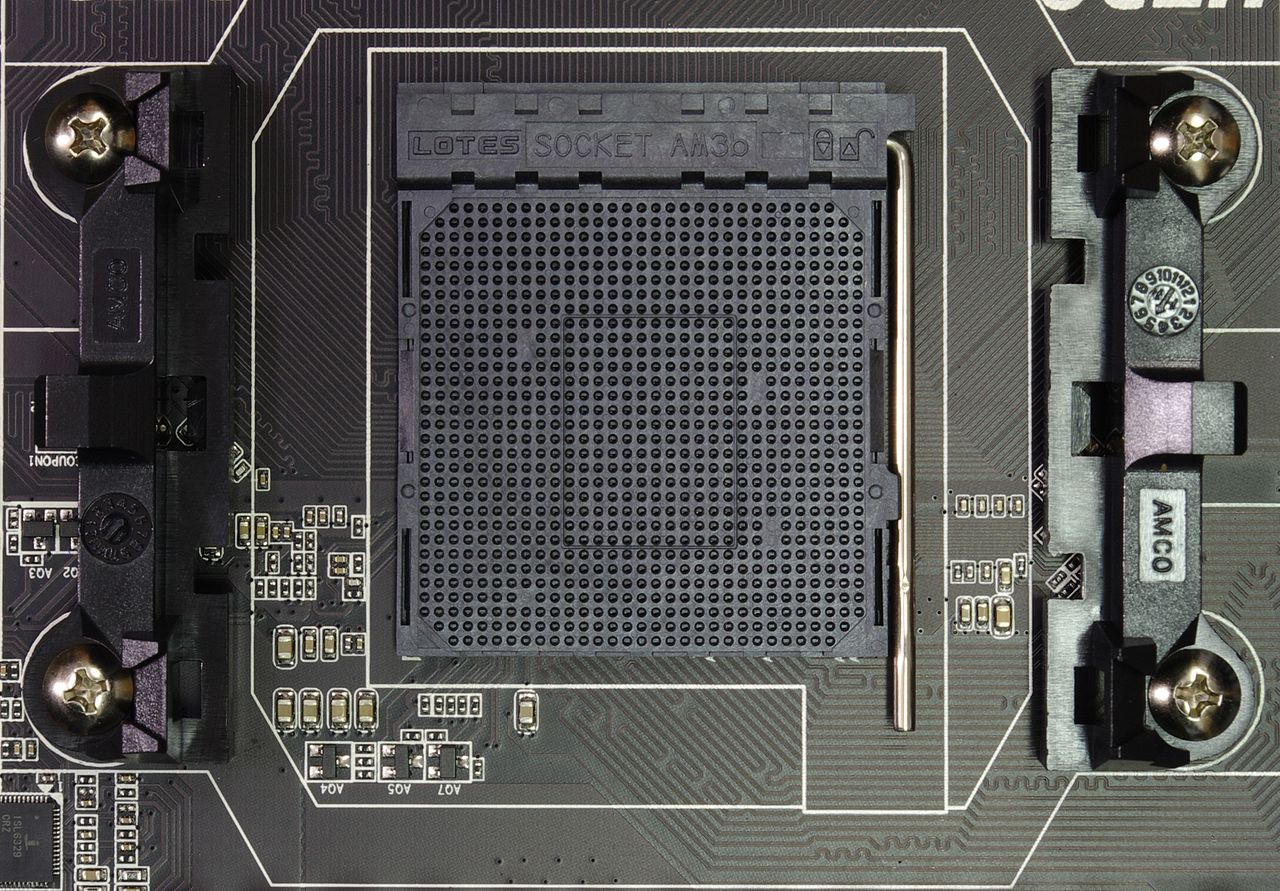
Today, AMD is promoting the following processor sockets:
- the main computing platform for such a developer is considered AM3+. The most productive CPUs are considered to be the FX range, which includes up to eight computing modules. In addition, such a platform supports an integrated graphics subsystem. However, here the graphics core is included in the motherboard, and is not integrated into semiconductor crystals;
- the latest modern AMD processor socket - FM3+. AMD's new CPUs are intended to be used in desktop computers and media centers not only at the entry-level, but also at the middle level. Thanks to this ordinary user, for a fairly small amount, the most advanced integrated solution will be available.
Working Capabilities

Many people first of all pay attention to the price of the processor. It is also important for them that he can easily solve the tasks assigned to him.
So, what can both organizations offer on this point. AMD is not known for outstanding achievements.
But this processor is an excellent value for money and good performance. If configured correctly, you can expect stable work no complaints.
It is worth noting that AMD has managed to implement multitasking. Thanks to such a processor, various applications are easily launched.
With it, you can simultaneously install the game and surf the vast expanses of the Internet.
But Intel is known for more modest results in this area, which confirms the comparison of processors.
It will not be superfluous to pay attention to the possibility of overclocking, during which the performance of the AMD processor can easily be increased by twenty percent compared to the standard settings.
To do this, you just need to use additional software.
Intel outperforms AMD in almost everything except multitasking. In addition, Intel is working with
So you should choose the motherboard and power supply much more carefully to prevent freezes with insufficient power.
Intel and AMD Power Consumption Graph Same story with heat dissipation. It is high enough for older models. As a result, a standard cooler can hardly cope with increased cooling.
Therefore, when buying a CPU from AMD, you must additionally purchase high-quality cooling from any decent company. Do not forget that high-quality fans make much less noise.
socket type and performance

Separately, it should be said about performance. After AMD acquired ATI, its creators managed to successfully integrate most graphic capabilities processing in the processor cores. Such efforts have paid off.
Those who use AMD chips for games should have no doubts that they get good performance, which is much better than equivalent chips from Intel (this is especially true for those who use a card with ATI graphics).
If it comes to a lot of multitasking, then it is better to opt for Intel, as it has HyperTreasing technology.
However, this advantage can only be used when software application able to support multitasking, that is, the ability to divide tasks into several small parts.
If the user needs game processor, it is better to combine an AMD processor with a video card.
So, there is a big difference between intel and amd processor sockets. When choosing suitable option, keep in mind the differences between them listed in this article. This will greatly simplify the choice of the appropriate option.
Part 1: 53 Integrated Graphics Configurations
A change of the year on the calendar, as a rule, leads to an update in the methods of testing computer systems, and, therefore, to summing up the results of testing of central processors (which is a special case of testing systems) conducted in the past year. In principle, we received the bulk of the results long before the end of the year, but we wanted to add the "seventh generation" Core to the results (at least in limited quantity). Unfortunately, this did not work out: the “original” version of Windows 10 used in tests according to the 2016 method is incompatible with graphic Intel drivers suitable for HD Graphics 630. More precisely, of course, on the contrary: this driver requires at least Anniversary update. Basically, there is nothing new in this. latest versions graphics drivers Nvidia, for example, behave similarly, but changing the set of software test stand violates the concept of tests "in as close conditions as possible". However, tests of new processors according to the 2017 methodology have already shown that there is nothing truly “new” in them - as expected. Therefore, it is possible to do without the results of Skylake Refresh for the time being, which we will do.
The second point that should also be taken into account is the number of subjects. In last year's results, the results of 62 processors were presented, 14 of which were tested with two "video cards" - an integrated GPU (each one is different) and a discrete Radeon R7 260X, and four with different types of memory. In total, 80 configurations were obtained. It’s not so difficult to “cram” them all into one article (after all, not so long ago we had 149 test configurations in one article ), but the diagrams turned out, to put it mildly, not very convenient for viewing. In addition, there is no great need for a direct comparison of the “atomic” Celeron N3150 and the extreme ten-core Core i7-6950X either: this is still fundamental different platforms. The “immensity” of the final articles according to the “old” methods was mainly due to the fact that in the main line of tests all participants worked with the same discrete video card, but this approach was not always applicable before - as a result, part of the computer systems had to be taken out into a separate line of tests, and then summarize individual test results.
This year we have decided to the same way. Today's article will present the results of 53 different configurations: 47 processors, five of which were tested with two different types of memory, and one with different levels TDP. But everything - exclusively using the integrated GPU (also different for everyone). To some extent, this is a return to the results of 2014 - only more results. And in the near future, those who wish will be able to get acquainted with the summary material based on testing 21 processors with the same Radeon R9 380. Some of the participants intersect, and in general the test results are “compatible” with each other, but in order to improve their perception, it seems to us, better two separate materials. Those readers who are only interested in dry numbers can (and for a long time) compare them in any set using the traditional one, which, by the way, also includes information on several “specialized” tests, which is somewhat difficult to add to the final materials.
Test stand configuration
Since there are many subjects, it is not possible to describe in detail their characteristics. After some thought, we decided to abandon the usual short table: anyway, it becomes too vast, and at the request of the workers, we still put some parameters directly on the diagrams, as in the past year. In particular, since some people ask to indicate right there the number of cores / modules and computational threads performed simultaneously, as well as the ranges of operating clock frequencies, we tried to do just that, adding information about the heat pack at the same time. The format is simple: “cores (or modules)/threads; minimum-maximum core clock frequency in GHz; TDP in Watts.
Well, all other characteristics will have to be looked at in other places - the easiest way is from manufacturers, and prices - in stores. Moreover, prices for some devices are still not determined, since these processors themselves are not available in retail (all BGA models, for example). However, all this information is, of course, in our review articles devoted to these models, and today we are engaged in a slightly different task than the actual study of processors: we collect the data obtained together and look at the resulting patterns. Including, paying attention to the relative position of not processors, but of entire platforms that include them. Because of this, the grouping of data on the charts is by platform.
Therefore, it remains only to say a few words about the environment. As for memory, the fastest supported by the specification was always used, with the exception of the case that we called "Intel LGA1151 (DDR3)" - processors under LGA1151, but paired with DDR3-1600, and not faster (and "main" according to specifications) DDR4-2133. The amount of memory has always been the same - 8 GB. System drive () - the same for all subjects. As for the video part, everything has already been said above: in this article, only data obtained with the built-in video core was used. Accordingly, those processors where it is not present are automatically sent to the next part of the totals.
Test Methodology
The methodology is described in detail. Here we will briefly inform you that for the results, two of the four standard “modules” are the main ones: and. As for gaming performance, then, as has been demonstrated more than once, it is mainly determined by the video card used, so these applications are primarily relevant for GPU tests, and discrete ones at that. For serious gaming applications, discrete video cards are still needed, and if for some reason you have to limit yourself to IGP, then you will have to responsibly approach the choice and configuration of the game for a specific system. On the other hand, for a quick assessment of the capabilities of integrated graphics, our “Integrated Gaming Result” is quite suitable (first of all, this is a qualitative, not a quantitative assessment), so we will also give it.
Let's pretend that the detailed results of all tests are available as . Directly in the articles, we already use relative results, divided into groups and normalized relative to the reference system (like last year, a laptop based on the Core i5-3317U with 4 GB of memory and a 128 GB SSD). The same approach is used when testing laptops and other off-the-shelf systems, so that all results in different articles (of course, using the same version of the methodology) can be compared, despite the different environment.
Working with video content
This group of applications traditionally gravitates towards multi-core processors. But when comparing formally identical models from different years of production, it is clearly seen that the quality of the cores is no less important here than their number, and the functionality (primarily) of the integrated GPU is also important here. However, lovers maximum performance"All the same, there is nothing special to please: AMD has never played in this market (even the company plans the most fast processors IGP will be deprived), while Intel has solutions for LGA115x, where performance per thread and clock frequency increase little by little with the platform number, but while maintaining the formula "four cores - eight threads", and the frequencies cannot be said to be very actively increased. Eventually Core comparison The i7-3770 and Core i7-6700K gives us a 25% increase in performance over five years: the same notorious “5% per year” that is commonly complained about. On the other hand, in a pair of Pentium G4520/G2130 the difference is already quite significant 40%, and the new models of these processors for LGA1151 have got support for Hyper-Threading, so they behave like the Core i3-6100 with all the consequences. In the field of non-tablet solutions, there is still room for intensive methods of improving performance, which is brilliantly demonstrated by the Celeron J3455, which already overtakes some fully desktop processors. In general, progress in different market segments proceeds at different speeds, but the reasons for this have been voiced for a long time and repeatedly: desktop computers have ceased to be the main purpose, and there are times when it was necessary to increase productivity at any cost, since in principle it was not enough to solve problems mass users, too, ran out in the last decade. Of course there is, server platforms, but (again - unlike the situation at the end of the last century), this has long been a separate area, where considerable attention is also paid to efficiency, and not just performance.
Digital photo processing

We continue to observe similar trends, adjusted for the fact that Photoshop, for example, has only partial multi-threaded optimization, but some of the filters used actively use new sets of commands, so that to some extent one compensates for the other in the case of budget desktop processors, but not "atomic" ones. » platforms. In general, there is an increase in performance over a long time interval, and with a certain devaluation of old processor families (Core i7 for LGA1155 is about Core i5 for LGA1151), but there are global “breakthroughs” that some people dream of " potential buyers' is long gone. Perhaps they are not there because changes generally occur only in the Intel assortment, and even those are planned :)
Vector graphics

From use Adobe Illustrator we refused the new version of the methodology, and the final diagram clearly shows the reason for this decision: the last thing for which this program was seriously optimized is Core 2 Duo, so for work (note: this is not a household application, and very expensive) a modern Celeron is quite enough or five years ago Pentium, but even paying seven times more, you can get only one and a half times faster. In general, at least in this case performance is interesting to many, it makes no sense to test it - in such a narrow range it is easier to consider that all colas are the same:) Only “atomic” solutions are “in flight” - so it was not in vain that they were said about them for 10 years in a row that they are intended for content consumption, and not for its production.
Audio processing

Adobe Audition is another program that has been dropped from the list of our testing programs since this year. The main claim to it is the same: the “necessary level of performance” is reached too quickly, and the “maximum” differs too little from it. Although there is already a difference between Celeron and Core i7 in each iteration of LGA115x, it’s easy to see that most of it is still “played out” within, if not budget, then inexpensive processor lines. Moreover, this is true only for Intel processors- the application generally treats today's AMD platforms somewhat biased.
Text recognising

The times of rapid progress in character recognition technologies are long gone, so the corresponding applications develop without changing the basic algorithms: they, as a rule, are integer-based and do not use new instruction sets, but they scale well in terms of the number of computational threads. The second provides a good spread of values within the platform - up to three times, which is close to the maximum possible (after all, the effect of code parallelization is usually not linear). The first one fails to notice significant difference between processors different generations one architecture - a maximum of 20 percent in five years, which is even less than the "average". But processors of different architectures behave differently, so this application continues to be an interesting tool.
Archiving and unarchiving data

Archivers also, in principle, have reached such a level of performance that in practice you can no longer pay attention to their speed. On the other hand, they are good because they quickly respond to changes in performance characteristics within the same family of processors. But comparing different ones with them is a dangerous occupation: the fastest among those tested by us (of those included in today's article, of course) was the Core i7-4970K for an already formally "obsolete" platform. And in the "atomic" family, too, not everything is going smoothly.
File operations

The diagram clearly shows why since 2017 these tests will no longer be taken into account in the overall score and “go away” to their own: with the same fast drive, the results are too even. In principle, this could be assumed a priori, but it did not hurt to check. Moreover, as we can see, the results are even, but not perfectly even: "surrogate" solutions, junior mobile processors and old AMD APUs do not squeeze the maximum out of the used SSD. SATA600 is supported in their case, so no one seems to interfere with copying data at least at the same speed as that of "adult" platforms, but there is a decrease in performance. More precisely, it was until recently, but now it ceases to matter.
scientific calculations

Regarding the use of SolidWorks Flow Simulation for testing low-end systems, questions regularly arose in the forum, but in general the results of this program are quite interesting: as you can see, it scales well across cores, but only in “physical” ones - different implementations of SMT are contraindicated for it. From a methodological point of view, the case is interesting, and not unique; while most of the programs in our set, if multi-threaded, then fully. But in general, the results of this scenario fit into the big picture.
iXBT Application Benchmark 2016

So, what do we have in the bottom line? Mobile processors are still a thing in themselves: they intersect in performance with desktop processors, but of lower classes. This is not surprising - but their energy consumption is significantly lower. The increase in performance between identically positioned Intel desktop processors over five years is 20-30%, and the more “top-end” the family, the slower it grew. This, however, does not interfere with “social justice” in any way: it is in the budget segment that higher performance is needed, as well as more powerful graphics (there may simply not be enough money for a discrete one). In general, economical buyers were lucky - one can say that the primary focus on portable computers has also contributed to budget desktops. And not only in performance and purchase price, but also in the cost of ownership.
In any case, this is true for Intel solutions - the second manufacturer of x86 processors remaining on the market has been doing worse in recent years, to put it mildly. FM1 is a five-year-old solution, FM2+ remained the most modern and powerful integrated platform of the company until the end of 2016, but they differ ... literally by the same 20% as different Generation Core i7. However, it cannot be said that nothing has changed at all over the past years: the graphics have become more powerful, and the energy efficiency has grown, but as the main niche of these processors was gaming, it has remained so. And for graphics performance at the level of junior discrete video cards, you have to pay with both low performance of the processor part and high energy consumption - to which we are just moving on.
Energy consumption and energy efficiency
In principle, the diagram clearly explains why budget processors“grow” in speed faster than “non-budget” ones: power consumption is more limited than, generally speaking, necessary for desktop computers (although this is better than the horrors of the 90s and “zero”), but the relative share of “full-size desktops” has also greatly decreased over past years and continues to fall. And for laptops or tablets, even the older "atomic" models are no longer very comfortable - not to mention the quad-core Core. Which, in a good way, it is high time to make the main mass product - you look, and the software industry will find useful use for such capacities.

It should be noted that not only the efficiency grew, but first of all, energy efficiency increased, since the solution of any problem in the same or even less time is more modern processors spend less energy. Moreover, working quickly is useful: it will turn out to stay in energy-saving mode longer. Recall that these technologies have been actively used in mobile processors - when there was such a division at all, because now all processors are like that to a certain extent. AMD has the same trend, but in this case, the company failed to repeat the success at least Sandy Bridge, as a result of which the most “delicious” market segments were lost. Let's hope that the release of processors and APUs based on a new microarchitecture and a new technical process will solve this problem.
iXBT Game Benchmark 2016
As it was said in the description of the methodology, we restrict ourselves to a qualitative assessment. At the same time, let's recall its essence: if the system demonstrates a result above 30 FPS at a resolution of 1366 × 768, it receives one point, and for the same at a resolution of 1920 × 1080 - two more points. Thus, given that we have 13 games, the maximum score can be 39 points - it does not mean that the system is gaming, but such a system at least copes with 100% of our game tests. It is by the maximum result that we will normalize all the rest: the points were calculated, multiplied by 100, divided by 39 - this will be the “Integral game result”. For really gaming systems, it is not needed, since everyone is more interested in the nuances there, and for evaluating “universal” it will do. It turned out more than 50 - it means that sometimes you can play something more or less comfortably; about 30 - even reducing the resolution will not help; well, if 10-20 points (not to mention zero), then it's better not to even stutter about games with more or less present 3D graphics.

As you can see, with this approach, everything is simple: only AMD APUs for FM2 + (most likely, FM2) or any Intel processors with a fourth-level cache (with eDRAM) can be considered "conditionally gaming" solutions. The latter are faster, but rather specific: firstly, they are quite expensive (it’s easier to buy inexpensive processor and a discrete graphics card, which will provide higher comfort in games), and secondly, most of them have a BGA-version, so they are sold only as part of ready-made systems. AMD, on the other hand, is playing on a different field - its desktop A8 / A10 are practically uncontested if you need to build a computer that is more or less suitable for games, but has a minimal cost.
Other Intel solutions, as well as junior (A4 / A6) and / or outdated AMD APUs, should not be considered as gaming solutions at all. From which it does not follow that their owner will not have anything to play at all - but the entire range of available games will also include either old or undemanding applications for graphic performance. Or both at once. For other things, they will have to purchase at least an inexpensive discrete video card - but not the cheapest, since "grassroots" solutions (as has been shown more than once in the relevant reviews) are comparable to the best integrated solutions, that is, money will be thrown away.
Total
In principle, we made the main conclusions on processor families directly in their reviews, so they are not required in this article - this is primarily a generalization of all the information received earlier, nothing more. More precisely, almost all - as mentioned above, we put aside some systems for a separate article, but there will be fewer of them, and the systems will be less massive. The main segment is here. In any case, if we talk about desktop systems, which are now different in execution.
Generally speaking, the past year, of course, was rather poor in processor events: both Intel and AMD continued to sell on the mass market what debuted in 2015, or even earlier. As a result, many participants in these and last year's results turned out to be the same - especially since we once again tested the "historical" platforms (we hope that for the last time :)) But the Celeron N3150 was the slowest last year: 54.6 points, and the fastest - Core i7-6700K: 258.4 points. In the same position, the positions have not changed, and the results are actually the same - 53.5 and 251.2 points. The top system had even worse :) Note: this is despite the significant reworking of the software used, and just in the direction of the most demanding tasks for computer performance. The budget "old man" in the face of the Pentium G2130, on the contrary, has grown from 109 to 115 points over the year, as well as the "non-budget old man" Core i7-3770 after the software update began to look even a little more attractive than before. On this, in fact, the idea of acquiring "performance for the future" can be closed - if someone has not done this yet;)

The heart of a computer is called the processor (processor), which is its main data processing device. The part looks like a chipset and is responsible for computing processes. How to choose a processor for a computer is the most important issue when buying equipment. The overall speed of the system largely depends on the performance of this part. In order not to regret your purchase, choose components based on their characteristics.
Main characteristics of the processor
- Manufacturer. There are two main competitors that produce processors for computers - these are AMD and Intel. The second firm is considered a leader in developing cutting-edge technologies. The main advantage of AMD over Intel is relatively low prices. Moreover, the products of the first are inferior to the second in productivity slightly (on average, by 10%), but the cost is 1.5-2 times lower.
- What is the clock speed of a processor? This parameter determines how many operations the device can perform per second. What does the processor frequency affect: a high indicator of this characteristic promises fast processing computer data. The parameter is considered one of the most important when choosing a device. How to find out the frequency in Windows: you need to right-click the properties menu on the "My Computer" icon.
- Number of Cores. This indicator affects the number of programs that can be run on a PC without losing its performance. Older computer models are equipped with quad-core or dual-core processors. New devices released during the last years have 6- and 8-core parts. However, if software optimized for a dual-core PC, more cores will not speed it up. On the part box, you can see an alphanumeric marking, the decoding of which will provide data on the number of cores.
- System bus frequency. The characteristic indicates the speed of the flows of incoming or outgoing information. The higher the score, the faster the exchange of information.
- cache memory. A large role in the operation of the PC is played by the processor cache, which has the form of a high-speed memory block. The part is located directly on the core and is necessary to improve performance. Thanks to it, data processing is faster than in the case of RAM. There are 3 levels of cache memory - from L1 to L3. The first two have small volumes, but the third ones confidently win, providing for a large capacity - due to the speed of work.
- Connector type (socket). This characteristic is not considered paramount, but it has a certain relevance when choosing a device. The socket is the "socket" on the motherboard that the processor is placed in, so it must be compatible with the part chosen. For example, if the socket is labeled AMZ, you need a corresponding connector on the motherboard. The latest models are equipped with modern types of "sockets" and often have improved characteristics (bus frequency and others).
- Power consumption and cooling. Powerful modern devices have a negative impact on the power consumption of the computer. To avoid overheating of parts and their breakdown, special fans (coolers) are used. For use the TDP indicator, indicating the amount of heat required in the outlet. Based on this value, a specific model of the cooling system is selected.

What is the difference between AMD and Intel
A frequently asked question among those wishing to purchase a processor is: "Which is better AMD or Intel?". The main difference is the hyper-strength technology and the increased computational pipeline that Intel models have. Thanks to this, devices perform a number of tasks faster: archive files, encode video, and perform other tasks. Parts from AMD cope with the listed tasks just as well, but they spend more time on it. Everyone determines for himself: which processor is better than Intel or AMD.
To simplify the choice, check out the advantages of products from both manufacturers. Comparison of AMD and Intel processors:
| Intel Benefits | Advantages of AMD |
| High speed PC work | The optimum ratio of price and quality |
| Economical power consumption | System stability |
| High performance in games | multitasking |
| Core i7 and i3 multithreading gives extra performance | Ability to speed up processes by 5-20% |
| Perfectly tuned work with RAM | Multiplatform (the ability to assemble a PC from parts of different generations of AMD) |
Which processor to choose for a computer
The answer to the question posed depends on the tasks that the PC will have to perform. So, when choosing a gaming computer, attention should be paid to the model of the video card, since the graphics adapter is responsible for supporting certain technologies and performance levels in games. However, without a properly matched CPU, the graphics card will not reveal its potential. Less demanding parts are suitable for working with other programs or using a PC in the office.
For games
How to choose a processor for a gaming computer? There are a number of requirements for a "gaming" PC. The device must be able to process at least four data streams. The test results proved that Intel technology Hyper-Treading increases the number of frames per second. Experts consider the Intel Core i5 models optimal for a gaming PC. Parts from AMD show less performance. If in the line from Intel 4-core devices cope with their tasks, then their competitors show the same result with 8-core counterparts. What processor to choose for games?
Top gaming devices:
- Intel Core-i5 Ivy Bridge (quad core);
- Intel Core i5-4440 Haswell (quad-core);
- AMD FX-8350 Vishera (octa-core).
For home or office use
Browsers and other necessary for office work programs need an impressive amount random access memory, but practically do not load the hard disk and processor. So choose better computer with a large amount of memory. However, processor performance should not be neglected either. According to the test results, models from the Intel Core i3 or i5 lines will be a good solution.
List of budget devices for the office:
- Intel Celeron G1820;
- AMD ATHLON II X2 255;
- AMD ATHLON II X4 750K;
- AMD A8-6600K.
To work with demanding programs
This category includes parts whose function is to provide fast work demanding programs, for example, video, graphic editors, etc. Devices of this type are expensive components and are characterized by maximum performance. This category of processors is often of interest to gamers who want to achieve best quality images while playing.
Overview of the best devices for demanding programs:
- AMD FX-8350 (8-core). Ideal for games and other programs designed for . Differs in speed and justified price.
- Intel i7-4770 (4-core). Runs games at the highest settings, works fast, perfectly optimized for Intel graphics cards.

Rating of the best processors for PC in 2019
- Intel Core i7-990x. Ideal for gaming PC latest generation. The device is designed for socket 1366, equipped with 6 cores, has a frequency of 3.46 GHz and 12 megabytes of cache memory. Approximate cost: 38,000 rubles.
- Intel Core i7-3970X Extreme Edition. One of the most popular models. Equipped with 6 cores, has 15 MB cache and 3.5 GHz clock speed. Works great with any new demanding games and programs. Approximate cost: 46,000 rubles.
- Intel Core i5-4690K. An inexpensive model will show excellent results in terms of performance. If we compare the i5-4690K with other devices, it stands out due to its price / quality ratio. The processor is equipped with a cache memory of the third level, has a clock speed of 3.5 GHz and 4 cores. Approximate cost: 22,000 rubles.
- AMD FX-9370. The most powerful AMD processor has a new socket AM3 + and 8 cores, developing a maximum frequency of up to 4.4 GHz. The model is equipped with 8 MB of cache memory, which allows you to improve the performance of your PC and use any programs, games. Approximate cost: 20-22 000 rubles.
- Intel Xeon E3-1230 v3. The quad-core device belongs to the fourth generation of processors from Intel. It is equipped with a socket type 1150, which is considered the best among the existing ones. Clock frequency Xeon E3-1230 v3 - 3.3 GHz, cache memory is 8 MB. Approximate cost: 22,000 rubles.
2015 processor test table
To understand how to choose a processor for a computer, you should read the results of their testing. Devices are being tested based on Windows 7 (64-bit). To do this, certain programs are selected to unlock the potential of multithreading, determine whether there is support for AMD Turbo CORE (dynamic overclocking) technologies, and Intel Turbo Boost Technology whether it is possible to use the new SIMD. Test results are expressed as a percentage of the performance of the fastest among existing devices, which has a 100% result.
Summary table of processor performance:
| Name | Result |
| Intel Core i7-5930K BOX | |
| Intel Core i7-4960X Extreme | |
| Intel Core i7-4960X Extreme BOX | |
| Intel Core i7-5820K BOX | |
| Intel Core i7-4790K | |
| Intel Core i7-4790K BOX | |
| Intel Core i7-4790 | |
| Intel Core i7-4790 BOX | |
| Intel Core i7-4820K BOX | |
| Intel Xeon E3-1240 V2 | |
| Intel Xeon E3-1230 V2 |
If you want to buy a processor, you should study its characteristics. For example, in pursuit of frequency, many people forget about the features of the kernel of a particular manufacturer, which negatively affects computer performance. To be satisfied with the purchase, it is necessary to take into account the parameters of the device and its compatibility with other parts. Find out how to choose suitable processor for a computer by watching the suggested video.
Holidays and vacations are in full swing, but the weather outside is not very good. What would you like to do? I propose to spend time with pleasure: to play in computer games. Your "old man" does not pull modern toys? Maybe, . But what?
Today's article is designed to help you decide on the choice of "pebble" for a gaming PC. The ranking of the best processors for mid-summer 2017 included models that showed the optimal balance in terms of performance and price. For your convenience, we have divided them into 3 groups: approximately $100, approximately $200 and approximately $300. So that no one feels left out, each group consists of a pair of processors - one Intel and one AMD.
About $100: Intel Core i3-7100 and AMD FX-8320
Intel Core i3-7100

Yes, it has only 2 cores, but this shortcoming is compensated by a high clock frequency (3900 Mhz), support for DDR4-2400 memory and, to some extent, technology Hyper Threading, which allows the operating system to use each physical core as 2 logical ones. In addition, the "pebble" has a good integrated graphics with support for 4k resolution at 60 Hz. Due to it, you can do without discrete graphics card if for some reason you put off buying it.
Specifications
- Microarchitecture: Kaby Lake(7th generation).
- Number of cores: 2.
- Clock frequency: 3900 Mhz.
- Socket: LGA1151.
- Manufacturing process: 14 nm.
- Multiplier: 34, unlocked.
- L1 cache: 64 Kb (instructions + data).
- L2 cache: 512 Kb.
- L3 cache: 3072 Kb.
- Controller PCI Express: eat.
- Technologies: Hyper Threading (hyperthreading), EM64T (x64 support), Virtualization Technology (virtualization), Enhanced SpeedStep (energy saving), hardware encryption, XD Bit, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSSE3, VT-x, MMX.
- Thermal power (TDP): 51 W.
- : 100°C
The most attractive qualities of the Core i3-7100: high performance, reasonable price, integrated graphics and low TDP - to cool the processor even at maximum load, the included small cooler is enough.
The downside is that it only works on Windows 10 (as well as Linux and Mac OS). Those who cannot part with the "seven" and "eight" will have to choose - either the system or the new processor. By the way, this shortcoming concerns not only the Intel Core i3-7100, but the entire Kaby Lake line and AMD Ryzen.
AMD FX-8320

8 cores, 4000 Mhz frequencies with the possibility of increasing up to 4600 Mhz and more due to overclocking by the multiplier (here, unlike the Intel competitor, it is free), as well as support for DDR3-1866 memory, they are excellent in multi-threaded games like Battlefield.
Specifications
- Microarchitecture: Vishera.
- Number of cores: 8.
- Clock frequency: 3500-4000
- Socket: AM3+.
- Manufacturing process: 32 nm.
- Multiplier: 17.5, free.
- Integrated Graphics: No.
- L1 cache: 96 Kb.
- L2 cache: 2048 Kb.
- L3 cache: 8192 Kb.
- PCI Express Controller: No.
- The maximum supported memory size: 128 Gb.
- Supported memory standards: DDR3-800/1066/1333/1600/1866. There is support for ECC.
- Technologies: AMD64 (x64 support), Virtualization Technology, AMD PowerNow (noise reduction), Turbo Core 3.0 (peak boost), NX Bit, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4, SSE1, SSE4.2, SSSE3, MMX, VT, XOP, TBM.
- Thermal power (TDP): 125 W.
Advantages of AMD FX-8320: high performance, nice price ($115-120), multiplier makes it possible to assemble an inexpensive gaming computer that will remain relevant for the next 3-4 years.
Disadvantages: very hot - requires a powerful cooling system, consumes a lot of energy, does not have a graphics core.
About $200: Intel Core i5-7500 and AMD Ryzen 5 1600
Intel Core i5-7500

The clock frequency of this processor reaches 3800 Mhz (or a little more) with dynamic overclocking, there is an integrated video - the same as that of the i3-7100, and support for DDR4-2400 memory.
Specifications
- Microarchitecture: Kaby Lake.
- Number of cores: 4.
- Clock frequency: 3400-3800
- Socket: LGA1151.
- Manufacturing process: 14 nm.
- Multiplier: 39, unlocked.
- Integrated Graphics: HD Graphics 630.
- Graphics core frequency: 1100 Mhz.
- L2 cache: 1024 Kb.
- L3 cache: 6144 Kb.
- PCI Express controller: yes.
- Number of PCI Express 3.0 lanes: 16.
- The maximum supported memory size: 64 Gb.
- Supported memory standards: DDR3L-1333/1600, DDR4-2133/2400.
- Technologies: Turbo Boost0 (frequency increase at peak loads), EM64T, Virtualization Technology, Enhanced SpeedStep, Intel vPro ( remote control non-OS computer), hardware encryption, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSE4a, SSSE3, MMX, TBT 2.0, VT-x , XD Bit.
- Maximum temperature: 80°C
Advantages of the Intel Core i5-7500: fast, cool (TDP 65 W), supports dynamic overclocking (Turbo Boost 2.0), has integrated graphics, the Intel vPro function is implemented. The latter allows you to remotely edit the BIOS and run diagnostic tests outside operating system by connecting to a computer over a network.
Disadvantages - no popular support beloved Windows 7, no hyperthreading, locked multiplier (for this price, many people think they could implement Hyper Threading and make multiplication free).
AMD Ryzen 5 1600

Processors based on the Zen microarchitecture, one of which is the Ryzen 5 1600, are characterized by low power consumption and TDP (which is unusual for the bulk of AMD products). In addition, a compact, efficient and quiet cooler is included in the boxed package of the model, the power of which is sufficient even with some overclocking.
Specifications
- Number of cores: 6.
- Clock frequency: 3200-3600 Mhz.
- Socket: AM4.
- Manufacturing process: 14 nm.
- Multiplier: 32, free.
- Integrated Graphics: No.
- L1 cache: 96 Kb.
- L2 cache: 3072 Kb.
- L3 cache: 16384 Kb.
- PCI Express controller: yes.
- Number of PCI Express 3.0 lanes: 16.
- The maximum supported memory size: 64 Gb.
- Supported memory standards: DDR4-1866/2666.
- Technology Support: Multithreading, AMD64, Virtualization, Hardware Encryption, Precision Boost (increased clock cycles at peak loads), Pure Power (power saving), SSE instructions, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSE4a, SSSE3, MMX .
- Thermal power (TDP): 65 W.
AMD Ryzen 5 1600 Pros: Outstanding performance with moderate price($200-210), low heat, low power consumption, multiplier overclocking, the ability to unleash the potential of any modern video card.
Cons: no integrated graphics, no support for Windows 7.
About $300: Intel Core i7-7700K and AMD Ryzen 7 1700
Intel Core i7-7700K

Specifications
- Microarchitecture: Kaby Lake.
- Number of cores: 4.
- Clock frequency: 4200-4500
- Socket: LGA1151.
- Manufacturing process: 14 nm.
- Multiplier: 42, free.
- Integrated Graphics: HD Graphics 630.
- Graphics core frequency: 1150 Mhz.
- L1 cache: 128 Kb (instructions + data).
- L2 cache: 1024 Kb.
- L3 cache: 8192 Kb.
- PCI Express controller: yes.
- Number of PCI Express 3.0 lanes: 16.
- The maximum supported memory size: 64 Gb.
- Supported memory standards: DDR3L-1333-1600, DDR4-2133-2400.
- Technology Support: Hyper-Threading,Turbo Boost0, EM64T, Virtualization Technology, Enhanced SpeedStep, Hardware Encryption, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSSE3, MMX, XD Bit.
- Thermal power (TDP): 91 W.
- Maximum temperature: 100°C
Strengths of the Intel Core i7-7700K: best ratio performance in games and purchase costs ($300-315), unlocked multiplier, powerful video core. In short, a good start for the future.
Weaknesses: in case of overclocking, it requires a powerful and expensive cooling system, does not support Windows 7.
AMD Ryzen 7 1700

"Under the hood" of this processor: 8 physical and 16 virtual cores, free multiplier, 16 Mb L3, DDR4-2933 support, 24 PCI Express lanes (competitors have 16), the frequency of each core in dynamic overclocking is 3700 MHz, in multiplier overclocking – up to approximately 4100 MHz. There is no integrated graphics card, but the systems for which the Ryzen 7 1700 is designed do not need it. Besides, it's cold. Even under intense load (by the way, it is extremely difficult to load it at 100%), it does not heat up above 50 ° C.
The cost of the model is comparable to the Core i7-7700K.
Specifications
- Microarchitecture: Summit Ridge (Zen).
- Number of cores: 8.
- Clock frequency: 3000-3700 MHz.
- Socket: AM4.
- Manufacturing process: 14 nm.
- Multiplier: 30, free.
- Integrated Graphics: No.
- L1 cache: 256 Kb (instructions + data).
- L2 cache: 4096 Kb.
- L3 cache: 16384 Kb.
- PCI Express controller: yes.
- Number of PCI Express 3.0 lanes: 24.
- The maximum supported memory size: 64 Gb.
- Supported memory standards: DDR4-1866/2933.
- Technology Support: Multithreading, AMD64, Virtualization, Hardware Encryption, Precision Boost, Pure Power, SSE instructions, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSE4a, SSSE3, MMX.
- Thermal power (TDP): 65 W.
- Maximum temperature: 90 °C
Advantages of AMD Ryzen 7 1700: amazing power, multitasking, versatility, energy efficiency. The disadvantage is that there is no support for older versions of Windows.
According to many owners and experts, the Ryzen 7 1700 is a huge leap forward for AMD. The release of this processor showed that the “reds” are far from being as hopelessly behind as they are thought to be, and are still able to set the heat on the “blues”. As they say, they harness for a long time, but they go fast.



