Lesson # 66. What is removable media
Removable storage media are designed to store your data outside of your computer. They are very convenient to use for transferring your files from one computer to another. I am sure that you are well aware of such removable media.
The most popular removable media are currently flash drives, flash cards, removable hard drives and optical discs (CDs and DVDs). I think that using a computer and not knowing anything about them is impossible.
Let's take a closer look at each of listed devices and learn how to work with them.
But before we start, I want to talk about some of the parameters of removable media, which primarily affect their cost:
- Volume- this is the main parameter of any storage medium and not only removable ones. To measure volume, use the same units as to measure the volume of data (information). We know that all information on a computer is stored in the form of files. To somehow measure the amount of information, a special unit of measurement was introduced, which was named - byte.There are also smaller units - bits, and 1 byte = 8 bits... What are bits and why 1 byte is equal to 8 bits, we will not disassemble. This is absolutely optional information for regular user... But still I will give an example that will give an idea of what is byte... The amount of information in 1 byte is one letter in a text document. 1 byte as you can imagine, there is a small amount of information (just one symbol), so usually larger units are used.
1 kilobyte (KB) = 1024 bytes;
1 megabyte (MB) = 1024 kilobytes;
1 gigabyte (GB) = 1024 megabytes;
1 terabyte (TB) = 1,024 gigabytes.
The prefixes "kilo", "mega", etc. are borrowed from ordinary life, but unlike, for example, 1 kilometer, which contains 1000 meters, 1 kilobyte contains 1024 bytes. Why this happened is not necessary for us to know. The amount of information is a very conditional value, and in ordinary life everyone has long rounded 1024 to 1000.
So, the volume of a storage medium is its main indicator that affects its cost. The larger the volume of the information carrier, the higher its cost.
- Reading (writing) speed information from the carrier (to the carrier). Since the volume of removable media grows every year, this figure becomes important. Of course, if you buy a USB flash drive to transfer your text documents from computer to computer, then speed in this case is practically not important, since text files are usually small in size. But if you need to rewrite to a USB flash drive a large number of video or music files, then the write speed plays an important role, and the time after which the files are transferred to the USB flash drive will directly depend on it. The same goes for flash cards that are used in digital cameras. How faster speed writing such a flash card, the faster the photo is recorded on it and the faster the camera is ready to shoot the next frame. Let's understand the concept of data transfer rate, since it is used very often and beginners have problems with this. the speed of information transfer in the computer world was adopted bit per second, also denoted - bit / s (English bits per second, bps). The speed of information transfer can be indicated not only as a characteristic of information carriers, but also used in networks, including the speed of connection to the Internet is indicated precisely in bits per second.
We already know that bit, this is the minimum amount of information and is mainly used great value – byte equal to eight bits. Therefore, when you are told that the speed of your Internet connection is 1 Mbps, then this is DOES NOT MEAN that you download 1 Megabyte of information per second. To translate Megabits v Megabytes we need to divide the speed of your connection by 8 and in our case we will get 0.125 MB / s, which is 125 kilobytes per second... This designation is often found:
Kilobits per second - Kb / s
Kilobyte Per Second - KB / s
Pay attention to whether the capital or lowercase letter"B" in this designation.
- Device size... This parameter is very conditional and is not suitable for all types of devices, but basically the tendency is as follows - the smaller the device, the higher its price
Lesson # 67. Optical discs
CD disks (Fig. 197) or they are also called compact disks ( CD comes from the English. Compact Disc) have practically fallen out of use, although they long time were the main medium for transferring information between computers. Their volume was usually about 700 MB. To read such discs, a special device is used - a CD-drive (Fig. 198).
 |
|
| Rice. 197. Optical disc | Rice. 198. CD Drive optical discs |
Data from disk is read using laser beam... There are drives that only allow reading data from CDs, and there are also so-called recorders that allow you to write to disk.
Blank discs to be recorded on computer slang are called blank... There are two main groups of CDs (blanks):
- CD-R- such a disc can only record information once;
- CD-RW- discs intended for multiple recording... Information on such discs can be erased and rewritten.
Usually the read / write speed is indicated on the CD-drive, for example, 24X. This is the speed at which the drive is able to read data from a disk or write information to a disk. The speed is indicated in multiples of 150 Kb / s (i.e. 153 600 bps). For example, a 24-speed drive provides maximum speed read (or write) a CD equal to 24 × 150 = 3600 Kb / s. This means that, for example, when copying information from a CD to your computer, the drive will transfer 450 kilobytes of data in one second. If you copy a movie that is 650 megabytes in size, it will take about 24 minutes to copy it to your computer. Here's a simple arithmetic.
Over time, CDs have been supplanted DVD disc amy.
DVD (dvd, eng. Digital Versatile Disc- digital multipurpose disk; also English. Digital Video Disc- digital video disc) - has the same size as a compact disc, but uses a different technology that can significantly increase the amount of information that it can hold. DVD drives are used to read DVDs, which can also read CDs. CD drives, on the other hand, cannot read DVDs.
V currently the most popular DVDs are DVD-5 and DVD-9. DVD-5 discs can store 4.37 GB (Gigabytes) of information, and DVD-9 discs can store 7.95GB.
The unit of speed (1x) for DVD read / write is 1,385,000 bps (i.e. about 1352 Kbps = 1.32 Mbps), which roughly corresponds to 9x speed (9x) of CD read / write. which is 9 × 150 = 1350 Kb / s. Thus, a 16-speed drive provides a DVD read (or write) speed of 16 x 1.32 = 21.12 MB / s.
Just like CDs, DVDs are divided into groups:
- DVD-R- designed for one-time recording;
- DVD-RW- rewritable discs.
Also, historically, another division of DVD discs into "plus" ones (denoted DVD + R and DVD + RW) and "minus" (denoted DVD-R and DVD-RW).
"Plus" blanks appeared later and are an improved version of "minus" ones. The main, significant for the end user, difference between "plus" and "minus" blanks is as follows. When rewriting DVD-RW disk, you must first delete the information from it, but when rewriting DVD + RW You do not need to delete the information on the disc, the drive is able to overwrite the old information with new information. But to work with "plus" discs, you need to have a DVD burner that supports this format (almost all modern DVD drives support this format).
In pursuit of an increase in the volume of storage media, manufacturers are constantly creating something new. This is how another format appeared - Blu-ray Disc, BD(blue-ray, eng. blue ray- blue ray). Format discs Blu-ray have the same dimensions as CD and DVD discs (120 mm), but differ significantly in capacity. By technology Blu-ray make discs having one or two layers for recording data. Single-layer discs can hold up to 25GB of information, and double-layer discs - up to 50GB. There are discs for one-time recording - BD-R, and for reusable writing - BD-RE.
Of course, to read and write such discs, you need a special drive that supports Blu-ray technology... The write speed has also increased significantly. The unit of speed (1x) read / write Blu-ray is 36 Mbps, which allows you to write 25GB of information on a single layer disc at 12 speed in about 8 minutes.
Most computers nowadays are equipped with optical disc drives. In order to install the disc into the drive, you need to click on the button located on it (Fig. 199).
After placing the disc in the tray, close the tray with a light pressure. After that, the information recorded on the disc will become available and it will be possible to familiarize with it, for example, using the program Conductor.
Lesson # 68. Flash drives
Flash drives or simply flash drives- These are the most popular and widespread removable media today. In computer stores, you can find a huge selection of flash drives. They differ in color, shape and body material, and you can always choose a flash drive to your liking (fig. 202). But still, the main parameter of a flash drive is its size, i.e. the amount of information that can be recorded on it.
On sale you will find flash drives ranging in size from hundreds of megabytes to several tens and even hundreds of gigabytes. Moreover, the difference in price may not be proportional to the difference in volume, therefore, before buying a flash drive, compare the prices of devices of different sizes and choose the best price-volume combination for yourself.
The flash drive is connected to the computer through the so-called universal connector - USB(Universal serial bus- universal serial bus, fig. 203).
This connector has become very popular and a huge number of various devices, starting with flash drives and ending with printers, scanners, cameras and camcorders.
Usually on your computer, you can find several USB connectors(2, 4 and even 8). They are located on the back of the computer. But since these connectors have become very popular, manufacturers computer cases began to be placed on the front or side wall of the computer, which made it possible to obtain fast access and connect devices without unnecessary movements. Usually these connectors are marked with a special icon (fig. 204).
On laptops, two or three USB connectors are usually installed (fig. 203).
The USB connector, unlike other connectors on a computer, allows you to connect and disconnect devices while the computer is running. This means that you can turn off the device, for example, remove the USB flash drive without turning off the computer, but there are nuances of work and we will talk about them a little later.
Lesson # 69. external HDs
Along with flash drives, and are used external HDs(Fig. 205). They have larger dimensions than flash drives, but the amount of information stored on them is much larger. The volumes of modern removable hard drives are hundreds of gigabytes and reach several terabytes. Accordingly, the price hard disk will depend on its volume. In addition, the price of a hard drive is also affected by its geometric size - the smaller the hard drive, the more you will have to pay for it, as a rule.
Hard drives are often abbreviated HDD- from the English. Hard drive Disk(HDD). In colloquial speech, you can also hear the name "Winchester" or "screw".
External hard drives are connected to the computer through the already familiar connector USB(Fig. 206).
Lesson # 70. Memory cards
Memory cards or flash cards are compact electronic storage devices used to store information (Fig. 207). Modern memory cards are made on the basis of flash memory, i.e. on the same principle as flash drives.
if you have digital camera, then one of the memory cards shown in Figure 207 will definitely be installed in it. The type of memory that is installed in specific model the camera is determined by the manufacturer.
The most popular SD cards today are Secure Digital Memory Card(Fig. 208). These cards have several standard sizes and are mainly used in portable devices (cameras, cell phones, PDAs, etc.).
Memory cards are used precisely as storage devices, i.e. the camera records the captured photos on them, and in a pocket computer (PDA) you can use the card as a hard disk of your computer, i.e. save your files to the card or install programs on it.
When working with portable devices, you inevitably need to connect the device to a computer in order to transfer information to or from the device. It's the same with a digital camera - sooner or later it becomes necessary to transfer photos to a computer. How can this be done?
 |
| Rice. 209. Card Reader |
It is very convenient to work with flash memory cards through a device called card reader, from the English. card reader(fig. 209).
Usually a card reader is a small box with different connectors and you can connect memory cards to your computer at the same time. different formats.
The card reader itself is connected to a computer via a USB connector.
On sale you can find card readers of various configurations and sizes, but when purchasing a card reader, pay attention to what types of flash memory cards it supports. There are card readers that support, for example, only cards Secure digital... If you want to purchase a universal card reader, then look for the inscription in its designation “ all in one" or " all in 1". This means that this device works with all types of memory.
Lesson # 71. How to download photos from a camera
If you have a digital camera, but no card reader, then you can use to transfer photos in the following way.
- The set with the camera always comes with a cable for connecting to the USB connector. Connect the camera to the computer with this cable.
- Turn on the camera.
- The operating system will try to independently determine what kind of device was connected to the computer.
If you have an Internet connection, then most likely you just need to wait about a minute until Windows will detect your camera and install the necessary driver.
Driver Is a program that is a kind of intermediary between the operating system and the device. The driver “explains” to the operating system what kind of device it is installed and how to work with it.
If you do not have an Internet connection, then most likely you will need to install the driver yourself. The set with the camera always comes with a disk, which usually contains the driver for the device. Read the instructions for the camera and install required programs according to the description.
- After installing the driver, a dialog box will appear (Fig. 210):
- The easiest option is to select the item View files... The program window will open Conductor, in which you can work with photos on the flash card of your camera in the same way as on a computer. Those. you can just copy the files and paste them into desired folder on the computer.
The second way is to use the item Import pictures and videos... A window will appear Importing images and videos(Fig. 211).
 |
| Rice. 211. Importing Images and Videos |
In this window, you can configure the parameters for importing images by selecting the appropriate item. A window will open Importing parameters(Fig. 212). In this window, you can configure the folder to which the photos will be copied from the camera. By default, photos are imported to the folder Images which is in Libraries... Next, you can specify the name of the folder that will be created when importing photos from the camera.
Look at figure 212. Now the following settings are selected - photos will be imported (copied) from the camera to the library Images, while in the folder Images will be created new folder and it will be named as today's date.
 |
| Rice. 212. Importing parameters |
After you complete the import settings, click OK and in the window Importing images and videos press the button Import(Fig. 211). Your photos will be copied to your computer.
Lesson # 72. We work with removable media
When working with removable media, there are nuances that you should be aware of. When we insert a disc into an optical disc drive or connect an external storage device (USB flash drive, removable hard disk or card reader with a memory card), then in the operating system Windows autorun is triggered. It means that operating system automatically detects a new storage medium and, trying to predict our actions, displays a window with a list of operations that we can carry out (Figs. 213 and 214).
You can choose an action convenient for you from the list or close the window Autostart and get access to the information of the removable storage medium through the program Conductor... By the way, item Open folder to view files will just lead to launch Conductor, which will display the contents of the removable storage medium.
Window Autostart may not appear at you. The point is that the opportunity Windows automatic launch is used by cybercriminals to activate their viruses and malware on your computer. For this reason, some antivirus programs and some programs designed to protect your computer may block Autostart... In this case, access to the information on the removable device can be obtained through the program Conductor.
Launch Conductor and display the contents of the folder Computer(Fig. 215). I connected a USB flash drive, about two gigabytes in size, to my computer and inserted the DVD into my optical drive.
In Figure 215, you see that appeared new section in the folder Computer which is called Removable media devices... This section displays the optical disc drive icon (denoted by the letter E), and a removable disk G- this is my flash drive.
To start working with the information of these disks ( E and G) I need to enter them by double-clicking the left mouse button on the corresponding icon of the removable device.
Working with files located on flash devices (flash drives and memory cards) and on removable hard drives is no different from working with files on a computer. This means that you can copy, move and delete information from these devices. Just be careful - when deleting information from removable media, it DOES NOT FIT v Shopping cart, but is immediately removed.
 |
| Rice. 215. Displaying removable devices in Explorer |
Files located on optical discs can only be copied or run. To delete or write information to optical discs, you need to use an additional program, which we will talk about later.
Now let's figure out how to properly remove removable media from a computer. There are a few rules here that I follow and recommend to you.
If you are working with information located on an optical disc, before extracting optical disc from the drive, make sure that no file or program is running from this disk. It's okay if you eject the disc while the file is running from it. The operating system simply loses its connection with this file and asks you to reinstall the disk. Those. you will not do any harm to either the disk or the files located on it, you just waste a little time on reinstallation disk and eject it again after closing the file.
With flash drives, memory cards and removable hard drives, the situation is different. If you simply remove the device from the connector, then you can damage the information that is on this device, and in some cases, the device itself.
Before removing the device from the computer, you must turn it off. For this in Windows there is a tool called. To access it you need to Notification areas select the appropriate icon (Fig. 216), then click on it with the left mouse button and a menu will appear (Fig. 217), which will list all the disks available on your computer. From the list, you must select the disk that you want to disconnect, i.e. our USB flash drive, card reader with memory cards or removable hard drive.
After that, in the Notification area will appear Announcement(fig. 218):
Homework:
1. If your computer has an optical disc drive, check which discs it works with (CD, DVD, Blu-ray). This information is usually found on the drive tray (fig. 199). If the drive can record discs, it will be labeled "RW" or "Recoder".
2. If you have a memory card, for example, in a camera, then find out its size and type. You will need this information if you decide to purchase a larger card or card reader.
3. If you do not have a card reader, copy the photos from the memory card using Windows(fig. 210).
4. Connect your USB flash drive to the computer via the USB connector, run any file from it and try to disconnect it via Safe removal devices and disks(fig. 216). A warning window should appear (Fig. 219). Then close the file you started earlier and repeat the action. An informational message should appear as in Figure 218.
Almost every person who works at a computer knows about the existence of a device called a "flash drive" (USB drive). Initially, these drives were quite expensive and were considered exotic devices. Then they were not widespread, and people exchanged information using disks, hard drives and floppy disks. Today, these drives have almost completely replaced the above methods of transferring information.
A USB storage device is an electronic device that is used as a storage device and storage medium. It connects to a personal computer, laptop, etc. The main advantages of this device are ease of use, a wide range of models and a fairly low price. Its main characteristics include compactness, a significant amount of memory, and a high data transfer rate. The drive is universal device and is perfectly protected from mechanical stress. You can easily carry it in your pocket and use it if necessary.
Kinds
A flash drive can be completely different in its performance. A wide variety of drives can be purchased in stores, which will vary in capacity, design, interface type and capabilities.
- In terms of memory capacity, drives can reach 1 terabyte, that is, 1024 Gb. However, today the most widespread are devices with a capacity of 4-32 Gb. Their cost varies between 150-3000 rubles. The multiplicity of the memory capacity corresponds to the number 2, that is, 32, 64, 128 Gb. Devices up to 4GB are great for storing and moving text files. For the purpose of storing music, photos or videos small size a 16 GB drive is enough. The 32 Gb device is well suited for video storage.

- According to the standards of the USB interface, drives can be of the following types:
USB 1.0;
1.1;
2.0;
3.0;
3.1.
The main distinguishing feature of these types of drives is the speed of data transfer. So USB 1.1 transfers data at a speed of 600-800 Kb per second. At the same time, recording is supported up to 700 Kb per second. USB 2.0 more advanced, they can transfer data at a speed of 480 Mbps. USB 3.0 is the new kind drives that can transfer data at speeds up to 5 Gbps. Standard devices USB 3.1 capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 10-12 Gbps.

However, you should not delude yourself with the desire to have the most perfect device. Actually a drive USB 3.1 is unlikely to support most of your devices. The fact is that on the USB receivers themselves, in most cases, devices of the standard USB 2.0... As a result, when connected to a USB 2.0 port or reverse order the drive will operate in data transfer mode USB 2.0, that is, the speed will be significantly limited.
- Today you can buy an incredible number of drives of a wide variety of designs, which are made from various materials... It can be plastic, wood, glass, silicone, leather, metal, rubber, and so on. Various drawings, engravings and other design elements can be applied to the drive body. However, the use of one or another design effect does not in any way affect the technical indicators in the form of the speed and volume of data transfer.

- Availability of additional functions. For example, a flash drive may have a code entry device. Therefore, to start working with it, you will need to enter the correct code. This helps protect against data theft. There may also be drives with a fingerprint reader. In this case, to be able to work with the device, you will have to put your finger on the scanner, which is located on the body.

There may also be drives working with voice control... Such a device recognizes the owner's voice, after which it unlocks the ability to work with data. There are devices with an antibacterial coating. The body of such a drive is made with the use of special antibacterial materials, so that microbes do not multiply on it.
There are also double-sided drives. The flash drive has two USB connectors. With such a drive, you can separately store working information and personal. This is convenient when you can accidentally overwrite important document... Devices are being sold that combine a storage device and a digital camera.
Device
In most cases, a flash drive consists of the following main elements:

The USB connector allows you to connect to a computer or other electronic device. With the help of a stabilizer, the voltage is converted and stabilized, which comes from the PC directly to the controller and flash memory.
The controller represents the circuitry that manages memory as well as data transfer. It has a microcircuit that contains all the information about the memory, the manufacturer. It also stores service information, which is required for normal operation of the drive. In some models, the controller may be built-in or absent altogether.
With the help of a quartz resonator, a reference frequency of operation is created flash memory and controller logic. The housing serves to protect against mechanical damage and placement of all elements of the drive. The switch is required to enable write mode or write protection. The flashing LED indicates to the user that the drive is working. At this time, it is highly discouraged to remove the drive from the USB connector. This can lead to loss of data and even damage to the device.
Application

A flash drive is a universal device on which you can store any information, rewrite, erase and transfer it. The drive can record text documents, photos, videos, music, including reading, erasing and editing information. The peculiarity of the drive is that it can be connected infinite number once.
The device can even be plugged in while the computer is running. The body of the device helps to protect well all the elements of the device. Thanks to this, the drive is practically not afraid of falling, prolonged wearing in trouser pockets and other mechanical influences. The drive does not need an external power source, as it has enough power supplied to it via the USB port.
How to choose

A flash drive is a fairly simple device, but you also need to be smart about choosing it.
- For selection suitable device you must first take a closer look at the amount of memory outward appearance and data transfer rates.
- On the this moment time most the best option is a storage device with a storage capacity of 32 GB or more. This is due to the fact that the cost of such devices is not high, but this amount of memory is quite enough to record several high quality films, a huge amount of Word documents or pictures.
- You should not save a lot and acquire a little-known brand of a carrier without a name. So you can run into a Chinese craft. In addition, the difference in price between branded and “unknown” media will be negligible. Therefore, if you do not know which brand to choose, then take a look at such manufacturers as Transcend, silicon-power, San Disk, Kingston and so on.
- It is not recommended to purchase a drive with a retractable connector. Many models have a connector that slides out rather than hiding behind a cap. On the one hand, it looks nice and convenient, but in practice everything happens a little differently. Such a device is rather fragile and unreliable. If you apply force, the drive may break, requiring the purchase of a new device.
- When purchasing a drive, take a closer look at its design. Quite often they are made in the form of pendants or key chains, which allows using the drive not only as a useful device, but also as a rather fashionable accessory. Paying attention to the size, it is advisable that the flash drive takes up a minimum of space. At the same time, overly miniature devices are very fragile. Therefore, decide for yourself what is more important to you: beauty or reliability.
- If you want to protect the data on the drive from unauthorized persons, then you need to buy devices with additional security features. For example, it can be protection in the form of a special program on a USB flash drive that will ask for a password, or a device with a fingerprint scanner.
The still very popular USB-drives at one time practically ousted much cheaper CDs and DVDs from the market. There are many reasons for this, but the main one can be called high level trust in technology. But USB drives also have a number of disadvantages: theft, loss, substitution, uncontrolled removal outside the enterprise. In this article, we will look at the pros and cons, the main problems and ways to solve them in the use of USB drives.
Mikhail Gruntovich
Ph.D., Penza State University
Successful combination of properties
The persistent popularity of USB storage devices is primarily due to the successful combination of the properties of these storage media:
A USB flash drive (or just a USB media) is a compact storage device that uses a flash memory as a storage medium and connects to a reader via a USB interface.
- universality and availability - almost all modern software and hardware have hardware ports and drivers for accessing USB devices;
- mobility and compactness - USB-carriers are striking in their miniature size;
- reliability - flash memory is resistant to mechanical stress, scratches, dust; able to work in a wide temperature range;
- long autonomous service life - up to 5 years (they say that even up to 10);
- low power consumption;
- noiselessness;
- various attractive designs;
- acceptable read and write speed - these devices, of course, are inferior in speed to hard disks, but they certainly work faster than CDs, DVDs and old floppy disks;
- acceptable amount of internal memory - modern flash drives are capable of storing information up to 128 GB, which, of course, is incomparable with hard and solid state drives but quite acceptable for typical use;
- acceptable cost - the price of a unit of information storage on USB media does not compete with hard drives, but it does not bother the mass user;
- high level of trust in technology.
Moreover, the latter is often decisive when choosing in favor of a USB-drive. Indeed, when deciding which information storage / transmission technology to use, the owner of the information proceeds from the fact that the flash drive, which is almost always controlled by the user, is safe. Which is not always the case with other technologies, such as network technologies.
In addition, a number of aspects play an important role, which can be grouped under the name "psychology of ownership". The mastery of this tool and its use allows a person to feel their significance. This is also facilitated by the trust of the management, which instructs to use such sophisticated technology.
Headache of information security administrators
Once appeared, USB-media turned into a serious headache for information security administrators, since an IC using USB-media is exposed to threats of violation of the confidentiality and integrity of information, imposing false information, defeat by malware.
According to results reported by SanDisk endpoint security survey, employees of the organization most often copy customer data to personal USB-flash drives (25%); financial information (17%); information related to commercial planning (15%); personnel information (13%); product sales plans (13%); objects intellectual property(6%); source codes of programs (6%).
Typical method protecting information from various kinds of attacks - restricting access to this information. The same is done with regard to information processed using USB drives. First, a number of organizations are taking drastic measures such as removing or sealing USB connectors. Of course, it works, but what to do if USB-drives are still needed or, more often than not, they would not be needed, but USB port universal, you can connect other devices to it, for example, a mouse, a printer, a scanner. And in the modern world there are more and more such "goodies".
Let's highlight three real methods of protection against threats from USB drives:
- software and hardware protection against unauthorized access (SZI NSD);
- DLP systems;
- file-by-file or sector-by-sector ("transparent") encryption of data on a USB-drive.
SZI NSD
The use of the capabilities of the information security information system is a more preferable solution from the point of view of reliability and management, since it allows you to use a single control center, unified system user authentication and authorization, provides hardware security support and is able to control access to a variety of interfaces, not just USB. However, the functions of controlling access to external media are not the main purpose of such tools, and therefore are inferior in functionality to DLP systems.
DLP systems
A keylogger is a software or hardware device that records various actions user - keystrokes on a computer keyboard, movement and mouse keystrokes, etc.
DLP systems are designed to provide control over the distribution confidential information outside the enterprise via all available channels, including USB. Thus, controlling access to USB drives is one of their main "responsibilities". In addition, DLP systems "close" other IP vulnerabilities. However, additional efforts are required to integrate them into a unified information security system. These systems themselves do not ensure the security of the computing environment, and therefore, for their safe operation, the installation of the same information security system is required. So, in our opinion, the use of DLP systems to control user access to USB drives is justified in two cases. Firstly, when these funds are not as burdensome in price as the SIS NSD, and the use of the latter is not something necessary. These are systems with an intruder of class no higher than H2 according to the FSB classification. And secondly, DLP-systems can be used to expand the functionality of the information security system of the NSD, but only if they are able to prove the performance of their extended functionality.
USB media encryption
The use of encryption tools for a USB drive also solves the problem of controlling access to the information stored on it. After all, if the information in the memory of the flash drive is recorded only in encrypted form, then it can be read only if you know the true key. The main disadvantage of these tools is the complexity of managing the tool. cryptographic protection information (SKZI), in particular with encryption keys. In the simplest cases, keys are calculated based on the user's password. For example, this is done when the encryption tool is used virtual disk TrueCrypt. But at the same time, the USB stick can be used by the same user outside the enterprise. In our opinion, it should be more correct to use a key management system that would only work in a corporate environment and would not allow the user to correctly generate an encryption key outside this environment. However, being a full-fledged cryptographic information protection tool, such a tool is difficult to manage. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that the ISS NSD may also be required to ensure a safe software environment for using the cryptographic information system. In addition, USB encryption does not provide access control to other interfaces at all.
Ways to solve the problem
Unfortunately, all of the above solutions to the problem of USB-drives perform the task of controlling access to them one-way. They control access to the USB drive from the computer on which this access is just allowed. However, in addition to this, it is still necessary to solve, perhaps, a more important task: to deny access to information recorded on an approved USB drive from all other computers, that is, theft and loss of authorized flash drives is still dangerous.

The use of hardware solutions: specialized USB-drives allows you to finally get rid of the residual risk.
All the previously considered methods of protecting information on a USB drive implicitly proceeded from the fact that this medium is a passive storage of information, as was the case with a floppy disk, CD, DVD. If we remember that a USB drive is actually a USB drive containing a programmable controller that provides access to the internal flash memory, then the problem of ensuring the protection of recorded information outside the controlled perimeter is solved simply: you need to create a USB drive with built-in the security system that operates on this controller.
USB storage protection
Currently, there are a number of products on the market made using this technology.
Among them are the following: Kingston DataTraveler 5000 and 6000, SanDisk Cruzer Profile, IronKey S200, D200, LockHeed Martin IronClad, Corsair Flash Padlock 2, MXI Security Stealth MXP, Runtex Samurai, Verbatim Secure 'n' Go Small Business Security Pack, Chinavasion USB Fingerprint Security CVGI K38, ZamLock Pro Secure Flash Drive, Kanguru Defender Elite, Secret family.
Efficiency correct decision due to its architecture. Each such product consists of three components: external software, a hardware module (actually a flash drive, called a special medium) and its internal software. External software running on controlled computer, when a special medium is detected in the USB port, it provides the user password entry and the execution of the mutual authentication protocol with the firmware of the hardware module. Internal software running on the controller of the hardware module ensures the execution of this protocol from its side. Only complete coincidence of secret protocol parameters (user password and authentication keys of special media and computer) ensure its successful completion and enable access to the internal memory of special media from the computer. Since this decision is made by the controller of special media, and not by the computer, access to it from the side of the computer on which it was not previously registered by the administrator is blocked.
Almost all of them provide restriction of access to information in the internal flash memory by means of password or biometric user authentication. A number of products have a keyboard located on the product body, which allows you to avoid interception of the password by keyloggers. Also, they all use flash disk encryption and technological measures to protect keys when they are stored in the non-volatile memory of the controller. Some of these USB sticks have significant physical protection potential. They are made of materials that impede physical penetration into the housing. In addition, upon detection of attempts at physical intrusion, key information is destroyed and even the internal memory is completely erased. In the listed products, with a few exceptions, there is no logging function necessary for the information security system.
Unfortunately, almost all manufactured USB-drives do not even try to determine on which computer access to the information they protect is taking place. Thus, the listed SZI is a symbiosis of a conventional flash drive and a CIPF. They should have been called "encrypted" rather than protected USB media. They, of course, allow us to solve the problems of protecting USB media, but they do not do it to the fullest, since again there is a residual risk of using such media outside the enterprise.
Of course, no special media can completely solve the problem of the safe use of USB drives. However, its competent use in combination with other means of protection, such as information security information system and DLP systems, can bring the desired results.
In our opinion, only those products that control whether they are connected to an authorized computer or not, and are mounted only on authorized computers, should be considered a fully protected USB storage medium. Such solutions - domestic ones - are in the listed range of products.
Literature
- SanDisk endpoint security survey, SanDisk, April 2008.
- Second Annual Benchmark Study on Patient Privacy and Data Security, Ponemon, 2011.
- Global Leak Research 2010 // Info-Watch. - 2011.
- SanDisk Survey "Secure USB Flash Drives ", June 2008.
In this article, we will show you how to make sure that USBflash drive or SDthe map was defined in Windows system
like a normal local hard drive... You are probably asking, why is this necessary? The fact is that Windows by default defines USB flash drives and memory cards as removable drives that cannot be divided into several partitions using Windows standards. And even if you split the USB flash drive into two or more partitions using third party utilities(in the same Linux), then in the OS Windows family only the first of them will be available (by the way, a built-in one appeared in Windows 10 1703). Those. Windows supports normal work with multi-partitions only for HDD disks, which are defined in the system as local (i.e. non-removable).
RMB bits and USB sticks
Windows operating systems recognize USB flash drives as removable / removable devices due to the presence of a special bit descriptor on each device RMB(removablemediabit) ... If, when polling a connected device via the StorageDeviceProperty function, the system determines that RMB = 1, it concludes that the connected device is a removable storage device. Thus, in order from the system's point of view to convert a USB-flex to a hard disk, it is enough to modify this descriptor. This can be done directly (which is quite risky due to differences in hardware implementations of specific devices, and it is not always possible), or indirectly, by replacing the answer USB devices using a special driver that allows you to filter information in the response of the device.
Advice... Some manufacturers produce special utilities for flashing the controller of your flash drives. First of all, try to find such a utility and / or firmware on the manufacturer's website. This is the most correct way. If such a utility is not found, follow the recommendations from this article.
Connect a USB flash drive to any free port on your computer, then open the Disk Management Manager ( diskmgmt.msc) and make sure that its type is defined in the system as Removable(Removable device) .
Also, the device type can be viewed on the Volumes tab in the disk properties (as we can see here Type: Removable). 
Or using the diskpart command:
List volume

In this article, we will consider two ways to change the RMB bit on a USB flash drive - using the Hitachi filter driver (changes are made only at the driver level of a specific computer) and changing the bit in the controller firmware using the BootIt utility from Lexar (a more universal method, but there is a number of restrictions and does not apply to all models of flash drives and SD cards). While both of these methods are quite old and I initially tested them on Windows 7, they continue to be relevant and work equally well on modern Windows 10.
Lexar BootIt Utility
Recently, I came across a rather interesting utility - LexarBootIt... It is a free portable program that can change the RMB of a removable storage device to a fixed USB device (or vice versa). Despite the fact that the Lexar BootIt utility is designed for Lexar devices (Micron, Crucial), it can work with flash drives from other manufacturers. BootIt utility supports all Windows versions from Windows XP to Windows 10.
Important... The utility is guaranteed to work for Lexar drives. Judging by the reviews, the "Flip removable bit" function does not work on fast USB 3.0 flash drives. In addition, when you reflash the controller, you void the warranty for the USB flash drive and can make it inoperable.
You can download BootIt on the Lexar website (lexar_usb_tool) or from our website ().
- Run BootIt.exe as administrator
- In the list of devices, select your USB flash drive
- Click on the button Flip Removable Bit
- Save your changes by clicking OK.

Reconnect the device and use Device Manager to make sure it has changed from Removable to Basic.

If the BootIt utility did not help to change the RMB bit on the removable drive, try the following method based on the filter driver Hitachi microdrive
Filter driver for flash drives Hitachi Microdrive
In order for a USB flash drive or SD card to be recognized in the system as a hard drive, we need a special filter driver that allows us to modify the data passed through the system stack of the current device driver. We will use Hitachi's USB flash drive filter driver ( Hitachi Microdrive driver), which at the OS driver level allows you to change the type of flash drive from removable to fixed (USB-ZIP -> USB-HDD). Through the use of this driver, you can hide from the system that the connected device is removable. As a result, the system will consider that it is working with the usual hard disk, which can be divided into sections that will be simultaneously available in the system.
Hitachi Microdrive Driver Archives:
- 32 bit systems - (3.0 Kb)
- Hitachi Microdrive version for 64 bit systems - (3.8 Kb)
It is necessary to download the driver version for your system in accordance with its bitness. Both archives have the same structure and consist of two files:
- cfadisk.inf- installation file, with driver settings
- cfadisk.sys- Hitachi driver file
The next step is to identify the device code of our flash drive. To do this, in the properties of the disk on the tab Details in parameter Device Instance Path select and copy ( Ctrl + C) device instance code. 
In our example, this will be:
USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_Linux & Prod_File-CD_Gadget & Rev_0000 \ 0123456789ABCDEF & 0
Suppose we are planning to install a driver on 64 bit system... Using any test editor, open the file for editing cfadisk.inf... We are interested in the sections cfadisk_device and cfadisk_device.NTamd64.
% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, IDE \ DiskTS64GCF400 ______________________________ 20101008% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, IDE \ DiskTS64GCF400 ______________________________ 20101008
We change the value of DiskTS64GCF400______________________________20101008 to the code of our device.
Important! In the code of the device instance, it is necessary to discard the part after the second "\" (in our example, discard 0123456789ABCDEF & 0).
We get:
% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, IDE \ USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_Linux & Prod_File-CD_Gadget & Rev_0000% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, IDE \ USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_Linux & Prod_File-CD_Gadget & Rev_0000
We save the file.
If the driver is installed on a 32 bit system, you need to download the recommended archive, unpack it and open the cfadisk.inf file for editing. Find the section :
% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_LEXAR & Prod_JD_LIGHTNING_II & Rev_1100% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_JetFlash & Prod_TS1GJF110 & cf.
Then we will change the data in the last line by specifying the code of the instance of our flash drive, i.e. in our example we get:
% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_LEXAR & Prod_JD_LIGHTNING_II & Rev_1100% Microdrive_devdesc% = cfadisk_install, USBSTOR \ Disk & Ven_JetFlash & Prod_TS1GJF110 & Rev_0dev% Microdisk

Advice... If you want the USB flash drive to be displayed with a specific name in the device manager, you need to edit the value of the Microdrive_devdesc variable, for example:
Microdrive_devdesc = "Transcend 64GB DIY SSD"
Installing Hitachi Microdrive Driver Instead of Native USB Drive Driver
It remains to replace the driver used by the USB flash drive.
Important! If USB driver Hitachi Microdrive is installed on a 64-bit system. there is no digital signature for this driver, you have to either.
Open the Drivers tab and click the button Update Drivers. 
Specify the folder to the directory into which the downloaded archive with the Hitachi driver is unpacked: 
Let's choose new driver. 
We ignore the warning about the missing digital signature of the driver. 
Advice... In Windows 10 and Windows 8, when installing the driver, the following error appears:
Windows found drivers for this device, but an error occurred while trying to install those drivers.
Hitachi microdrive
Third party inf does not contain signature information

To disable verification of the digital signature of the driver, run the commands:
bcdedit.exe / set nointegritychecks ON
bcdedit.exe / set TESTSIGNING ON
Restart your computer and try to install the driver again.
It remains to restart the computer and, opening the disk manager, make sure that your flash drive has become recognized as a regular hard drive ( Type: Basic), and the driver is the Hitachi driver.
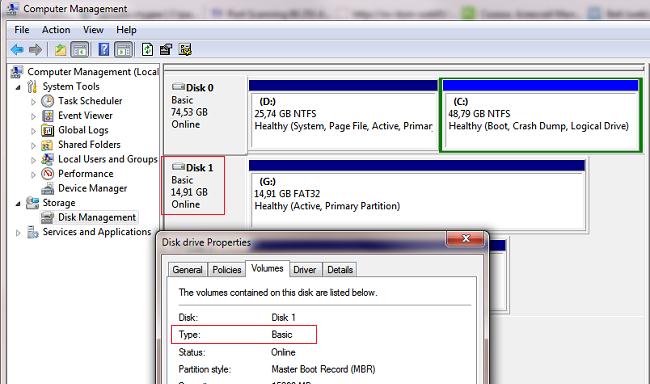
Opening the explorer, you can also make sure that the flash drive icon has changed, it began to appear as a hard drive regular disk. 
Now you can work with this flash drive as with a regular HDD: create partitions, specify active section, create dynamic disks, install software that does not work from flash drives, etc.
Important... On others Windows computers without this driver, the second section of the device will not be available.
To uninstall the Hitachi Microdrive driver, open the disk properties and on the driver tab, click the Update Driver button - the system will install the native driver by itself.

Advice... If, after installing the Hitachi driver, the system stops booting with BSOD, you need to boot the computer from the Windows / Live CD and manually delete the following files:
- cfadisk.sys in the% windir% \ System32 \ drivers directory
- Directory "cfadisk.inf_amd64_ ..." from% windir% \ System32 \ DriverStore \ FileRepositoty
Reboot your computer
You need to understand that this solution will only work on the system on which the corresponding driver is installed.



